Learning electronics can seem daunting, but with the right approach, anyone can master it. LEARNS.EDU.VN provides a structured path and resources to help you understand electronic circuits, components, and design principles. By focusing on essential concepts and practical skills, you’ll gain the knowledge to build your own electronic gadgets and explore the exciting world of electrical engineering, circuit analysis, and embedded systems.
1. Understand Your Learning Style
Before diving into the technical aspects, consider your individual learning preferences. Are you a visual, auditory, or kinesthetic learner? Tailoring your study methods to your strengths can significantly enhance your learning experience.
- Visual Learners: Benefit from diagrams, videos, and graphical representations of electronic circuits and components.
- Auditory Learners: Learn best through lectures, podcasts, and discussions about electrical concepts.
- Kinesthetic Learners: Thrive on hands-on activities, building circuits, and experimenting with components.
2. Define Your Goals for Learning Electronics
Clearly defining your objectives is crucial for a focused learning path. Are you interested in robotics, home automation, circuit design, or simply understanding how electronic devices work? Your goals will guide your curriculum and the specific areas of electronics you should prioritize.
2.1. Examples of Learning Goals
- Build a simple robot that can navigate a room.
- Design a custom circuit board for a specific application.
- Understand how smartphones and computers work at a fundamental level.
- Create a home automation system using microcontrollers.
3. Essential Tools and Equipment
Having the right tools and equipment is fundamental for hands-on learning in electronics. Start with a basic set and expand as your projects become more complex.
3.1. Breadboard
A breadboard is a solderless device for temporary prototypes and experimenting with circuit designs. It allows you to quickly build and modify circuits without soldering.
3.2. Multimeter
A multimeter is an essential tool for measuring voltage, current, and resistance in electronic circuits. It helps you diagnose issues and verify the functionality of your designs.
3.3. Soldering Iron and Solder
Soldering is necessary for creating permanent connections in your electronic projects. A soldering iron and solder are used to securely join components to circuit boards.
3.4. Wire Strippers and Cutters
These tools are used to prepare wires for connections and to trim excess leads on components.
3.5. Electronic Components Kit
A basic kit should include resistors, capacitors, diodes, transistors, LEDs, and integrated circuits (ICs). This provides a variety of components for building different types of circuits.
3.6. Power Supply
A stable power supply is crucial for powering your circuits. Adjustable power supplies allow you to test circuits at different voltage levels.
4. Foundational Concepts in Electronics
Understanding the core principles of electronics is essential for building a solid foundation.
4.1. Current, Voltage, and Resistance
These are the three fundamental properties of electricity. Current is the flow of electric charge, voltage is the electric potential difference, and resistance opposes the flow of current. Ohm’s Law (V = IR) describes the relationship between them. According to research from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), understanding Ohm’s Law is critical for analyzing and designing electronic circuits.
4.2. Ohm’s Law
Ohm’s Law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points and inversely proportional to the resistance between them. Mathematically, it’s expressed as V = IR, where V is voltage, I is current, and R is resistance.
4.3. Series and Parallel Circuits
Components in a series circuit are connected along a single path, so the same current flows through each component. In a parallel circuit, components are connected along multiple paths, so the voltage across each component is the same.
4.4. Kirchhoff’s Laws
Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL) states that the total current entering a junction must equal the total current leaving the junction. Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL) states that the sum of the voltage drops in a closed loop must equal zero. These laws are essential for analyzing complex circuits.
5. Understanding Basic Electronic Components
Familiarize yourself with the most common electronic components and their functions.
5.1. Resistors
Resistors limit the flow of current in a circuit. They are color-coded to indicate their resistance value.
5.2. Capacitors
Capacitors store electrical energy in an electric field. They are used for filtering, smoothing, and energy storage.
5.3. Diodes
Diodes allow current to flow in one direction only. They are used for rectification, signal demodulation, and protection.
5.4. Transistors
Transistors are semiconductor devices used to amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power. They are fundamental to modern electronics.
5.5. Integrated Circuits (ICs)
ICs are complex circuits fabricated on a single semiconductor chip. They perform a wide variety of functions, from simple logic gates to complex microprocessors.
5.6. Inductors
Inductors store energy in a magnetic field when electric current flows through them. They are used in filters, power supplies, and radio frequency circuits.
6. Learning from Circuit Diagrams
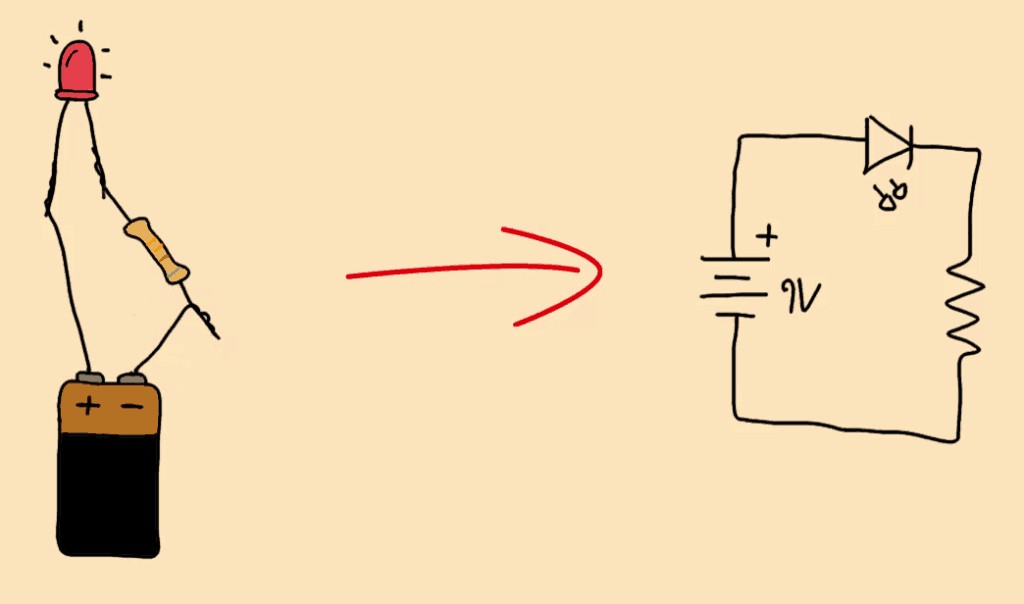
The ability to read and understand circuit diagrams (also known as schematics) is essential for building and troubleshooting electronic circuits. Circuit diagrams use symbols to represent components and their connections.
6.1. Understanding Symbols
Each component has a specific symbol in a circuit diagram. For example, a resistor is represented by a zigzag line, a capacitor by two parallel lines, and a transistor by a more complex symbol that indicates its type (NPN or PNP).
6.2. Tracing Circuit Paths
Follow the lines in the diagram to understand how components are connected. This helps you visualize the flow of current and the function of each part of the circuit.
6.3. Using Online Resources
Websites like LEARNS.EDU.VN offer numerous circuit diagrams with explanations, making it easier to understand and build circuits.
7. Building Your First Circuits
Start with simple circuits to gain hands-on experience and reinforce your understanding of basic concepts.
7.1. LED Circuit
A basic LED circuit consists of a resistor, an LED, and a power source. The resistor limits the current to protect the LED from burning out.
7.2. Transistor Switch Circuit
Use a transistor to control a larger current with a smaller current. This is fundamental to many electronic devices.
7.3. 555 Timer Circuit
The 555 timer is a versatile integrated circuit used for generating timing signals. Build circuits that create blinking LEDs or generate audio tones.
7.4. LDR Circuit
An LDR (Light Dependent Resistor) circuit varies its resistance based on the amount of light it receives, allowing it to act as a light sensor.
8. Diving Deeper into Electronics
As you become more comfortable with the basics, explore more advanced topics to broaden your knowledge.
8.1. Digital Electronics
Digital electronics deals with digital signals and logic gates. It is the foundation of computers, microcontrollers, and digital devices.
8.2. Microcontrollers
Microcontrollers are small, programmable computers on a single integrated circuit. They are used in embedded systems to control various devices and processes. Arduino and Raspberry Pi are popular platforms for learning microcontrollers. A study by the University of California, Berkeley, found that hands-on microcontroller projects significantly improve student understanding of embedded systems.
8.3. Analog Electronics
Analog electronics deals with continuous signals and circuits. It includes topics such as amplifiers, filters, and signal processing.
8.4. Power Electronics
Power electronics focuses on efficient conversion and control of electrical power. It includes topics such as power supplies, inverters, and motor drives.
8.5. Signal Processing
Signal processing involves analyzing and manipulating signals to extract information or improve their quality. It is used in audio, video, and communication systems.
9. Learning Resources
Utilize a variety of resources to support your learning journey.
9.1. Online Courses
Platforms like Coursera, edX, and Udemy offer courses on electronics taught by experts from leading universities.
9.2. Books
There are many excellent books on electronics for beginners and advanced learners. Some popular titles include “Electronics for Dummies” and “The Art of Electronics.”
9.3. Websites and Blogs
Websites like LEARNS.EDU.VN, and All About Circuits provide articles, tutorials, and projects for electronics enthusiasts.
9.4. YouTube Channels
Channels like GreatScott! and ElectroBOOM offer entertaining and educational content on electronics.
9.5. Online Communities
Join online forums and communities to connect with other learners, ask questions, and share your projects.
10. Hands-On Projects
The best way to learn electronics is by doing. Work on hands-on projects to apply your knowledge and develop practical skills.
10.1. Simple Robot
Build a robot that can follow a line or avoid obstacles using sensors and microcontrollers.
10.2. Home Automation System
Create a system to control lights, temperature, and other appliances in your home using a microcontroller.
10.3. Audio Amplifier
Design and build an audio amplifier using transistors or integrated circuits.
10.4. Electronic Instrument
Create a simple electronic instrument, such as a theremin or a synthesizer.
11. Understanding Integrated Circuits (ICs)
Integrated circuits (ICs) are at the heart of modern electronics, containing numerous components on a single chip. Learning how to use them is crucial.
11.1. Types of ICs
- Analog ICs: Operational amplifiers, voltage regulators, and audio amplifiers.
- Digital ICs: Logic gates, microprocessors, memory chips.
- Mixed-Signal ICs: Analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) and digital-to-analog converters (DACs).
11.2. Reading Datasheets
Datasheets provide essential information about ICs, including their functions, pin configurations, electrical characteristics, and application circuits.
11.3. Example Project: Using an Operational Amplifier
Build an amplifier circuit using an op-amp to amplify audio signals or sensor outputs.
12. Working with Microcontrollers
Microcontrollers are versatile tools for controlling electronic devices and systems.
12.1. Popular Microcontroller Platforms
- Arduino: User-friendly platform with a large community and extensive libraries.
- Raspberry Pi: More powerful single-board computer suitable for complex projects.
- ESP32: Low-cost microcontroller with Wi-Fi and Bluetooth connectivity.
12.2. Programming Microcontrollers
Learn to program microcontrollers using languages like C/C++ (for Arduino) or Python (for Raspberry Pi).
12.3. Example Project: Controlling an LED with Arduino
Write a program to blink an LED using an Arduino board, demonstrating basic input/output operations.
13. Designing Your Own Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs)
Designing PCBs allows you to create professional and reliable electronic devices.
13.1. PCB Design Software
- KiCad: Open-source PCB design software with a wide range of features.
- Eagle: Popular PCB design software with a free version for small projects.
- Altium Designer: Professional-grade PCB design software for complex projects.
13.2. PCB Design Process
- Schematic Capture: Create a circuit diagram using PCB design software.
- Component Placement: Arrange components on the PCB layout.
- Routing: Connect components with copper traces.
- Design Rule Check (DRC): Verify that the design meets manufacturing requirements.
- Gerber File Generation: Create files for PCB fabrication.
13.3. Ordering PCBs
Order PCBs from online manufacturers like JLCPCB or PCBWay.
14. Soldering Techniques
Soldering is a fundamental skill for creating reliable electronic connections.
14.1. Preparing Components
Clean component leads and tin them with solder to ensure good contact.
14.2. Soldering Process
- Heat the component lead and pad with the soldering iron.
- Apply solder to the heated joint until it flows smoothly.
- Remove the soldering iron and let the joint cool.
14.3. Desoldering
Use a desoldering pump or wick to remove solder from joints when troubleshooting or replacing components.
15. Troubleshooting Electronic Circuits
Troubleshooting is an essential skill for fixing electronic circuits.
15.1. Common Problems
- Open Circuits: Broken connections or component failures.
- Short Circuits: Unintended connections between points in the circuit.
- Component Failures: Resistors, capacitors, transistors, or ICs may fail.
15.2. Troubleshooting Techniques
- Visual Inspection: Look for obvious problems like broken wires or burnt components.
- Voltage Measurements: Use a multimeter to check voltages at various points in the circuit.
- Continuity Testing: Use a multimeter to check for continuity between connected points.
- Component Testing: Use a multimeter or component tester to verify component values and functionality.
16. Understanding Wireless Communication
Wireless communication is integral to many modern electronic systems.
16.1. Common Wireless Technologies
- Wi-Fi: High-speed wireless internet access.
- Bluetooth: Short-range wireless communication for connecting devices.
- Zigbee: Low-power wireless communication for home automation and sensor networks.
- LoRaWAN: Long-range, low-power wireless communication for IoT applications.
16.2. Wireless Modules
Use wireless modules like ESP8266 (Wi-Fi) or HC-05 (Bluetooth) to add wireless communication to your projects.
16.3. Example Project: Wireless Sensor Network
Create a network of sensors that transmit data wirelessly to a central hub.
17. Exploring Robotics
Robotics combines electronics, mechanics, and programming to create automated machines.
17.1. Key Components of a Robot
- Microcontroller: Processes sensor data and controls actuators.
- Sensors: Detect the robot’s environment (e.g., distance sensors, light sensors).
- Actuators: Motors and servos that move the robot.
- Power Supply: Provides energy to the robot’s components.
17.2. Robot Types
- Line Follower: Follows a line on the ground.
- Obstacle Avoidance Robot: Avoids obstacles using sensors.
- Remote-Controlled Robot: Controlled wirelessly by a human operator.
17.3. Example Project: Building a Simple Line Follower Robot
Construct a robot that uses infrared sensors to follow a black line on a white surface.
18. Advanced Topics in Electronics
To further enhance your electronics knowledge, consider exploring these specialized areas:
18.1. Digital Signal Processing (DSP)
DSP involves using algorithms to analyze and manipulate digital signals. It is used in audio processing, image processing, and communication systems.
18.2. Radio Frequency (RF) Engineering
RF engineering deals with the design of circuits and systems that operate at radio frequencies. It is used in wireless communication, radar, and satellite systems.
18.3. Embedded Systems
Embedded systems are specialized computer systems designed for specific tasks. They are used in automobiles, appliances, and industrial equipment.
18.4. Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT involves connecting everyday objects to the internet, allowing them to collect and exchange data.
19. Staying Updated
Electronics is a rapidly evolving field. Stay updated with the latest trends and technologies by:
- Reading Industry Publications: Follow electronics magazines and journals.
- Attending Conferences and Workshops: Participate in industry events to learn from experts.
- Joining Online Communities: Engage with other professionals in online forums and groups.
- Experimenting with New Technologies: Try out new components, tools, and techniques.
20. Career Opportunities in Electronics
A strong foundation in electronics can open up a variety of career paths.
20.1. Electrical Engineer
Design, develop, and test electrical equipment and systems.
20.2. Electronics Technician
Install, maintain, and repair electronic equipment.
20.3. Embedded Systems Engineer
Design and develop embedded systems for various applications.
20.4. Robotics Engineer
Design and build robots and automated systems.
20.5. IoT Engineer
Develop and deploy IoT solutions for various industries.
By following this comprehensive guide and utilizing the resources at LEARNS.EDU.VN, you can confidently embark on your journey to master electronics. Remember to stay curious, practice consistently, and never stop learning.
FAQ: Learning Electronics
1. What is the best way to start learning electronics?
Start with the basics: understand current, voltage, resistance, and basic components. Then, build simple circuits to gain hands-on experience.
2. What tools do I need to start learning electronics?
A breadboard, multimeter, soldering iron, wire strippers, and a basic components kit are essential.
3. How important is it to understand circuit diagrams?
Understanding circuit diagrams is crucial for building and troubleshooting electronic circuits.
4. Which online resources are helpful for learning electronics?
Platforms like Coursera, edX, Udemy, websites like LEARNS.EDU.VN, and YouTube channels like GreatScott! are excellent resources.
5. What are some good beginner projects in electronics?
LED circuits, transistor switch circuits, and 555 timer circuits are great starting points.
6. How can I improve my troubleshooting skills in electronics?
Practice with visual inspection, voltage measurements, continuity testing, and component testing.
7. What are the key concepts in digital electronics?
Logic gates, binary numbers, Boolean algebra, and digital circuits.
8. What is a microcontroller, and how is it used?
A microcontroller is a small, programmable computer on a single chip used in embedded systems to control devices.
9. How do I design my own printed circuit board (PCB)?
Use PCB design software like KiCad or Eagle, follow the PCB design process, and order PCBs from online manufacturers.
10. What career opportunities are available with electronics knowledge?
Electrical engineer, electronics technician, embedded systems engineer, robotics engineer, and IoT engineer are some options.
Ready to take your electronics learning to the next level? LEARNS.EDU.VN offers a wealth of in-depth articles, tutorials, and courses designed to help you master electronics. Whether you’re looking to understand complex concepts, develop practical skills, or connect with other electronics enthusiasts, LEARNS.EDU.VN has the resources you need. Don’t wait—visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today and start your journey to becoming an electronics expert. For more information, contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States, or call us at +1 555-555-1212. You can also reach us via WhatsApp at the same number. Let learns.edu.vn be your guide in the exciting world of electronics!