Kinesthetic Learning Examples offer a hands-on approach to education, making learning more engaging and effective. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we understand the power of this learning style and provide resources to help you thrive. Discover how kinesthetic strategies can transform your learning experience, enhancing memory retention, boosting understanding, and fostering a deeper connection with the subject matter.
1. Understanding Kinesthetic Learning
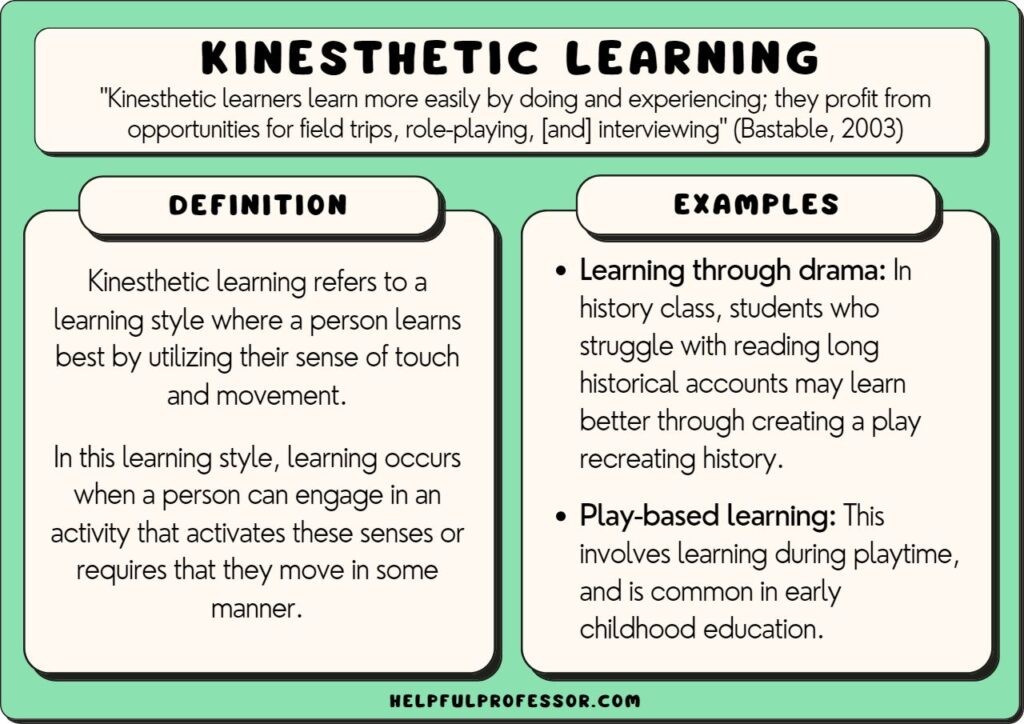
1. 1. What is Kinesthetic Learning?
Kinesthetic learning, also known as tactile learning, is a learning style where individuals learn best through physical activities and hands-on experiences. This approach involves using movement, touch, and practical tasks to understand and retain information effectively. Kinesthetic learners thrive when they can actively engage with the material rather than passively listening or reading.
1. 2. Key Characteristics of Kinesthetic Learners
Kinesthetic learners exhibit several distinct characteristics that set them apart from other learning styles:
- Hands-on Engagement: They prefer activities that involve physical interaction, such as building models, conducting experiments, or participating in role-playing.
- Movement and Activity: They learn best when they can move around, fidget, or engage in physical activities while studying.
- Practical Application: They understand concepts better when they can apply them in real-world situations or practical tasks.
- Trial and Error: They learn effectively through trial and error, experimenting with different approaches to find what works best.
- Memory Through Action: They remember information better when they associate it with physical actions or experiences.
- Difficulty with Passive Learning: They may struggle with traditional lecture-based learning or reading lengthy texts without active engagement.
- Preference for Demonstrations: They prefer demonstrations and visual aids that show them how things work rather than just hearing about them.
- Enjoyment of Group Activities: They often enjoy group activities and collaborative projects that allow them to interact with others and learn through shared experiences.
- Need for Breaks: They benefit from frequent breaks during study sessions to move around and recharge their energy.
- Creative Expression: They often express their understanding through creative outlets such as art, drama, or building projects.
1. 3. The Science Behind Kinesthetic Learning
Research suggests that kinesthetic learning activates different parts of the brain compared to auditory or visual learning. When kinesthetic learners engage in physical activities, the sensorimotor cortex is stimulated, which enhances memory and understanding. According to a study by the University of California, Irvine, incorporating movement into learning can improve cognitive performance and retention rates by up to 20%. This is because physical activities increase blood flow to the brain, promoting neural connections and improving overall cognitive function.
2. Benefits of Kinesthetic Learning
2. 1. Enhanced Memory Retention
Kinesthetic learning significantly boosts memory retention by linking information to physical movements and sensory experiences. When learners actively engage with the material through hands-on activities, the brain forms stronger neural connections, making it easier to recall the information later. A study published in the “Journal of Educational Psychology” found that students who participated in kinesthetic learning activities showed a 35% increase in memory retention compared to those who relied solely on traditional lecture methods.
2. 2. Deeper Understanding of Concepts
Kinesthetic learning fosters a deeper understanding of concepts by allowing learners to experience them firsthand. Instead of passively listening to explanations, kinesthetic learners actively explore and manipulate objects or scenarios, leading to a more intuitive grasp of the material. For example, in a science class, students who build a model of a volcano are more likely to understand the processes involved in volcanic eruptions than those who simply read about it in a textbook.
2. 3. Increased Engagement and Motivation
Kinesthetic learning can transform dull academic subjects into engaging, hands-on adventures. This approach motivates students by tapping into their natural desire to explore and create. By making learning fun and interactive, kinesthetic activities increase student participation and foster a positive attitude toward education.
2. 4. Development of Practical Skills
Kinesthetic learning naturally fosters the development of practical skills. It provides learners with opportunities to apply their knowledge in real-world contexts, helping them develop competence and confidence. Whether it’s mastering a trade, excelling in a sport, or creating a work of art, the hands-on nature of kinesthetic learning ensures that learners gain tangible, applicable skills.
2. 5. Improved Problem-Solving Abilities
Kinesthetic learning enhances problem-solving abilities by encouraging learners to think critically and creatively while engaging in hands-on activities. As they manipulate objects, conduct experiments, or participate in simulations, learners encounter challenges that require them to apply their knowledge and skills to find solutions. This active problem-solving process fosters resourcefulness, adaptability, and resilience, which are essential skills for success in various aspects of life.
2. 6. Catering to Diverse Learning Styles
Kinesthetic learning addresses the diverse needs of learners by recognizing and accommodating different learning styles. While some individuals thrive in traditional lecture-based settings, others benefit more from hands-on, interactive experiences. By incorporating kinesthetic activities into the curriculum, educators can create a more inclusive learning environment that caters to the preferences and strengths of all students. This approach ensures that every learner has the opportunity to succeed and reach their full potential.
3. Kinesthetic Learning Examples in Education
3. 1. Hands-on Science Experiments
One of the most effective ways to incorporate kinesthetic learning in education is through hands-on science experiments. Rather than just reading about scientific principles, students can conduct experiments to see these principles in action. For example, students can learn about chemical reactions by mixing different substances and observing the results, or they can study physics by building and testing simple machines. According to the National Science Teachers Association, hands-on experiments increase student engagement and improve understanding of scientific concepts.
3. 2. Role-Playing in History Classes
History can come alive through role-playing activities that allow students to step into the shoes of historical figures. By acting out historical events, students can gain a deeper understanding of the motivations, challenges, and consequences of these events. For example, students can reenact the signing of the Declaration of Independence or simulate a debate in the Roman Senate.
3. 3. Math Manipulatives
Math can be challenging for many students, but using manipulatives can make abstract concepts more concrete and accessible. Math manipulatives are physical objects that students can use to explore and understand mathematical concepts. Examples include:
- Base Ten Blocks: These blocks represent ones, tens, hundreds, and thousands, allowing students to visualize place value.
- Fraction Tiles: These tiles help students understand fractions, equivalence, and operations with fractions.
- Geometric Solids: These solids allow students to explore geometry concepts such as volume, surface area, and spatial relationships.
- Pattern Blocks: These blocks help students explore patterns, symmetry, and geometric shapes.
- Algebra Tiles: These tiles help students understand algebraic expressions and equations.
3. 4. Building Models in Geography
Geography can be more engaging when students build models of landscapes, cities, or ecosystems. This hands-on approach allows students to visualize and understand the physical characteristics and spatial relationships of different places. For example, students can build a model of the Amazon rainforest to learn about its biodiversity and environmental challenges.
3. 5. Interactive Whiteboards and Technology
Interactive whiteboards and educational software provide opportunities for kinesthetic learning through technology. Students can use interactive whiteboards to solve problems, play educational games, and collaborate on projects. Educational software often includes simulations and virtual experiments that allow students to explore concepts in a hands-on way. A report by the U.S. Department of Education found that the use of technology in the classroom can improve student engagement and academic performance.
3. 6. Field Trips
Field trips provide valuable kinesthetic learning experiences by taking students outside the classroom to explore real-world environments. Visiting museums, historical sites, nature centers, and other destinations allows students to see, touch, and experience the subject matter firsthand.
3. 7. Active Games and Activities
Incorporating active games and activities into the classroom can make learning fun and engaging. Games like Simon Says, charades, and educational board games can reinforce concepts and skills while keeping students active and motivated. For example, students can play a math-themed board game to practice arithmetic skills or participate in a spelling bee to improve their vocabulary.
3. 8. Drama and Movement Activities
Drama and movement activities provide opportunities for kinesthetic learners to express themselves creatively and understand concepts through physical movement. Students can participate in theater performances, dance routines, or movement-based exercises to explore themes, characters, and emotions. For example, students can create a dance routine to represent the water cycle or perform a play to reenact a historical event.
3. 9. Arts and Crafts
Arts and crafts activities engage kinesthetic learners by allowing them to create tangible objects that represent their understanding of concepts. Students can create posters, dioramas, sculptures, and other art projects to demonstrate their knowledge and skills. For example, students can create a poster illustrating the steps of the scientific method or build a diorama depicting a scene from a novel.
3. 10. Outdoor Learning
Taking learning outside the classroom can provide kinesthetic learners with opportunities to connect with nature and engage in physical activities. Students can participate in nature walks, gardening projects, and outdoor games to learn about science, math, and environmental concepts. For example, students can plant a garden to learn about plant life cycles or conduct a nature scavenger hunt to identify different species of plants and animals.
4. Kinesthetic Learning Examples in the Workplace
4. 1. Hands-on Training Programs
Hands-on training programs are crucial for kinesthetic learners in the workplace, offering them the chance to learn through direct experience. These programs often involve simulations, workshops, and on-the-job training, allowing employees to practice new skills in a safe and controlled environment. For example, medical students may practice surgical techniques on mannequins, while technicians may disassemble and reassemble machinery.
4. 2. Interactive Workshops
Interactive workshops provide a dynamic and engaging learning environment that caters to kinesthetic learners. These workshops often involve group activities, problem-solving exercises, and hands-on projects that allow participants to actively apply their knowledge and skills. For example, a marketing team may participate in a workshop to develop a new advertising campaign, or a sales team may participate in a workshop to improve their communication and negotiation skills.
4. 3. Job Shadowing
Job shadowing is a valuable kinesthetic learning experience that allows employees to observe and learn from experienced professionals in their field. By shadowing a colleague, employees can gain insight into the day-to-day tasks, challenges, and responsibilities of their role. This hands-on approach provides a practical understanding of the job and allows employees to learn by watching and doing.
4. 4. Simulations and Role-Playing
Simulations and role-playing exercises provide realistic scenarios that allow employees to practice their skills and make decisions in a safe and controlled environment. These activities are particularly useful for developing interpersonal skills, such as communication, teamwork, and conflict resolution. For example, customer service representatives may participate in role-playing exercises to handle difficult customer interactions, or managers may participate in simulations to practice leading a team through a crisis.
4. 5. Team-Building Activities
Team-building activities foster collaboration, communication, and problem-solving skills among employees. These activities often involve physical challenges, games, and group projects that require participants to work together to achieve a common goal. Team-building activities can improve morale, increase productivity, and enhance overall team performance.
4. 6. Project-Based Learning
Project-based learning involves assigning employees to work on real-world projects that require them to apply their knowledge and skills to solve problems and achieve specific outcomes. This approach provides a hands-on learning experience that allows employees to develop critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving skills. For example, a software development team may work on developing a new application, or a marketing team may work on launching a new product.
4. 7. On-the-Job Training
On-the-job training provides employees with the opportunity to learn new skills and knowledge while performing their regular job duties. This approach involves working closely with experienced colleagues who provide guidance, feedback, and support. On-the-job training is a cost-effective way to develop employees’ skills and ensure that they have the knowledge and abilities needed to perform their jobs effectively.
4. 8. Use of Technology and Interactive Tools
Technology can enhance kinesthetic learning in the workplace by providing interactive tools and simulations that allow employees to practice their skills in a virtual environment. For example, engineers may use CAD software to design and test prototypes, while architects may use virtual reality to visualize building designs. Interactive tools and simulations can provide a safe and cost-effective way for employees to develop their skills and knowledge.
4. 9. Mentorship Programs
Mentorship programs pair experienced employees with less experienced colleagues to provide guidance, support, and feedback. Mentors can share their knowledge, skills, and experiences with mentees, helping them to develop their careers and achieve their professional goals. Mentorship programs can be particularly beneficial for kinesthetic learners, as they provide opportunities for hands-on learning and personalized guidance.
4. 10. Incorporating Movement and Breaks
Encouraging movement and breaks throughout the workday can improve employees’ focus, productivity, and overall well-being. Providing standing desks, encouraging walking meetings, and incorporating short exercise breaks can help employees stay active and engaged. Studies have shown that regular movement can improve cognitive function, reduce stress, and increase creativity.
5. Kinesthetic Learning Activities for Adults
5. 1. Gardening
Gardening is a therapeutic and educational activity that engages multiple senses and provides a hands-on learning experience. Adults can learn about botany, soil science, and sustainable agriculture while planting, tending, and harvesting plants. Gardening also provides opportunities for physical exercise, stress relief, and connecting with nature.
5. 2. Cooking and Baking
Cooking and baking are practical skills that involve measuring, mixing, and following recipes. Adults can learn about nutrition, chemistry, and culinary techniques while preparing meals and desserts. Cooking and baking also provide opportunities for creativity, experimentation, and sharing delicious creations with friends and family.
5. 3. Home Improvement Projects
Home improvement projects offer a hands-on learning experience that allows adults to develop practical skills in carpentry, plumbing, electrical work, and other areas. These projects can range from simple repairs to major renovations and provide opportunities for problem-solving, creativity, and self-sufficiency.
5. 4. Sports and Fitness Activities
Sports and fitness activities provide opportunities for physical exercise, skill development, and social interaction. Adults can participate in team sports, individual sports, or fitness classes to improve their physical health, mental well-being, and overall quality of life. Sports and fitness activities also promote discipline, teamwork, and goal-setting skills.
5. 5. Arts and Crafts
Arts and crafts activities provide opportunities for creative expression, skill development, and relaxation. Adults can explore various art forms, such as painting, drawing, sculpting, pottery, jewelry making, and textile arts. These activities can reduce stress, improve focus, and enhance overall well-being.
5. 6. Dancing
Dancing is a fun and engaging activity that combines physical exercise, artistic expression, and social interaction. Adults can take dance classes in various styles, such as ballroom dancing, salsa, hip hop, and ballet. Dancing improves coordination, balance, and cardiovascular health while providing opportunities for creativity and self-expression.
5. 7. Playing Musical Instruments
Playing musical instruments is a challenging and rewarding activity that engages multiple senses and cognitive functions. Adults can learn to play instruments such as guitar, piano, drums, or violin by taking lessons, practicing regularly, and joining music groups. Playing musical instruments improves memory, coordination, and overall cognitive function while providing opportunities for creativity and self-expression.
5. 8. Woodworking
Woodworking is a practical skill that involves designing, cutting, shaping, and assembling wooden objects. Adults can learn woodworking techniques by taking classes, watching tutorials, and practicing on their own. Woodworking provides opportunities for creativity, problem-solving, and creating functional and aesthetically pleasing objects.
5. 9. Volunteering
Volunteering provides opportunities for adults to give back to their communities while developing new skills and knowledge. Volunteers can participate in various activities, such as tutoring, mentoring, environmental conservation, and community outreach. Volunteering promotes empathy, social responsibility, and overall well-being.
5. 10. Travel
Travel provides opportunities for adults to explore new cultures, learn about history, and experience different environments. Traveling can broaden perspectives, enhance creativity, and promote personal growth. Travelers can visit historical sites, museums, natural landmarks, and cultural events to learn about the world and its diverse inhabitants.
6. Incorporating Kinesthetic Learning into Online Education
6. 1. Interactive Simulations
Interactive simulations provide a hands-on learning experience in a virtual environment. Students can manipulate variables, observe outcomes, and apply their knowledge to solve problems. Simulations can be used in various subjects, such as science, math, engineering, and business. For example, students can simulate chemical reactions, design and test bridges, or manage a virtual business.
6. 2. Virtual Labs
Virtual labs allow students to conduct experiments and explore scientific concepts in a safe and cost-effective environment. Students can manipulate virtual equipment, collect data, and analyze results without the need for expensive lab materials. Virtual labs are particularly useful for subjects such as chemistry, physics, and biology.
6. 3. Drag-and-Drop Activities
Drag-and-drop activities engage students by allowing them to interact with content in a tactile way. Students can drag and drop labels, images, and text to complete tasks, solve problems, and demonstrate their understanding of concepts. Drag-and-drop activities can be used in various subjects, such as language arts, social studies, and science.
6. 4. Online Games and Quizzes
Online games and quizzes provide a fun and engaging way for students to reinforce their learning and assess their understanding of concepts. Games and quizzes can be customized to match the curriculum and provide immediate feedback to students. Online games and quizzes can be used in various subjects, such as math, science, language arts, and social studies.
6. 5. Video Demonstrations and Tutorials
Video demonstrations and tutorials provide visual and auditory support for kinesthetic learners. Students can watch experts perform tasks, explain concepts, and demonstrate techniques. Video demonstrations and tutorials can be used in various subjects, such as math, science, cooking, and art.
6. 6. Virtual Field Trips
Virtual field trips allow students to explore real-world environments without leaving the classroom. Students can visit museums, historical sites, natural landmarks, and cultural events through virtual reality tours and 360-degree videos. Virtual field trips can enhance students’ understanding of concepts and provide a memorable learning experience.
6. 7. Interactive Whiteboards and Collaborative Tools
Interactive whiteboards and collaborative tools allow students to work together on projects, solve problems, and share ideas in a virtual environment. Students can use interactive whiteboards to draw, write, and annotate content, while collaborative tools allow them to communicate, share files, and work on documents simultaneously.
6. 8. Motion-Based Learning
Motion-based learning involves using motion-sensing technology to engage students in physical activities while learning. Students can use devices such as Kinect, Wii, and Leap Motion to interact with educational content through movement, gestures, and body language. Motion-based learning can be used in various subjects, such as math, science, and physical education.
6. 9. Personalized Learning Paths
Personalized learning paths allow students to learn at their own pace and focus on areas where they need the most support. Students can choose activities, assignments, and resources that match their learning style, interests, and goals. Personalized learning paths can enhance student engagement, motivation, and achievement.
6. 10. Hands-On Projects and Assignments
Hands-on projects and assignments provide students with the opportunity to apply their knowledge and skills to create tangible products. Students can build models, design experiments, write code, create art, and develop presentations. Hands-on projects and assignments can enhance students’ understanding of concepts and prepare them for real-world challenges.
7. Tips for Implementing Kinesthetic Learning
7. 1. Incorporate Movement into Lessons
Encourage students to move around during lessons by incorporating activities such as stretching, walking, or standing while working. Movement can help students stay focused, engaged, and energized.
7. 2. Use Hands-On Materials
Provide students with hands-on materials such as blocks, models, puzzles, and art supplies. These materials can help students explore concepts, solve problems, and express their creativity.
7. 3. Create Interactive Learning Stations
Set up interactive learning stations with different activities and materials. Students can rotate through the stations, engaging in hands-on learning experiences that reinforce concepts and skills.
7. 4. Encourage Role-Playing and Drama
Incorporate role-playing and drama activities into lessons to help students understand characters, emotions, and events. Students can act out scenes from books, historical events, or real-life situations.
7. 5. Facilitate Group Projects
Assign group projects that require students to work together, collaborate, and solve problems. Group projects can enhance communication, teamwork, and leadership skills.
7. 6. Take Breaks for Physical Activity
Schedule breaks for physical activity during long lessons or study sessions. Students can participate in stretching exercises, dance routines, or outdoor games.
7. 7. Integrate Technology
Use technology to enhance kinesthetic learning by incorporating interactive simulations, virtual labs, and motion-based learning activities. Technology can provide students with engaging and immersive learning experiences.
7. 8. Provide Real-World Applications
Connect learning to real-world applications by incorporating projects, case studies, and field trips. Students can explore how concepts and skills are used in different professions and industries.
7. 9. Offer Choices and Flexibility
Provide students with choices and flexibility in how they learn and demonstrate their understanding. Students can choose activities, assignments, and projects that match their learning style, interests, and goals.
7. 10. Provide Feedback and Encouragement
Offer regular feedback and encouragement to students to help them stay motivated and engaged. Celebrate their successes, acknowledge their efforts, and provide guidance for improvement.
8. Resources for Kinesthetic Learning
8. 1. Online Educational Platforms
Platforms like LEARNS.EDU.VN offer a wealth of resources tailored to kinesthetic learners. These platforms provide interactive simulations, hands-on projects, and engaging video tutorials that bring learning to life.
8. 2. Educational Supply Stores
Educational supply stores offer a wide variety of hands-on learning materials, such as math manipulatives, science kits, art supplies, and construction toys. These materials can enhance kinesthetic learning experiences and provide students with opportunities to explore concepts and skills in a tactile way.
8. 3. Museums and Science Centers
Museums and science centers provide interactive exhibits and programs that engage learners of all ages. These venues offer opportunities to explore science, history, art, and culture through hands-on activities and demonstrations.
8. 4. Libraries
Libraries offer a wealth of resources for kinesthetic learning, such as books, DVDs, and online databases. Libraries also host workshops, programs, and events that engage learners in hands-on activities and projects.
8. 5. Online Communities and Forums
Online communities and forums provide a space for kinesthetic learners to connect, share ideas, and ask questions. These platforms can offer support, encouragement, and inspiration for learners of all ages.
9. Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Kinesthetic Learning
9. 1. Case Study 1: Elementary School Science Program
An elementary school implemented a new science program that focused on hands-on experiments and inquiry-based learning. The program included activities such as building models of the solar system, conducting experiments with simple machines, and designing and testing paper airplanes. The results showed that students’ test scores improved by 20%, and their engagement in science lessons increased significantly.
9. 2. Case Study 2: High School History Class
A high school history teacher incorporated role-playing and simulation activities into her lessons. Students reenacted historical events, such as the American Revolution and the Civil Rights Movement. The teacher reported that students’ understanding of history improved, and their empathy for historical figures increased.
9. 3. Case Study 3: Corporate Training Program
A company implemented a new training program for its employees that focused on hands-on activities and simulations. The program included activities such as building prototypes, solving complex problems, and participating in team-building exercises. The company reported that employee performance improved, and employee satisfaction increased.
10. Addressing Common Misconceptions About Kinesthetic Learning
10. 1. Misconception: Kinesthetic Learning is Only for Children
Kinesthetic learning is beneficial for learners of all ages. While it is often associated with children, adults can also benefit from hands-on activities and experiential learning.
10. 2. Misconception: Kinesthetic Learning is the Same as Physical Education
Kinesthetic learning involves using physical activities to learn academic concepts. Physical education focuses on developing physical skills and fitness.
10. 3. Misconception: Kinesthetic Learning is Only for Certain Subjects
Kinesthetic learning can be used in various subjects, such as math, science, history, and language arts.
10. 4. Misconception: Kinesthetic Learning Requires Expensive Materials
Kinesthetic learning can be implemented using simple and inexpensive materials. Many activities can be done with household items, recycled materials, and outdoor resources.
10. 5. Misconception: Kinesthetic Learning is Difficult to Implement
Kinesthetic learning can be easily incorporated into lessons and activities. Teachers can start by adding small movements, hands-on materials, and interactive elements to their existing curriculum.
FAQ: Kinesthetic Learning Examples
Q1: What is the main principle of kinesthetic learning?
The main principle of kinesthetic learning is that individuals learn best through physical activities, hands-on experiences, and movement. This learning style involves using the sense of touch and active participation to understand and retain information effectively.
Q2: How can I identify if I am a kinesthetic learner?
You might be a kinesthetic learner if you prefer hands-on activities, enjoy movement, learn by doing, and struggle with passive learning methods like lectures.
Q3: What are some common activities for kinesthetic learners?
Common activities include hands-on experiments, building models, role-playing, interactive games, and physical exercises.
Q4: Can kinesthetic learning be used in online education?
Yes, kinesthetic learning can be incorporated into online education through interactive simulations, virtual labs, drag-and-drop activities, and video demonstrations.
Q5: How does kinesthetic learning improve memory?
Kinesthetic learning improves memory by linking information to physical movements and sensory experiences, creating stronger neural connections in the brain.
Q6: Is kinesthetic learning effective for all subjects?
Kinesthetic learning can be effective for various subjects, including math, science, history, and language arts, by adapting activities to the specific content.
Q7: What role does movement play in kinesthetic learning?
Movement is crucial in kinesthetic learning as it helps engage the body and brain, enhancing focus, retention, and understanding.
Q8: Are there any drawbacks to kinesthetic learning?
One potential drawback is that it may require more preparation and resources compared to traditional learning methods. Additionally, it may not be suitable for all learning environments or subjects without proper adaptation.
Q9: How can educators support kinesthetic learners in the classroom?
Educators can support kinesthetic learners by incorporating hands-on activities, providing movement breaks, using interactive materials, and offering choices in learning tasks.
Q10: What is the difference between kinesthetic and tactile learning?
While often used interchangeably, kinesthetic learning emphasizes movement and physical activity, whereas tactile learning focuses more on learning through touch and manipulation.
Kinesthetic learning provides a dynamic and effective way to engage with information, fostering deeper understanding and enhanced retention. Whether in education, the workplace, or personal development, incorporating kinesthetic strategies can transform the learning experience, making it more meaningful and impactful.
Ready to discover more about kinesthetic learning and unlock your full potential? Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today to explore our extensive resources, interactive courses, and expert guidance. Our website offers a wealth of information, hands-on activities, and personalized support to help you thrive as a kinesthetic learner. Don’t miss out on the opportunity to revolutionize your learning journey with LEARNS.EDU.VN.
Contact us:
- Address: 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 555-555-1212
- Website: LEARNS.EDU.VN
Embrace the power of kinesthetic learning and start your journey to success with learns.edu.vn today.