Learning pharmacology for the NCLEX exam can feel overwhelming, but it doesn’t have to be! This comprehensive guide from LEARNS.EDU.VN provides a clear roadmap to mastering essential medication information for success. By focusing on key classifications, mechanisms of action, and nursing considerations, you’ll gain the confidence and knowledge needed to excel on the NCLEX and provide safe, effective patient care with our test preparation. Explore this useful information to help you with exam success, study techniques, and medication mastery.
1. What Key Areas Should You Focus On When Learning Pharmacology for the NCLEX?
To effectively learn pharmacology for the NCLEX, focus on medication classifications, prefixes and suffixes, generic names, indications, mechanisms of action, side effects (both common and severe), and nursing considerations. Mastering these interconnected elements is crucial for exam success and safe nursing practice.
Pharmacology is often cited as one of the most challenging subjects for nursing students preparing for the NCLEX. The sheer volume of information, including countless medications, their mechanisms of action, side effects, and nursing considerations, can feel daunting. However, by focusing on key areas and employing effective study strategies, you can conquer this subject and confidently approach the NCLEX. Here’s a breakdown of the essential areas to concentrate on:
-
Medication Classifications: Understanding how medications are categorized (e.g., antibiotics, beta-blockers, diuretics) is foundational. This knowledge provides a framework for organizing and recalling information about individual drugs within each class. For instance, knowing that a drug belongs to the “ACE inhibitor” class immediately tells you something about its mechanism of action and common side effects.
-
Prefixes and Suffixes: Many medication names share common prefixes and suffixes that indicate their class or mechanism of action. Learning these patterns can significantly reduce the amount of memorization required. For example, beta-blockers often end in “-lol” (e.g., metoprolol, atenolol), while proton pump inhibitors typically end in “-azole” (e.g., omeprazole, lansoprazole). Recognizing these patterns allows you to make educated guesses about unfamiliar medications.
-
Generic Names: The NCLEX primarily uses generic names, not brand names. Therefore, it’s crucial to focus your study efforts on learning the generic names of frequently prescribed medications. While brand names can vary from country to country, generic names are standardized, making them a reliable foundation for your knowledge.
-
Indications: Knowing what a drug is used to treat is fundamental. Understanding the indications for various medications allows you to anticipate their effects and potential side effects. For example, knowing that a medication is an “antihypertensive” tells you that it’s used to lower blood pressure.
-
Mechanisms of Action: The mechanism of action describes how a drug works at the cellular or molecular level to produce its therapeutic effect. Understanding the mechanism of action helps you connect the drug to its indication and potential side effects. For instance, knowing that a diuretic works by increasing urine production explains its use in treating hypertension and edema.
-
Side Effects (Common and Severe): It’s essential to differentiate between common and severe side effects. While common side effects are generally mild and manageable, severe side effects (also known as adverse reactions) can be life-threatening and require immediate intervention. The NCLEX often tests your ability to recognize and prioritize interventions for severe adverse reactions.
-
Nursing Considerations: Nursing considerations encompass the actions a nurse must take before, during, and after administering a medication. These include assessing the patient’s condition, checking laboratory values, educating the patient about the medication, and monitoring for therapeutic effects and side effects. Nursing considerations are crucial for ensuring patient safety and optimizing medication effectiveness.
Remember, these elements are interconnected. Understanding the mechanism of action can help you predict side effects and nursing considerations. Organizing your study around these key areas will make learning pharmacology for the NCLEX more manageable and effective.
2. How Can Understanding Medication Classifications Help with NCLEX Pharmacology?
Understanding medication classifications provides a framework for organizing and recalling drug information. Knowing a drug’s classification helps you anticipate its effects, indications, and potential side effects, making learning more efficient.
Medication classifications serve as a fundamental organizing principle in pharmacology. Instead of memorizing each drug in isolation, understanding how drugs are grouped together based on shared characteristics allows you to learn more efficiently and effectively. Here’s how:
-
Shared Properties: Drugs within the same classification often share similar mechanisms of action, indications, and side effects. For example, all beta-blockers work by blocking beta-adrenergic receptors, leading to decreased heart rate and blood pressure. They are commonly used to treat hypertension, angina, and arrhythmias. Recognizing these shared properties reduces the amount of information you need to memorize for each individual drug.
-
Predictive Value: Knowing a drug’s classification allows you to anticipate its effects, even if you’ve never encountered that specific drug before. For instance, if you know that a drug is a “calcium channel blocker,” you can predict that it will likely lower blood pressure and may cause side effects such as dizziness or headache.
-
Organization and Recall: Classifications provide a mental framework for organizing and recalling drug information. When studying, you can group drugs by classification and focus on the common characteristics of each group. This approach makes it easier to retrieve information during the NCLEX.
-
Efficient Learning: By focusing on the general principles that apply to entire classes of drugs, you can avoid rote memorization of individual drug facts. This approach is more efficient and promotes a deeper understanding of pharmacology.
Here’s a list of common NCLEX medication classifications you’ll need to learn:
| Classification | Examples | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Amphetamines | Adderall, Ritalin | ADHD, narcolepsy |
| Anti-Allergy Drugs | Antihistamines, corticosteroids | Allergies, allergic reactions |
| Anti-Alzheimer’s | Donepezil, Rivastigmine | Alzheimer’s disease |
| Antibiotics | Penicillin, Azithromycin | Bacterial infections |
| Anticonvulsants | Phenytoin, Carbamazepine | Seizures |
| Antidepressants | Sertraline, Fluoxetine | Depression, anxiety |
| Anti-Diarrheals | Loperamide, Bismuth subsalicylate | Diarrhea |
| Antiemetics | Ondansetron, Metoclopramide | Nausea, vomiting |
| Anti-Gout | Allopurinol, Colchicine | Gout |
| Anti-Lipidemics | Atorvastatin, Simvastatin | High cholesterol |
| Anti-Neoplastics | Chemotherapy drugs | Cancer |
| Anti-Osteoporotic | Alendronate, Risendronate | Osteoporosis |
| Anti-Parkinsonians | Levodopa, Carbidopa | Parkinson’s disease |
| Anti-Psychotics | Haloperidol, Risperidone | Psychotic disorders |
| Anti-Spasmodics | Hyoscyamine, Dicyclomine | Muscle spasms |
| Anxiolytics | Alprazolam, Lorazepam | Anxiety |
| Bronchodilators | Albuterol, Ipratropium | Asthma, COPD |
| Corticosteroids | Prednisone, Methylprednisolone | Inflammation, autoimmune disorders |
| Diuretics | Furosemide, Hydrochlorothiazide | Edema, hypertension |
| Erectile Dysfunction Drugs | Sildenafil, Tadalafil | Erectile dysfunction |
| H2 Receptor Blockers | Ranitidine, Famotidine | Heartburn, GERD |
| Insulins | Insulin lispro, Insulin glargine | Diabetes |
| Laxatives | Senna, Polyethylene glycol | Constipation |
| Muscle Relaxers | Cyclobenzaprine, Baclofen | Muscle spasms |
| NSAIDs | Ibuprofen, Naproxen | Pain, inflammation |
| Opioids | Morphine, Oxycodone | Pain |
| Proton Pump Inhibitors | Omeprazole, Pantoprazole | Heartburn, GERD |
| Stool Softeners | Docusate sodium | Constipation |
| Thrombolytics | Alteplase | Blood clots |
By focusing on understanding the characteristics and principles associated with each classification, you can build a strong foundation for mastering NCLEX pharmacology.
3. How Do Medication Prefixes and Suffixes Aid NCLEX Study?
Learning common prefixes and suffixes provides clues to a medication’s classification and mechanism of action. This knowledge helps you recognize unfamiliar drugs and quickly recall their properties, making your study more efficient.
Medication names are often derived from their chemical structure or mechanism of action. As a result, many drugs within the same class share common prefixes and suffixes. Recognizing these patterns can significantly enhance your ability to learn and remember pharmacology for the NCLEX. Here’s how:
-
Identifying Classifications: Certain prefixes and suffixes are strongly associated with specific drug classifications. For example, as mentioned earlier, beta-blockers often end in “-lol,” while proton pump inhibitors typically end in “-azole.” Recognizing these patterns allows you to quickly identify the classification of an unfamiliar drug.
-
Understanding Mechanisms of Action: Some prefixes and suffixes provide clues to a drug’s mechanism of action. For example, the prefix “anti-” often indicates that a drug opposes a particular action or substance. “ACE” stands for Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme. ACE inhibitors block the action of this enzyme.
-
Reducing Memorization: By learning common prefixes and suffixes, you can reduce the amount of memorization required. Instead of memorizing the properties of each individual drug, you can focus on understanding the patterns and principles that apply to entire groups of drugs.
-
Making Educated Guesses: Even if you’ve never encountered a specific drug before, recognizing its prefix or suffix can help you make an educated guess about its classification, mechanism of action, and potential side effects. This can be particularly helpful on the NCLEX when you encounter unfamiliar drug names.
Examples of Common Prefixes and Suffixes:
| Prefix/Suffix | Indication | Example |
|---|---|---|
| -azole | Antifungal | Ketoconazole |
| -cillin | Penicillin antibiotic | Amoxicillin |
| -cycline | Tetracycline antibiotic | Doxycycline |
| -dipine | Calcium channel blocker | Amlodipine |
| -ipramine | Tricyclic antidepressant | Imipramine |
| -mycin | Macrolide antibiotic | Erythromycin |
| -olol | Beta-blocker | Metoprolol |
| -pril | ACE inhibitor | Lisinopril |
| -sartan | Angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) | Losartan |
| -statin | HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor (statin); lowers cholesterol | Atorvastatin |
| -vir | Antiviral | Acyclovir |
| ceph- or cef- | Cephalosporin antibiotic | Cephalexin |
| gluco- or gly- | Related to glucose | Glipizide |
| sulf- | Sulfonamide | Sulfamethoxazole |
| ter- | Usually a beta agonist bronchodilator (but not always: e.g. terbutaline) | Terbutaline |
By actively learning and applying these prefixes and suffixes, you can significantly enhance your pharmacology knowledge and improve your performance on the NCLEX.
4. Why Focus on Generic Names Over Brand Names for the NCLEX?
The NCLEX primarily uses generic names because they are standardized and consistent, unlike brand names which can vary by manufacturer and region. Focusing on generic names ensures you’re learning universally recognized drug information.
While brand names may be more familiar in everyday use, the NCLEX primarily uses generic names for several important reasons:
-
Standardization: Generic names are standardized and universally recognized, regardless of the manufacturer or region. This ensures that all candidates are tested on the same terminology.
-
Consistency: Brand names can vary from country to country, and a single drug may have multiple brand names. Using generic names eliminates this confusion and ensures consistency across the exam.
-
Focus on Pharmacology: The NCLEX is designed to assess your understanding of pharmacology principles, not your ability to memorize brand names. Generic names are more closely linked to the drug’s chemical structure and mechanism of action, making them more relevant for this purpose.
-
Safe Practice: In clinical practice, nurses must be able to recognize and use generic names to ensure accurate medication administration and prevent errors. Focusing on generic names during your NCLEX preparation reinforces this essential skill.
For example, instead of learning multiple brand names for the same drug, such as Sublimaze, Actiq, Duragesic, Fentora, Abstral, and Lazanda, you only need to know the generic name: Fentanyl.
Tips for Learning Generic Names:
- Use Flashcards: Create flashcards with the generic name on one side and the drug’s classification, indication, and mechanism of action on the other.
- Practice Questions: Focus on NCLEX practice questions that use generic names.
- Clinical Experience: Pay attention to the generic names of medications you encounter during your clinical rotations.
- Mnemonics: Develop mnemonics to help you remember challenging generic names.
By prioritizing generic names in your NCLEX pharmacology studies, you’ll be well-prepared to answer exam questions accurately and confidently.
5. How Does Knowing a Medication’s Indication Aid NCLEX Preparation?
Knowing a medication’s indication (what it’s used for) is essential for understanding its therapeutic effects and potential side effects. This knowledge is vital for answering NCLEX questions related to medication administration and patient education.
The indication of a medication refers to the specific condition or disease it is used to treat. Understanding a drug’s indication is crucial for several reasons:
-
Anticipating Therapeutic Effects: Knowing the indication allows you to anticipate the desired therapeutic effects of the medication. For example, if you know that a drug is an “antihypertensive,” you can expect it to lower blood pressure.
-
Predicting Side Effects: Many side effects are directly related to a drug’s indication. For example, diuretics, which are used to treat edema and hypertension, can cause dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
-
Answering NCLEX Questions: The NCLEX often presents scenarios in which you must determine the appropriate medication for a given condition. Knowing the indications for various medications is essential for answering these questions correctly.
-
Patient Education: As a nurse, you’ll be responsible for educating patients about their medications. Understanding the indication allows you to explain to patients why they are taking a particular drug and what benefits they can expect.
-
Safe Medication Administration: Knowing the indication helps you ensure that the medication is being used appropriately and that the patient is receiving the correct dose.
For instance, ACE inhibitors are used to decrease blood pressure and heart rate to prevent myocardial infarction.
Tips for Learning Indications:
- Connect Indications to Classifications: Group medications by classification and learn the common indications for each class.
- Use Mnemonics: Develop mnemonics to help you remember the indications for specific medications.
- Practice Questions: Focus on NCLEX practice questions that require you to identify the appropriate medication for a given condition.
- Clinical Experience: Pay attention to the indications for medications you encounter during your clinical rotations.
By making a conscious effort to learn the indications for various medications, you’ll be well-prepared to answer NCLEX questions and provide safe, effective patient care.
6. Why Is Understanding the Mechanism of Action Important for the NCLEX?
Understanding the mechanism of action (how a drug works at the cellular level) helps you connect the drug to its indication and side effects. This deeper understanding strengthens your ability to answer complex NCLEX questions and apply pharmacological knowledge in clinical practice.
The mechanism of action (MOA) describes how a drug works at the cellular or molecular level to produce its therapeutic effect. Understanding the MOA is crucial for several reasons:
-
Connecting Drug to Indication: The MOA explains why a drug is effective for a particular indication. For example, understanding that ACE inhibitors prevent the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II (a potent vasoconstrictor) explains why they are used to treat hypertension.
-
Predicting Side Effects: Many side effects are directly related to a drug’s MOA. For example, knowing that a diuretic works by increasing urine production helps you understand why it can cause dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
-
Answering Complex NCLEX Questions: The NCLEX often presents complex scenarios that require you to apply your understanding of pharmacology principles. Knowing the MOA allows you to reason through these questions and arrive at the correct answer.
-
Applying Knowledge in Clinical Practice: Understanding the MOA helps you make informed decisions about medication administration and patient care.
Understanding how the facts fit together is a powerful way to incorporate new knowledge into your memory inventory. When you connect cause and effect in a strong framework, you’re adding extra ‘hooks’ your brain can use to retrieve information during any exam or even on the job.
For example, ACE inhibitors treat hypertension: that’s the indication. The way they do this, (the mechanism of action) is by preventing the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II. Angiotensin II is a potent vasoconstrictor. In other words, ACE inhibitors help to enlarge blood vessels, which, therefore, decreases blood pressure.
Tips for Learning Mechanisms of Action:
- Focus on Key Concepts: Don’t get bogged down in the minute details of every MOA. Focus on understanding the key concepts and how they relate to the drug’s therapeutic effect.
- Use Visual Aids: Use diagrams and animations to visualize how drugs interact with cells and molecules.
- Connect MOA to Side Effects: Always consider how the MOA can lead to potential side effects.
- Practice Questions: Focus on NCLEX practice questions that require you to apply your understanding of MOA.
By investing the time to understand the mechanisms of action of various medications, you’ll not only improve your performance on the NCLEX but also develop a deeper understanding of pharmacology that will serve you well throughout your nursing career.
7. What’s the Best Way to Remember Medication Side Effects for the NCLEX?
Focus on common and “killer” (severe) side effects. Common side effects are frequently tested, while recognizing and prioritizing interventions for severe adverse reactions is crucial for patient safety and NCLEX success.
Remembering the side effects of medications can be challenging due to the sheer volume of information. However, by focusing on the most important side effects and using effective study strategies, you can master this aspect of NCLEX pharmacology. Here’s a breakdown of how to approach this task:
-
Common vs. Severe Side Effects: Prioritize learning the common and severe side effects of frequently prescribed medications. Common side effects are those that occur relatively frequently and are generally mild and manageable. Severe side effects (also known as adverse reactions) are less common but can be life-threatening and require immediate intervention.
-
Focus on “Killer” Side Effects: Pay special attention to “killer” side effects, which are those that can cause significant harm or death if not recognized and treated promptly. The NCLEX often tests your ability to identify and prioritize interventions for these adverse reactions.
-
Connect Side Effects to MOA: Whenever possible, connect side effects to the drug’s mechanism of action. This will help you understand why certain side effects occur and make them easier to remember.
-
Use Mnemonics: Develop mnemonics to help you remember challenging side effects. For example, the mnemonic “ABCD” can be used to remember the side effects of ACE inhibitors: Angioedema, Blood pressure decrease, Cough, Dizziness.
-
Practice Questions: Focus on NCLEX practice questions that require you to identify potential side effects and prioritize appropriate nursing interventions.
Examples of “Killer” Side Effects:
- Anaphylaxis: A severe allergic reaction that can cause difficulty breathing, swelling of the throat, and a drop in blood pressure.
- Stevens-Johnson Syndrome: A rare but serious skin disorder that can cause blistering and peeling of the skin.
- Agranulocytosis: A severe decrease in white blood cells, which can increase the risk of infection.
- Hepatotoxicity: Liver damage caused by certain medications.
- Nephrotoxicity: Kidney damage caused by certain medications.
- Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome: A rare but life-threatening reaction to antipsychotic medications.
If one misses a killer side effect, the patient could die so make it a priority to memorize these NCLEX medication facts!
By focusing on the most important side effects and using effective study strategies, you can master this challenging aspect of NCLEX pharmacology and ensure patient safety in your nursing practice.
8. What Are Nursing Considerations and Why Are They Important for the NCLEX?
Nursing considerations are the actions nurses take before, during, and after medication administration to ensure patient safety and effectiveness. They include assessments, lab monitoring, patient education, and recognizing contraindications. Mastering nursing considerations is vital for NCLEX success.
Nursing considerations encompass the actions a nurse must take before, during, and after administering a medication. These actions are designed to ensure patient safety, optimize medication effectiveness, and prevent adverse reactions. Here’s why nursing considerations are so important for the NCLEX:
- Patient Safety: The primary goal of nursing considerations is to protect patients from harm. By carefully assessing the patient’s condition, checking laboratory values, and monitoring for side effects, nurses can identify and prevent potential problems.
- Medication Effectiveness: Nursing considerations also aim to optimize the therapeutic effects of medications. By administering medications at the correct time, in the correct dose, and via the correct route, nurses can ensure that patients receive the maximum benefit from their treatment.
- NCLEX Focus: The NCLEX places a strong emphasis on patient safety and the nurse’s role in medication administration. You can expect to see numerous questions that require you to apply your knowledge of nursing considerations.
- Real-World Application: Nursing considerations are essential for safe and effective nursing practice. By mastering these concepts during your NCLEX preparation, you’ll be well-prepared to provide high-quality care to your patients.
For example: orthostatic hypotension can be a side effect of calcium channel blockers. Therefore, a nursing consideration when administering them would be to check the patient’s blood pressure to make sure it’s not too low (< 100/60).
Examples of Nursing Considerations:
- Assessment: Assessing the patient’s vital signs, medical history, allergies, and current medications before administering a new medication.
- Lab Monitoring: Checking relevant laboratory values (e.g., potassium levels for diuretics, liver function tests for hepatotoxic drugs) before and during medication administration.
- Patient Education: Educating the patient about the medication’s purpose, how to take it, potential side effects, and when to seek medical attention.
- Contraindications: Identifying any conditions or medications that would make the use of a particular drug unsafe.
- Administration Techniques: Using proper techniques for administering medications via various routes (e.g., oral, intramuscular, intravenous).
- Monitoring for Therapeutic Effects and Side Effects: Observing the patient for the desired therapeutic effects of the medication and monitoring for any potential side effects.
Answering NCLEX practice questions is a great way to test your ability to combine your knowledge of side effects and nursing considerations to make good decisions.
By mastering nursing considerations, you’ll be well-prepared to answer NCLEX questions and provide safe, effective patient care.
9. What Are the Most Effective Tools for Learning and Remembering NCLEX Medications?
Brainscape’s NCLEX flashcards are an effective tool. They leverage spaced repetition to optimize learning and retention of essential pharmacology facts. Consider also using practice questions, study groups, and real-world clinical experiences.
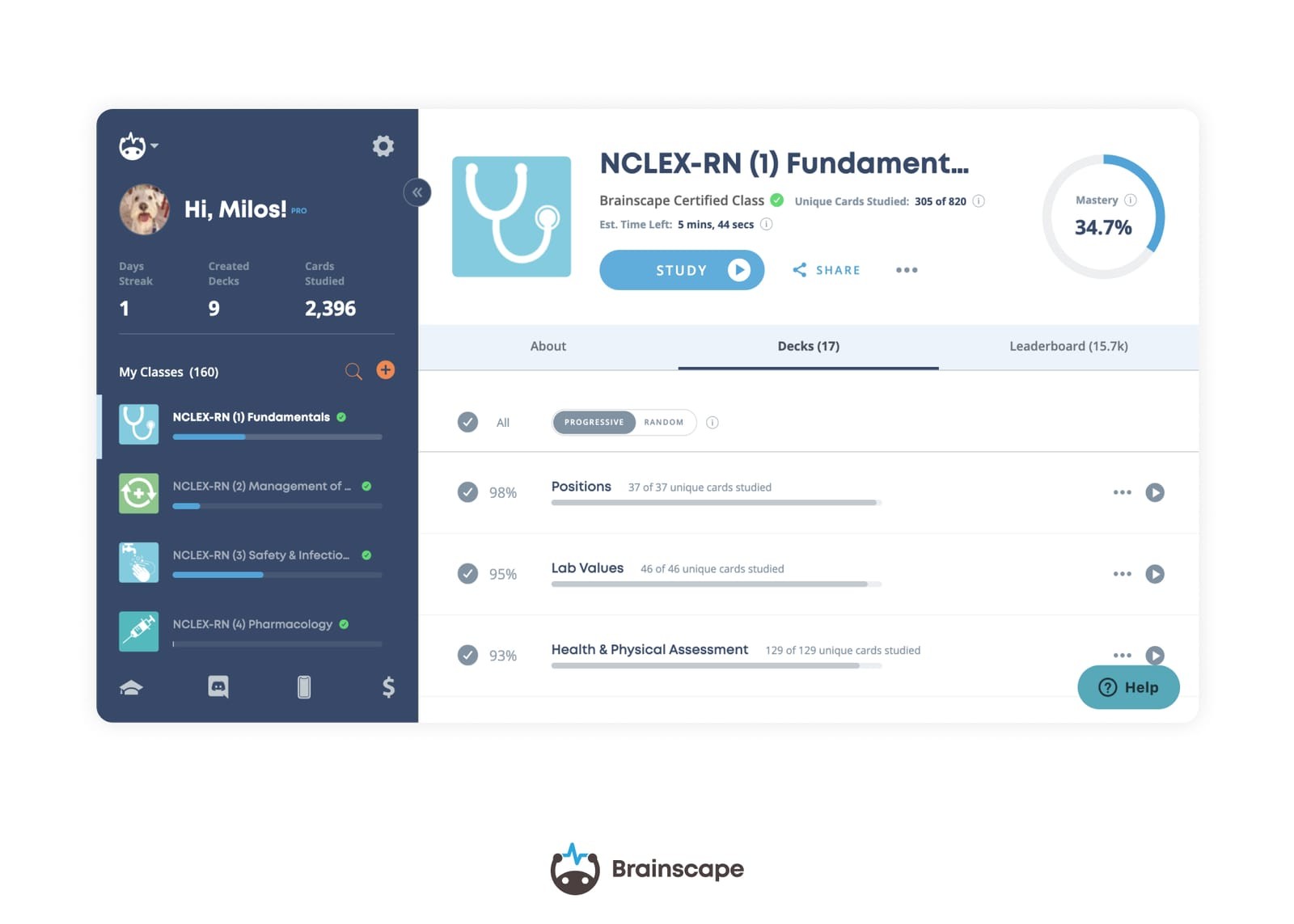
Now that we’ve covered what to learn when you’re studying NCLEX medications, it’s time to look at how you can best and most efficiently learn these facts. The answer is Brainscape’s expert-curated and vetted collection of flashcards for the NCLEX RN and NCLEX PN exams, both of which contain collections specifically for NCLEX meds.
| Tool | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Flashcards | Digital or physical cards with a question or term on one side and the answer or definition on the other. | Excellent for memorizing facts, definitions, and drug classifications. Spaced repetition software like Brainscape optimizes learning and retention. |
| Practice Questions | NCLEX-style questions that test your knowledge and application of pharmacology concepts. | Helps you apply your knowledge in a test-like setting, identify areas of weakness, and improve critical thinking skills. |
| Study Groups | Collaborative learning with other students. | Provides opportunities to discuss concepts, ask questions, and learn from others. Explaining concepts to others reinforces your own understanding. |
| Mnemonics | Memory aids that use acronyms, rhymes, or visual imagery to help you remember information. | Effective for memorizing lists of side effects, drug classifications, or nursing considerations. |
| Clinical Experience | Real-world experience administering medications and caring for patients. | Reinforces your knowledge and helps you apply what you’ve learned in a practical setting. Provides opportunities to ask questions and learn from experienced nurses. |
| Pharmacology Textbooks | Comprehensive resources that provide detailed information about medications, including their mechanisms of action, indications, and side effects. | Offer a solid foundation of knowledge and can be used as a reference source. |
| Online Resources | Websites, videos, and other online materials that provide information about pharmacology. | Offer a variety of learning formats and can be accessed anytime, anywhere. |
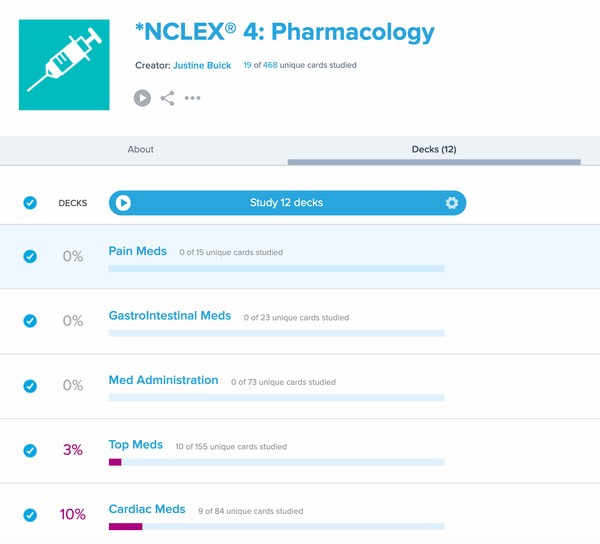
These flashcards cover all 8 sections of the exam and the most important facts you’ll need to know to crush the NCLEX, organized in a way that makes studying hyper-efficient and painless. The Pharmacology section is further broken down into 12 decks of almost 500 flashcards in total, which will drill you on every NCLEX medication (and the related fact) you need to know.
As you answer each card, you rate how well you knew the answer. Brainscape’s algorithm then uses spaced repetition to time how often you need to revisit cards to commit the information to your long term memory. This dramatically speeds up the learning time: by delivering the content to you at optimal intervals, engraving it deeper in your working memory.
You can also use Brainscape to make your own flashcards, using images and even audio (like voice recordings) to make a powerful set of study assets for the NCLEX.
Ultimately, the best tool for learning and remembering NCLEX medications is the one that works best for you. Experiment with different tools and strategies to find what helps you learn most effectively.
10. How Can I Summarize and Review NCLEX Pharmacology Effectively?
Regularly review medication classifications, prefixes/suffixes, generic names, indications, mechanisms of action, side effects, and nursing considerations. Use flashcards, practice questions, and create your own summaries to reinforce learning.
In summary, NCLEX medications are a body of knowledge many students find overwhelming. However, learning what you need to is not quite as difficult as it first appears. For common medications, you’ll need to know:
- Classification
- Prefixes and suffixes
- Generic names
- Indications (what the medication is for)
- How the medication works
- Side effects and adverse reactions
- Nursing considerations
To summarize and review NCLEX pharmacology effectively, consider these strategies:
- Regular Review: Schedule regular review sessions to reinforce your knowledge and prevent forgetting.
- Focus on Key Concepts: Prioritize the most important concepts, such as drug classifications, mechanisms of action, and nursing considerations.
- Use Active Recall: Test yourself frequently using flashcards, practice questions, or by explaining concepts to others.
- Create Your Own Summaries: Summarize the key information about each drug or drug class in your own words. This will help you understand and remember the material more effectively.
- Use Visual Aids: Create diagrams, charts, or tables to organize and visualize the information.
- Connect Concepts: Look for connections between different drugs and drug classes. This will help you build a deeper understanding of pharmacology.
By following these strategies, you can effectively summarize and review NCLEX pharmacology, ensuring that you are well-prepared for the exam.
Pharmacology is a critical component of the NCLEX-RN exam, and mastering this subject requires a strategic approach. By focusing on key areas such as drug classifications, prefixes/suffixes, generic names, indications, mechanisms of action, side effects, and nursing considerations, you can build a solid foundation of knowledge. Utilizing effective study tools, such as Brainscape’s NCLEX flashcards, practice questions, and study groups, can further enhance your learning and retention. Remember, consistency and active recall are key to success. With dedication and the right resources, you can confidently tackle the pharmacology section of the NCLEX-RN and embark on a rewarding career in nursing.
If you’re looking for more comprehensive resources and personalized guidance, visit LEARNS.EDU.VN. Our platform offers a wide range of NCLEX study materials, including detailed pharmacology guides, practice questions, and expert tutoring. We’re here to support you every step of the way on your journey to becoming a registered nurse.
Ready to take your NCLEX prep to the next level? Explore our resources and courses at LEARNS.EDU.VN today! Our expert team is dedicated to helping you achieve your goals and build a successful nursing career. Contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States or Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212. Your success is our priority.
**NCLEX-RN® is a registered trademark of the National Council of State Boards of Nursing (NCSBN), which neither sponsors nor endorses this product.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on Learning Pharmacology for NCLEX
1. How much pharmacology is on the NCLEX?
Pharmacology typically accounts for 12-18% of the questions on the NCLEX-RN.
2. Is pharmacology the hardest part of the NCLEX?
Many students find pharmacology challenging due to the volume of information, but with focused study, it can be mastered.
3. What are the best resources for NCLEX pharmacology?
Brainscape flashcards, NCLEX review books, practice questions, and online resources are all helpful.
4. How can I memorize drug classifications easily?
Use mnemonics, flashcards, and group drugs with similar characteristics.
5. What are the most important nursing considerations to know?
Patient assessments, lab monitoring, patient education, and recognizing contraindications are crucial.
6. How do I study side effects effectively?
Focus on common and severe side effects, and connect them to the drug’s mechanism of action.
7. Should I focus on brand names or generic names?
Focus on generic names, as the NCLEX primarily uses them.
8. How can I make pharmacology less overwhelming?
Break it down into smaller, manageable topics, and study consistently.
9. What is the best way to apply pharmacology knowledge?
Practice NCLEX-style questions and relate pharmacology to clinical scenarios.
10. Where can I find more help with NCLEX pharmacology?
Visit learns.edu.vn for comprehensive resources and expert guidance.