Is Learning The Drums Hard? At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we believe that while mastering the drums requires dedication, it’s an achievable goal for anyone with passion and persistence, regardless of musical background. We can help you unlock your rhythmic potential and discover the joy of drumming, offering expert guidance and resources for every step of your musical adventure. Let’s explore drum techniques, rhythmic training, and musical instrument education together.
1. Understanding The Initial Hurdle: Is Learning Drums Really Difficult?
Is learning the drums hard? The initial challenge of learning drums often lies in coordinating multiple limbs and understanding basic rhythms. However, this initial hurdle is surmountable with consistent practice and the right guidance. It’s essential to break down the learning process into manageable steps, focusing on building a solid foundation of fundamental skills.
1.1 The Coordination Challenge: Separating Limbs and Sounds
One of the primary reasons people ask, “Is learning the drums hard?” is the coordination required. Drummers must independently control their hands and feet to create complex rhythmic patterns. This can seem daunting at first, but it’s a skill that develops over time.
- Start Slow: Begin with simple exercises that isolate each limb, gradually increasing the complexity as you improve.
- Practice Regularly: Consistent, focused practice sessions are more effective than sporadic, lengthy ones.
- Use Metronome: A metronome is your best friend. It helps you maintain a steady tempo and develop a strong sense of timing.
1.2 The Rhythm Factor: Grasping Basic Beats and Timing
Understanding rhythm is crucial to drumming. It’s not just about hitting the drums; it’s about hitting them in time with the music. Many beginners struggle with internalizing the beat and maintaining a steady tempo.
- Listen Actively: Pay close attention to the rhythmic structure of different songs. Try to identify the drum patterns and count along.
- Learn Music Theory Basics: A basic understanding of music theory, including time signatures and note values, can significantly improve your rhythm.
- Record Yourself: Recording your practice sessions allows you to objectively assess your timing and identify areas for improvement.
1.3 Dispelling the Myth: Natural Talent vs. Dedicated Practice
Many aspiring drummers wonder if they have the “natural talent” needed to succeed. While some individuals may pick up the instrument more quickly, consistent practice and dedication are far more important than innate ability. As research from the Royal Conservatory of Music shows, dedication and practice are essential for enhancing musical skills. Remember, even the most renowned drummers started as beginners.
2. Time Investment: How Long Does It Take To Learn Drums?
The amount of time it takes to learn drums varies depending on your goals and dedication. While you can learn basic beats and play simple songs relatively quickly, mastering the instrument to a professional level requires years of consistent practice and study.
2.1 The Quick Wins: Playing Simple Songs in Weeks
One of the encouraging aspects of learning drums is that you can achieve noticeable progress in a relatively short time. Within a few weeks of consistent practice, you can learn to play basic beats and simple songs.
- Focus on Fundamentals: Start with basic rock and pop beats, which typically involve straightforward patterns.
- Learn Simple Songs: Choose songs with simple drum parts that you can easily replicate.
- Practice with Play-Along Tracks: Playing along with recordings helps you develop your timing and groove.
2.2 Building Proficiency: Months to Years of Dedicated Practice
Becoming a proficient drummer requires a more significant time investment. Developing the skills needed to play in a band, improvise, and tackle more complex genres takes months to years of dedicated practice.
- Consistent Practice Routine: Aim for at least 30 minutes to an hour of practice each day.
- Study Different Genres: Explore various musical styles, such as jazz, funk, and Latin, to broaden your rhythmic vocabulary.
- Seek Feedback: Regular lessons with an experienced drum teacher can provide valuable feedback and guidance.
2.3 Mastery and Beyond: A Lifelong Journey of Learning
Even professional drummers continue to learn and refine their skills throughout their careers. Drumming is a lifelong journey of exploration and discovery.
- Attend Workshops and Clinics: Learning from master drummers can provide new insights and techniques.
- Collaborate with Other Musicians: Playing with other musicians exposes you to new ideas and challenges.
- Stay Curious: Continuously seek out new music, styles, and approaches to drumming to keep your playing fresh and innovative.
3. The Learning Curve: What Skills Will You Need To Develop?
The journey of learning drums involves developing a variety of skills, from basic technique to advanced improvisation. Understanding the learning curve can help you set realistic goals and stay motivated.
3.1 Core Techniques: Mastering the Fundamentals
Mastering the fundamentals is essential for building a solid foundation in drumming. This includes proper grip, stroke technique, and posture.
- Grip: Learn the correct grip for both matched and traditional grip styles. The grip should be relaxed yet controlled, allowing you to generate power and finesse.
- Stroke Technique: Practice different stroke techniques, such as full strokes, down strokes, up strokes, and tap strokes, to develop control over dynamics and articulation.
- Posture: Maintain good posture while playing to prevent injuries and improve your overall technique.
3.2 Reading Music: Understanding Drum Notation
While not always essential, learning to read drum notation can significantly expand your musical horizons. It allows you to learn new patterns, transcribe drum parts, and communicate effectively with other musicians.
- Learn the Basics: Start with the basics of drum notation, including note values, rests, and time signatures.
- Practice Reading Rhythms: Practice reading and playing various rhythmic patterns to improve your sight-reading skills.
- Transcribe Drum Parts: Transcribing drum parts from your favorite songs can help you understand how drummers use notation in real-world scenarios.
3.3 Developing Your Own Style: Creativity and Expression
As you progress, it’s important to develop your own unique style and voice as a drummer. This involves experimenting with different sounds, patterns, and approaches to drumming.
- Listen Widely: Expose yourself to a wide variety of drumming styles and drummers to inspire your own playing.
- Improvise Regularly: Dedicate time to improvisation to develop your creativity and spontaneity.
- Record Your Ideas: Keep a recording device handy to capture any interesting ideas or patterns that come to you.
3.4 Rhythm and Groove: The Heart of Drumming
At its core, drumming is about creating a solid, infectious groove. Developing a strong sense of rhythm and groove is essential for any drummer.
- Metronome Practice: Regular metronome practice is crucial for developing your timing and consistency.
- Play with Others: Playing with other musicians forces you to lock in with the groove and listen to the overall musical context.
- Record and Analyze: Recording yourself playing with a band or play-along track allows you to objectively assess your groove and identify areas for improvement.
4. Available Resources: Can Technology Help You Learn Faster?
Fortunately, there are countless resources available to help you on your drumming journey, from traditional drum teachers to online courses and apps. Leveraging these resources can significantly accelerate your progress.
4.1 Drum Teachers: The Value of Personalized Instruction
Working with an experienced drum teacher can provide personalized instruction and guidance tailored to your specific needs and goals.
- Find a Qualified Teacher: Look for a teacher with a proven track record and experience teaching students at your level.
- Set Clear Goals: Discuss your goals with your teacher and develop a practice plan that aligns with your objectives.
- Be Open to Feedback: Be receptive to your teacher’s feedback and willing to make adjustments to your technique and approach.
4.2 Online Courses and Apps: Flexible and Accessible Learning
Online drum courses and apps offer a flexible and accessible way to learn at your own pace. These resources often include video lessons, practice exercises, and interactive features.
- Choose Reputable Platforms: Select online courses and apps from reputable sources with experienced instructors.
- Follow a Structured Curriculum: Look for courses that offer a structured curriculum that covers the fundamentals and progresses to more advanced topics.
- Utilize Interactive Features: Take advantage of interactive features such as practice exercises, quizzes, and feedback tools to enhance your learning experience.
4.3 Drumming Communities: Learning From Peers
Joining a drumming community can provide valuable support, motivation, and inspiration. You can connect with other drummers, share tips and advice, and learn from each other’s experiences.
- Online Forums and Groups: Participate in online drumming forums and social media groups to connect with drummers from around the world.
- Local Drumming Meetups: Attend local drumming meetups and workshops to network with drummers in your area.
- Collaborate on Projects: Collaborate with other drummers on recording projects, jam sessions, or performances to learn from each other and build your musical network.
5. The Right Mindset: How To Stay Motivated On Your Drumming Journey
Maintaining a positive and motivated mindset is crucial for long-term success in drumming. The journey can be challenging at times, but with the right approach, you can overcome obstacles and achieve your goals.
5.1 Setting Realistic Goals: Breaking Down the Big Picture
Setting realistic goals is essential for staying motivated. Break down your long-term goals into smaller, more manageable steps that you can achieve along the way.
- Start Small: Begin with simple, achievable goals that you can accomplish quickly.
- Track Your Progress: Keep a record of your practice sessions and track your progress over time.
- Celebrate Your Successes: Acknowledge and celebrate your achievements, no matter how small, to stay motivated and build momentum.
5.2 Embracing Challenges: Learning From Mistakes
Mistakes are a natural part of the learning process. Instead of getting discouraged, embrace challenges as opportunities for growth and learning.
- Analyze Your Mistakes: When you make a mistake, take the time to analyze what went wrong and identify areas for improvement.
- Practice Deliberately: Focus on practicing the specific skills or techniques that you find challenging.
- Seek Feedback: Ask your teacher or other drummers for feedback on your playing to gain new perspectives and insights.
5.3 Finding Joy in the Process: The Love of Music
Ultimately, the most important factor in staying motivated is finding joy in the process of making music. Drumming should be fun and rewarding, so make sure to prioritize enjoyment over perfection.
- Play Music You Love: Focus on playing music that you enjoy and that inspires you.
- Experiment and Explore: Don’t be afraid to experiment with different styles and approaches to drumming to discover new sounds and ideas.
- Share Your Music: Share your music with others by playing in a band, recording your own songs, or performing for friends and family.
6. Common Pitfalls: What Mistakes Should Beginners Avoid?
Even with the best resources and mindset, beginners often make common mistakes that can hinder their progress. Being aware of these pitfalls can help you avoid them and accelerate your learning.
6.1 Neglecting Fundamentals: Skipping the Basics
One of the most common mistakes is neglecting the fundamentals. Beginners are often eager to jump into complex patterns and songs without first mastering the basic techniques.
- Prioritize Technique: Focus on developing proper grip, stroke technique, and posture from the beginning.
- Practice Rudiments: Practice rudiments regularly to build your hand and foot coordination.
- Be Patient: Understand that mastering the fundamentals takes time and patience.
6.2 Lack of Consistency: Sporadic Practice Habits
Consistency is key to making progress in drumming. Sporadic practice habits can lead to slow progress and frustration.
- Establish a Routine: Set aside a specific time each day or week for practice.
- Stick to Your Schedule: Make a commitment to sticking to your practice schedule, even when you don’t feel like it.
- Short, Frequent Sessions: Short, frequent practice sessions are more effective than long, infrequent ones.
6.3 Ignoring Feedback: Not Seeking Expert Advice
Ignoring feedback from experienced drummers or teachers can prevent you from identifying and correcting mistakes in your technique and approach.
- Seek Out Feedback: Regularly seek out feedback from qualified teachers or experienced drummers.
- Be Open to Criticism: Be receptive to constructive criticism and willing to make adjustments to your playing.
- Record Yourself: Recording your practice sessions allows you to objectively assess your playing and identify areas for improvement.
6.4 Comparing Yourself to Others: The Comparison Trap
Comparing yourself to other drummers can be demotivating and discouraging. Remember that everyone progresses at their own pace, and it’s important to focus on your own journey.
- Focus on Your Own Progress: Compare yourself to your past self, not to others.
- Celebrate Your Achievements: Acknowledge and celebrate your own successes, no matter how small.
- Be Inspired, Not Intimidated: Use other drummers as inspiration, not as a source of intimidation.
7. Is Age a Factor? Debunking Myths About Learning at Different Ages
Many people wonder if age is a factor in learning drums. While it’s true that children’s brains are more flexible, adults are certainly capable of learning and excelling at drumming.
7.1 Learning as a Child: Advantages and Disadvantages
Children often have an easier time learning new skills due to their brain’s greater neuroplasticity. However, they may lack the focus and discipline needed for consistent practice.
- Advantages: Greater neuroplasticity, more time to dedicate to practice.
- Disadvantages: Lack of focus and discipline, limited musical experience.
7.2 Learning as an Adult: Embracing the Beginner Mindset
Adults may face challenges such as time constraints and preconceived notions about their abilities. However, they often have greater focus, discipline, and life experience to draw upon.
- Advantages: Greater focus and discipline, more life experience, can take advantage of diverse learning resources.
- Disadvantages: Time constraints, preconceived notions about abilities.
7.3 The Importance of Mindset: Overcoming Age-Related Concerns
Regardless of age, the most important factor in learning drums is mindset. A positive, motivated attitude can overcome any age-related challenges.
- Believe in Yourself: Believe that you are capable of learning drums, regardless of your age.
- Set Realistic Goals: Set realistic goals that align with your current abilities and time constraints.
- Embrace the Beginner Mindset: Be willing to embrace the beginner mindset and learn from your mistakes.
8. Budgeting for Drums: How Much Does It Cost To Learn?
The cost of learning drums can vary depending on the resources you choose to utilize. From purchasing a drum kit to taking lessons, it’s important to budget accordingly.
8.1 Drum Kit Costs: Acoustic vs. Electronic Drums
The cost of a drum kit can range from a few hundred dollars for a basic beginner kit to several thousand dollars for a professional-grade kit. Acoustic drums and electronic drums each have their own advantages and disadvantages in terms of cost, sound, and space requirements.
| Feature | Acoustic Drums | Electronic Drums |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Varies greatly, from beginner to professional kits | Mid-range prices, with some high-end options |
| Sound | Authentic and resonant | Customizable with digital sounds |
| Space | Requires more space | Compact designs available |
| Noise Level | Can be loud | Quiet practice with headphones |
| Maintenance | Tuning, head replacement | Minimal maintenance, software updates |

8.2 Lesson Costs: Private Lessons vs. Group Classes
Private drum lessons typically cost more than group classes, but they offer personalized instruction tailored to your specific needs. Group classes can be a more affordable option, but they may not provide as much individual attention.
- Private Lessons: Personalized instruction, tailored to your specific needs and goals.
- Group Classes: More affordable, opportunity to learn from other students.
- Online Lessons: Flexible and convenient, can be more affordable than in-person lessons.
8.3 Additional Expenses: Accessories and Resources
In addition to the cost of a drum kit and lessons, there are other expenses to consider, such as drumsticks, practice pads, headphones, and instructional materials.
- Drumsticks: Essential for playing the drums, come in various sizes and materials.
- Practice Pad: Useful for practicing quietly without a drum kit.
- Headphones: Essential for practicing electronic drums or playing along with recordings.
- Instructional Materials: Books, videos, and online resources can supplement your learning.
9. Setting Up Your Drum Space: Creating an Ideal Practice Environment
Creating an ideal practice environment can significantly enhance your drumming experience. Consider factors such as noise level, space, and ergonomics when setting up your drum space.
9.1 Noise Considerations: Minimizing Disturbances
Drumming can be loud, so it’s important to consider noise levels when setting up your practice space. Options include soundproofing your room, using electronic drums with headphones, or practicing during specific hours.
- Soundproofing: Installing soundproofing materials in your room can help to minimize noise.
- Electronic Drums: Electronic drums allow you to practice quietly with headphones.
- Practice Hours: Practicing during specific hours when noise is less likely to be an issue can help to avoid disturbing others.
9.2 Space Requirements: Maximizing Limited Areas
Drum kits can take up a significant amount of space, so it’s important to maximize your available area. Consider using compact drum kits or electronic drums to save space.
- Compact Drum Kits: Smaller drum kits designed for smaller spaces.
- Electronic Drums: Electronic drums take up less space than acoustic drums and can be folded up for storage.
- Vertical Storage: Utilize vertical storage solutions to store drum accessories and other gear.
9.3 Ergonomics: Prioritizing Comfort and Health
Maintaining good posture and ergonomics is essential for preventing injuries and maximizing your comfort while playing.
- Drum Throne: Invest in a comfortable and adjustable drum throne.
- Drum Placement: Position your drums so that you can reach them easily without straining.
- Posture: Maintain good posture while playing to prevent back pain and other injuries.
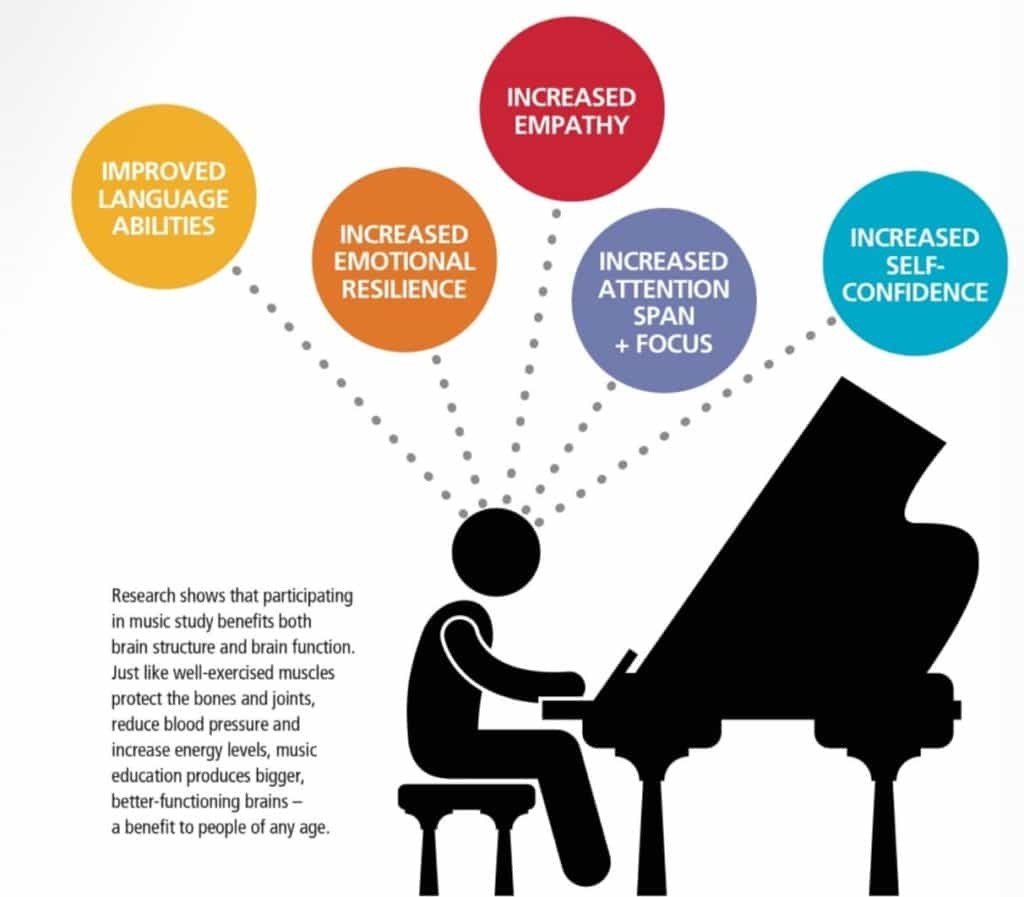
10. Drumming and Health: What are the Physical and Mental Benefits?
Beyond the joy of making music, drumming offers numerous physical and mental health benefits.
10.1 Physical Fitness: Coordination, Strength, and Endurance
Drumming is a physically demanding activity that can improve your coordination, strength, and endurance.
- Coordination: Drumming requires coordinating multiple limbs independently, improving your overall coordination.
- Strength: Drumming builds strength in your arms, legs, and core muscles.
- Endurance: Drumming can improve your cardiovascular health and increase your endurance.
10.2 Stress Relief: Expressing Emotions and Finding Flow
Drumming can be a powerful form of stress relief, allowing you to express your emotions and find a state of flow.
- Emotional Expression: Drumming provides a creative outlet for expressing your emotions.
- Flow State: Drumming can induce a state of flow, where you are fully immersed in the present moment and lose track of time.
- Mindfulness: Drumming can promote mindfulness and help you to focus on the present moment.
10.3 Cognitive Benefits: Improving Focus and Memory
Drumming has been shown to improve cognitive function, including focus, memory, and processing speed. According to a study from the University of Oxford, drumming and other musical activities can improve your brain.
- Focus: Drumming requires intense focus and concentration, improving your ability to focus on other tasks.
- Memory: Learning and memorizing drum patterns can improve your memory skills.
- Processing Speed: Drumming requires quick decision-making and coordination, improving your processing speed.
Is learning the drums hard? While it presents challenges, the benefits of drumming extend far beyond just learning an instrument. The discipline, coordination, and creativity fostered through drumming can enrich your life in countless ways. LEARNS.EDU.VN is here to guide you on this journey, offering resources and support to help you achieve your musical aspirations.
Ready to embark on your drumming adventure? Visit learns.edu.vn to explore our comprehensive range of drum lessons, resources, and expert guidance. Unlock your rhythmic potential and experience the joy of drumming today. Contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States, or reach out via Whatsapp at +1 555-555-1212. Your rhythmic journey starts here.
FAQ Section
1. Is it hard to learn drums if I have no musical background?
Not at all. While prior musical experience can be helpful, it’s not a prerequisite for learning drums. Many successful drummers started with no formal musical training.
2. How often should I practice drums as a beginner?
Aim for at least 30 minutes of practice each day. Consistency is key, so even short, focused practice sessions are more effective than infrequent, lengthy ones.
3. What is the best way to start learning drum notation?
Begin with the basics of drum notation, including note values, rests, and time signatures. Practice reading and playing simple rhythms, and gradually increase the complexity as you improve.
4. Can I learn drums effectively using online resources alone?
Online resources can be a valuable supplement to your learning, but they are often best used in conjunction with personalized instruction from a drum teacher.
5. How can I stay motivated when learning drums gets challenging?
Set realistic goals, celebrate your successes, and focus on playing music that you enjoy. Remember that challenges are a natural part of the learning process.
6. What is the difference between acoustic and electronic drums for beginners?
Acoustic drums offer an authentic sound and playing experience, while electronic drums allow for quiet practice and versatility. Electronic drums are often a good choice for beginners with noise concerns.
7. How important is it to develop my own drumming style?
Developing your own style is important for expressing your creativity and individuality as a drummer. Experiment with different sounds, patterns, and approaches to drumming to discover your unique voice.
8. What are some common mistakes that beginners make when learning drums?
Common mistakes include neglecting fundamentals, lack of consistency, ignoring feedback, and comparing yourself to others.
9. Can learning drums improve my mental health?
Yes, drumming can be a powerful form of stress relief, allowing you to express your emotions and find a state of flow. It has also been shown to improve cognitive function, including focus and memory.
10. Where can I find a supportive community of drummers to learn from?
Participate in online drumming forums and social media groups, or attend local drumming meetups and workshops to connect with drummers in your area.
