Learning statistics can be straightforward with the right strategies. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we provide a comprehensive approach, breaking down complex statistical concepts into understandable segments and offering tailored learning paths for everyone. Unlock your potential by mastering statistics through our resources, designed to help you excel in data analysis, statistical methods, and probabilistic reasoning.
1. What is the best way to start learning statistics?
The best way to start learning statistics is by grasping the fundamental concepts first. Begin with descriptive statistics, which includes measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode) and measures of dispersion (variance, standard deviation). Understanding these basics provides a solid foundation before moving on to more complex topics. Resources like Khan Academy and Stat Trek offer excellent introductory materials. According to a study by the National Center for Education Statistics, students who master basic statistical concepts early on are more likely to succeed in advanced courses.
2. How can I learn statistics quickly?
Learning statistics quickly involves a focused approach. Start by identifying your specific learning goals and prioritizing the most relevant topics. Use online courses and tutorials that offer hands-on exercises and real-world examples to reinforce your understanding. Platforms like Coursera and edX provide structured courses that can help you learn efficiently. A study from Stanford University’s Department of Statistics showed that students who engage in active learning techniques, such as problem-solving and data analysis projects, learn statistics more rapidly.
3. What are the essential topics to cover when learning statistics?
Essential topics in statistics include:
- Descriptive Statistics: Measures of central tendency and dispersion.
- Probability: Understanding probability distributions and concepts.
- Inferential Statistics: Hypothesis testing, confidence intervals, and statistical significance.
- Regression Analysis: Linear and multiple regression models.
- Data Analysis: Interpreting and visualizing data using statistical software.
A report by the American Statistical Association emphasizes that a strong foundation in these areas is crucial for anyone working with data.
4. Which online resources are best for learning statistics?
Several online resources are excellent for learning statistics:
- Khan Academy: Offers free video lessons and practice exercises covering basic to advanced statistics.
- Coursera: Provides courses and specializations from top universities.
- edX: Features courses on statistics, data science, and related topics.
- Stat Trek: Offers clear explanations and tutorials for statistical concepts.
- Udacity: Provides nanodegree programs focused on data analysis and statistics.
According to a survey by the Online Learning Consortium, these platforms are highly rated for their quality of instruction and comprehensive content.
5. How can I apply statistics in real-world scenarios?
To apply statistics in real-world scenarios, focus on practical applications. Work on projects that involve analyzing real data, such as market research data, financial data, or scientific data. Use statistical software like R, Python (with libraries like Pandas and NumPy), or SPSS to perform your analyses. Engage in internships or volunteer opportunities where you can apply your statistical skills. A study by Harvard Business Review found that professionals who can apply statistical analysis to solve business problems are highly valued in today’s job market.
6. What are the best statistical software programs for beginners?
For beginners, the best statistical software programs include:
- Excel: Widely accessible and suitable for basic statistical analysis.
- SPSS: User-friendly interface with powerful analytical capabilities.
- R: Open-source software with extensive libraries for statistical computing (RStudio is a popular IDE).
- Python: Versatile programming language with libraries like Pandas, NumPy, and SciPy for data analysis.
- JASP: Free, open-source program with a focus on Bayesian statistics.
A survey by KDnuggets indicated that Python and R are increasingly popular among data scientists and statisticians due to their flexibility and extensive community support.
7. How can I improve my understanding of statistical concepts?
To improve your understanding of statistical concepts:
- Practice Regularly: Work through problems and exercises.
- Seek Clarification: Ask questions when you don’t understand a concept.
- Use Visual Aids: Graphs, charts, and diagrams can help visualize data and concepts.
- Teach Others: Explaining concepts to others reinforces your own understanding.
- Apply Concepts: Use statistics in real-world projects and scenarios.
Research from the Journal of Educational Psychology suggests that active learning strategies, such as self-explanation and concept mapping, significantly improve students’ understanding of complex topics.
8. What are some common mistakes to avoid when learning statistics?
Common mistakes to avoid include:
- Skipping the Basics: Ensure you have a solid foundation in fundamental concepts.
- Memorizing Formulas: Focus on understanding the underlying principles.
- Ignoring Assumptions: Be aware of the assumptions underlying statistical tests.
- Misinterpreting Results: Understand the limitations of your analysis and avoid overgeneralizing.
- Not Seeking Help: Don’t hesitate to ask for help when you’re struggling.
A report by the American Statistical Association highlights the importance of statistical literacy and critical thinking to avoid misinterpretations and flawed conclusions.
9. How can I use statistics to improve my career prospects?
Using statistics to improve your career prospects involves developing in-demand skills and showcasing your abilities. Consider these steps:
- Learn Statistical Software: Master tools like R, Python, or SPSS.
- Build a Portfolio: Work on projects that demonstrate your data analysis skills.
- Obtain Certifications: Earn certifications in statistics or data science.
- Network: Connect with professionals in your field.
- Highlight Skills: Emphasize your statistical skills in your resume and interviews.
LinkedIn’s Skills Gap Report consistently identifies data analysis and statistical skills as highly sought-after by employers across various industries.
10. What are the best resources for learning advanced statistical techniques?
For learning advanced statistical techniques, consider these resources:
- Advanced Textbooks: “The Elements of Statistical Learning” by Hastie, Tibshirani, and Friedman.
- Specialized Courses: Advanced courses on Coursera, edX, and Udacity.
- Research Papers: Publications in journals like “The Annals of Statistics” and “The Journal of the American Statistical Association.”
- Conferences: Attend statistical conferences and workshops.
- Online Communities: Engage in forums and communities like Cross Validated and Stack Overflow.
According to a report by the National Science Foundation, continuous learning and engagement with the research community are essential for staying current in the field of statistics.
1. Grasping the Fundamentals: Why Learn Statistics?
Statistics is more than just numbers; it’s a powerful tool for understanding and interpreting the world around us. Whether you’re a student, a professional, or simply curious, mastering statistics opens doors to critical thinking, informed decision-making, and problem-solving across diverse fields. According to a 2023 report by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, jobs in statistics and related fields are projected to grow significantly over the next decade, highlighting the increasing demand for statistically literate individuals. From healthcare and finance to marketing and social sciences, statistics is the backbone of evidence-based analysis. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we recognize the importance of a solid statistical foundation and offer resources tailored to help you build that foundation effectively.
1.1. What Exactly is Statistics?
Statistics is the science of collecting, analyzing, interpreting, and presenting data. It provides a framework for making informed decisions based on evidence, rather than relying on intuition or guesswork. There are two main branches of statistics:
- Descriptive Statistics: This involves summarizing and presenting data in a meaningful way, using measures like mean, median, mode, standard deviation, and graphical representations.
- Inferential Statistics: This involves drawing conclusions about a population based on a sample of data, using techniques like hypothesis testing, confidence intervals, and regression analysis.
1.2. Why is Statistics Important?
Understanding statistics is crucial for several reasons:
- Informed Decision-Making: Statistics helps you make informed decisions by providing a framework for evaluating evidence and assessing risk.
- Critical Thinking: Statistics teaches you to think critically about data and to identify potential biases or flaws in reasoning.
- Problem-Solving: Statistics provides tools for analyzing complex problems and developing effective solutions.
- Career Advancement: Statistical skills are highly valued in many industries, offering opportunities for career advancement and increased earning potential.
- Understanding Research: Statistics is essential for understanding and evaluating research findings in various fields.
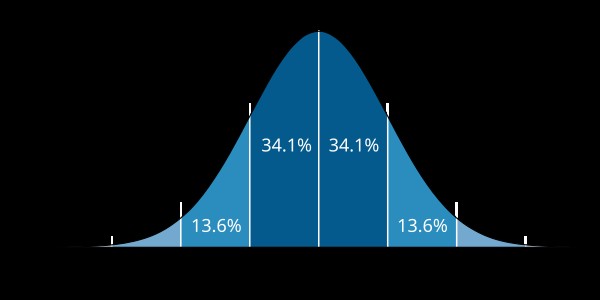 Statistical Distributions
Statistical Distributions
1.3. The Role of Statistics in Various Fields
Statistics plays a vital role in numerous fields:
| Field | Application |
|---|---|
| Healthcare | Analyzing clinical trial data, tracking disease outbreaks, improving patient care |
| Finance | Assessing investment risk, forecasting market trends, managing portfolios |
| Marketing | Understanding consumer behavior, measuring advertising effectiveness, optimizing campaigns |
| Social Sciences | Conducting surveys, analyzing social trends, evaluating policy interventions |
| Engineering | Improving product quality, optimizing manufacturing processes, ensuring reliability |
According to a study by McKinsey Global Institute, data-driven organizations are 23 times more likely to acquire customers and 6 times more likely to retain them.
2. Setting the Stage: Prerequisites and Foundational Knowledge
Before diving into the complexities of statistics, it’s essential to ensure you have a solid foundation in basic mathematical concepts. While advanced calculus isn’t always necessary, a good understanding of algebra and basic arithmetic is crucial. These prerequisites will make learning statistics smoother and more enjoyable. LEARNS.EDU.VN emphasizes building a strong foundation to ensure our learners can confidently tackle advanced statistical concepts.
2.1. Essential Mathematical Skills
- Algebra: A strong understanding of algebraic equations, inequalities, and functions is essential for manipulating statistical formulas and interpreting results.
- Basic Arithmetic: Proficiency in addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division is fundamental for performing statistical calculations.
- Fractions, Decimals, and Percentages: These concepts are used extensively in statistical analysis, so a solid grasp is necessary.
- Graphing and Charting: Understanding how to interpret and create graphs and charts is crucial for visualizing data.
2.2. Recommended Resources for Review
If you need to brush up on your math skills, several excellent resources are available:
- Khan Academy: Offers free video lessons and practice exercises covering a wide range of math topics.
- Mathway: Provides step-by-step solutions to math problems.
- Purplemath: Offers clear and concise explanations of algebra concepts.
2.3. The Importance of a Strong Foundation
Attempting to learn statistics without a solid mathematical foundation is like trying to build a house on sand. You’ll likely struggle with the concepts and become frustrated. Investing time in reviewing these prerequisites will pay off in the long run, making your statistics learning journey much more successful. A study by the National Mathematics Advisory Panel found that students with strong math skills are more likely to succeed in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) fields, including statistics.
3. Choosing Your Path: Learning Methods and Resources
Learning statistics can be approached in various ways, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Whether you prefer structured courses, self-study, or a combination of both, finding the right learning method is crucial for success. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we offer a variety of learning resources to cater to different learning styles and preferences.
3.1. Formal Education: Courses and Programs
- University Courses: Taking a statistics course at a university or college provides a structured learning environment with expert instruction and opportunities for interaction with peers.
- Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera, edX, and Udacity offer a wide range of online statistics courses, often taught by leading professors from top universities.
- Bootcamps: Data science bootcamps provide intensive, hands-on training in statistics and data analysis, often geared towards career changers.
3.2. Self-Study: Books and Online Resources
- Textbooks: There are many excellent statistics textbooks available, ranging from introductory to advanced levels. Some popular choices include “Statistics” by David Freedman, Robert Pisani, and Roger Purves, and “OpenIntro Statistics” by David Diez, Christopher Barr, and Mine Çetinkaya-Rundel.
- Online Tutorials: Websites like Khan Academy, Stat Trek, and Statistics How To offer free tutorials and explanations of statistical concepts.
- Practice Problems: Working through practice problems is essential for reinforcing your understanding of statistics. Many textbooks and online resources offer practice problems with solutions.
3.3. Combining Methods: A Hybrid Approach
Many learners find that a combination of formal education and self-study is the most effective approach. For example, you might take an online course to learn the fundamentals and then supplement your learning with textbooks and practice problems. According to a study by the U.S. Department of Education, students who combine online and face-to-face learning perform better than those who rely solely on one method.
4. Mastering the Basics: Descriptive Statistics
Descriptive statistics is the foundation of statistical analysis. It involves summarizing and presenting data in a meaningful way, allowing you to understand the key characteristics of a dataset. This includes measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode) and measures of dispersion (variance, standard deviation). At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we provide clear and concise explanations of descriptive statistics concepts, along with practical examples and exercises.
4.1. Measures of Central Tendency
- Mean: The average of a set of numbers.
- Median: The middle value in a sorted set of numbers.
- Mode: The value that appears most frequently in a set of numbers.
4.2. Measures of Dispersion
- Variance: A measure of how spread out the data is from the mean.
- Standard Deviation: The square root of the variance, providing a more interpretable measure of dispersion.
- Range: The difference between the largest and smallest values in a dataset.
4.3. Visualizing Data: Graphs and Charts
- Histograms: Used to display the distribution of a continuous variable.
- Bar Charts: Used to compare the values of different categories.
- Pie Charts: Used to show the proportion of different categories in a whole.
- Scatter Plots: Used to show the relationship between two continuous variables.
4.4. Practice with Real-World Datasets
To solidify your understanding of descriptive statistics, it’s essential to practice with real-world datasets. Here are some examples:
- Titanic Dataset: Analyze the survival rates of passengers on the Titanic based on factors like age, gender, and class.
- Iris Dataset: Explore the characteristics of different species of iris flowers based on measurements like sepal length and width.
- Boston Housing Dataset: Investigate the factors that influence housing prices in Boston.
5. Understanding Probability: The Language of Uncertainty
Probability is a fundamental concept in statistics, providing a way to quantify uncertainty and make predictions about future events. Understanding probability is crucial for grasping more advanced statistical concepts like hypothesis testing and confidence intervals. LEARNS.EDU.VN offers comprehensive resources on probability, including explanations of key concepts, examples, and practice problems.
5.1. Basic Probability Concepts
- Sample Space: The set of all possible outcomes of an experiment.
- Event: A subset of the sample space.
- Probability: The likelihood of an event occurring, expressed as a number between 0 and 1.
- Independent Events: Events that do not affect each other’s probabilities.
- Dependent Events: Events that do affect each other’s probabilities.
5.2. Probability Distributions
- Discrete Distributions: Used to model the probability of discrete events, such as the number of heads in a series of coin flips (Binomial distribution) or the number of events occurring in a fixed interval of time (Poisson distribution).
- Continuous Distributions: Used to model the probability of continuous variables, such as height or weight. The most common continuous distribution is the Normal distribution (also known as the Gaussian distribution).
5.3. Conditional Probability and Bayes’ Theorem
- Conditional Probability: The probability of an event occurring given that another event has already occurred.
- Bayes’ Theorem: A formula that relates conditional probabilities, allowing you to update your beliefs based on new evidence.
5.4. Applications of Probability in Real Life
Probability is used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Weather Forecasting: Predicting the likelihood of rain or snow.
- Medical Diagnosis: Assessing the probability of a patient having a particular disease.
- Financial Modeling: Estimating the risk of investments.
- Game Theory: Analyzing strategic interactions between individuals or organizations.
6. Inferential Statistics: Drawing Conclusions from Data
Inferential statistics involves using sample data to make inferences about a larger population. This includes techniques like hypothesis testing, confidence intervals, and regression analysis. Mastering inferential statistics is essential for making data-driven decisions in various fields. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we offer in-depth coverage of inferential statistics, with practical examples and step-by-step guidance.
6.1. Hypothesis Testing
- Null Hypothesis: A statement about the population that you are trying to disprove.
- Alternative Hypothesis: A statement that contradicts the null hypothesis.
- P-Value: The probability of observing a test statistic as extreme as or more extreme than the one observed, assuming the null hypothesis is true.
- Significance Level: A threshold for rejecting the null hypothesis (typically 0.05).
- Type I Error: Rejecting the null hypothesis when it is actually true (false positive).
- Type II Error: Failing to reject the null hypothesis when it is actually false (false negative).
6.2. Confidence Intervals
- Confidence Interval: A range of values that is likely to contain the true population parameter with a certain level of confidence.
- Confidence Level: The probability that the confidence interval contains the true population parameter (typically 95% or 99%).
- Margin of Error: The amount added and subtracted from the sample statistic to create the confidence interval.
6.3. Regression Analysis
- Linear Regression: A statistical technique used to model the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables.
- Multiple Regression: An extension of linear regression that allows for multiple independent variables.
- Regression Coefficients: Estimates of the change in the dependent variable for each unit change in the independent variable.
- R-Squared: A measure of how well the regression model fits the data (ranges from 0 to 1).
6.4. Applications of Inferential Statistics
Inferential statistics is used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Medical Research: Determining the effectiveness of new treatments.
- Market Research: Assessing consumer preferences.
- Political Polling: Predicting election outcomes.
- Quality Control: Monitoring the quality of manufactured products.
7. Statistical Software: Tools of the Trade
Statistical software programs are essential tools for data analysis. They allow you to perform complex calculations, create visualizations, and build statistical models. Choosing the right software depends on your needs and preferences. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we provide tutorials and resources for various statistical software packages.
7.1. Popular Statistical Software Packages
- R: A free, open-source programming language and software environment for statistical computing and graphics. R is highly flexible and customizable, with a vast library of packages for performing a wide range of statistical analyses.
- Python: A versatile programming language with powerful libraries for data analysis, such as Pandas, NumPy, and Scikit-learn. Python is easy to learn and has a large and active community.
- SPSS: A user-friendly statistical software package with a graphical interface. SPSS is widely used in social sciences, business, and healthcare.
- SAS: A comprehensive statistical software package used in various industries, including finance, healthcare, and manufacturing. SAS is known for its robust data management and analytical capabilities.
- Excel: A widely available spreadsheet program that can be used for basic statistical analysis and data visualization.
7.2. Choosing the Right Software
When choosing statistical software, consider the following factors:
- Ease of Use: How easy is the software to learn and use?
- Features: Does the software have the features you need for your specific analyses?
- Cost: How much does the software cost?
- Community Support: Is there a large and active community of users who can provide support and guidance?
- Platform Compatibility: Is the software compatible with your operating system?
7.3. Learning Resources for Statistical Software
Many online resources are available for learning statistical software:
- Official Documentation: The official documentation for each software package provides comprehensive information on its features and functionality.
- Online Tutorials: Websites like YouTube and Coursera offer tutorials on using various statistical software packages.
- Books: There are many excellent books available on statistical software, ranging from introductory to advanced levels.
8. Common Statistical Pitfalls: Avoiding Mistakes
Statistics can be tricky, and it’s easy to make mistakes if you’re not careful. Understanding common statistical pitfalls is essential for conducting sound analyses and drawing valid conclusions. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we highlight common statistical errors and provide guidance on how to avoid them.
8.1. Correlation vs. Causation
One of the most common mistakes in statistics is confusing correlation with causation. Just because two variables are correlated does not mean that one causes the other. There may be other factors at play, or the relationship may be coincidental.
8.2. Sampling Bias
Sampling bias occurs when the sample is not representative of the population. This can lead to inaccurate conclusions about the population. To avoid sampling bias, it’s essential to use random sampling techniques.
8.3. Overfitting
Overfitting occurs when a statistical model is too complex and fits the sample data too closely. This can lead to poor performance on new data. To avoid overfitting, it’s important to use simpler models and to validate your models on independent datasets.
8.4. Data Dredging
Data dredging (also known as p-hacking) occurs when you search through a dataset for statistically significant relationships without a specific hypothesis in mind. This can lead to spurious findings that are not replicable. To avoid data dredging, it’s important to have a clear hypothesis before analyzing the data.
8.5. Misinterpreting P-Values
P-values are often misinterpreted. A p-value is the probability of observing a test statistic as extreme as or more extreme than the one observed, assuming the null hypothesis is true. A small p-value does not necessarily mean that the alternative hypothesis is true, only that the data provide evidence against the null hypothesis.
9. Advanced Topics: Expanding Your Knowledge
Once you have a solid foundation in basic statistics, you can explore more advanced topics, such as:
- Bayesian Statistics: A statistical approach that incorporates prior beliefs into the analysis.
- Time Series Analysis: A statistical technique used to analyze data collected over time.
- Multivariate Analysis: A statistical technique used to analyze data with multiple variables.
- Machine Learning: A field of computer science that focuses on developing algorithms that can learn from data.
LEARNS.EDU.VN offers resources for learners to learn about all of these advanced topics.
9.1. Resources for Further Learning
- Advanced Textbooks: “The Elements of Statistical Learning” by Hastie, Tibshirani, and Friedman, “Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning” by Christopher Bishop.
- Specialized Courses: Advanced courses on Coursera, edX, and Udacity.
- Research Papers: Publications in journals like “The Annals of Statistics” and “The Journal of the American Statistical Association.”
10. Statistics in the Age of Data: The Future of Analytics
In today’s data-driven world, statistics is more important than ever. The ability to collect, analyze, and interpret data is a valuable skill in many industries. As technology advances, the demand for statisticians and data scientists will continue to grow. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing the resources and training you need to succeed in this exciting field.
10.1. The Rise of Data Science
Data science is an interdisciplinary field that combines statistics, computer science, and domain expertise to extract knowledge and insights from data. Data scientists use statistical techniques to analyze data, build models, and make predictions.
10.2. The Importance of Statistical Literacy
Even if you don’t plan to become a statistician or data scientist, statistical literacy is an essential skill for navigating the modern world. Understanding basic statistical concepts can help you make informed decisions in your personal and professional life.
10.3. Continuous Learning
The field of statistics is constantly evolving, with new techniques and tools being developed all the time. To stay current, it’s important to commit to continuous learning throughout your career.
Ready to dive deeper into the world of statistics? Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today to explore our comprehensive resources, including tutorials, courses, and practice problems. Whether you’re just starting or looking to advance your skills, we have something for everyone. Start your journey towards statistical mastery and unlock your potential in the age of data. For more information, contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States. Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212. Trang web: learns.edu.vn.
