Learning a new language can be a rewarding experience, but some languages pose more challenges than others for native English speakers. What Are The Top Five Hardest Languages To Learn? According to LEARNS.EDU.VN, Mandarin Chinese, Arabic, Japanese, Hungarian, and Korean present significant hurdles due to their unique writing systems, tonal qualities, and grammatical structures. Overcoming these challenges opens doors to new cultures and opportunities, and with resources from LEARNS.EDU.VN, you can confidently navigate the complexities of language acquisition and achieve fluency.
1. Mandarin Chinese
Mandarin Chinese is often cited as one of the most challenging languages for English speakers to learn. Why? Because of its tonal nature, complex writing system, and extensive use of idioms.
1.1. Tonal Language
Mandarin is a tonal language, which means the meaning of a word changes based on the tone in which it is spoken. There are four main tones in Mandarin:
- High-Level Tone: A steady, high-pitched sound.
- Rising Tone: Starts at a mid-pitch and rises.
- Falling-Rising Tone: Drops to a low pitch and then rises.
- Falling Tone: Starts high and falls sharply.
Mastering these tones is crucial because using the wrong tone can completely alter the meaning of a word. For example, the syllable “ma” can mean “mother,” “hemp,” “horse,” or “scold,” depending on the tone used. This tonal aspect can be difficult for English speakers, who are not accustomed to such nuances.
1.2. Writing System
The Chinese writing system uses characters (Hanzi) rather than an alphabet. Each character represents a word or a morpheme (a meaningful unit of language). There are thousands of characters, and while you don’t need to know them all to be functional, a basic level of literacy requires learning several hundred characters.
- Simplified vs. Traditional Chinese: Mainland China uses simplified characters, while Taiwan and Hong Kong use traditional characters.
- Radicals: Characters are composed of radicals, which are basic components that provide clues to meaning or pronunciation. Learning radicals can help in memorizing characters.
1.3. Homophones
Mandarin is rich in homophones, which are words that sound the same but have different meanings. This adds another layer of complexity, as you need to rely on context to understand the intended meaning. For instance, the sound “shi” has numerous meanings depending on the character used.
1.4. Idioms and Proverbs
Chinese makes extensive use of idioms (Chengyu) and proverbs, which are often derived from historical stories or classical literature. These idioms can be difficult to understand without cultural context and knowledge of their origins.
1.5. Resources for Learning Mandarin
To overcome these challenges, consider these resources:
- Language Learning Apps: Apps like Duolingo, Memrise, and HelloChinese offer interactive lessons and gamified learning experiences.
- Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera and edX offer comprehensive Mandarin courses taught by university professors.
- Language Exchange Partners: Websites like HelloTalk and Tandem connect you with native speakers for language exchange.
- Immersion: If possible, spending time in a Mandarin-speaking environment can greatly accelerate your learning.
- Textbooks: Integrated Chinese and HSK Standard Course are popular textbook series for Mandarin learners.
2. Arabic
Arabic is another language that presents significant challenges for English speakers. Its unique script, complex grammar, and regional dialects contribute to its difficulty.
2.1. Writing System
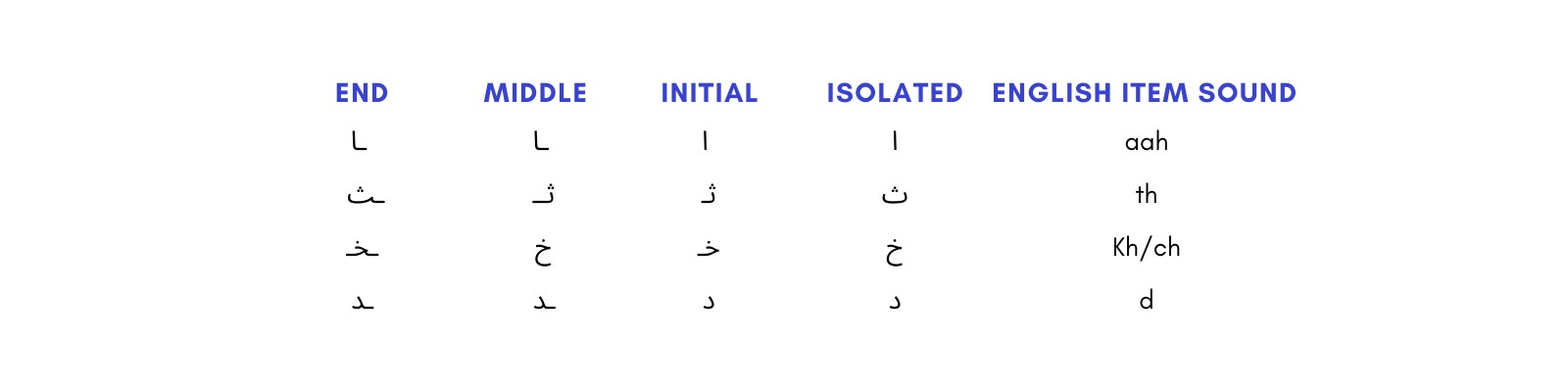
Arabic is written from right to left, which can be disorienting for English speakers. The Arabic alphabet consists of 28 letters, and the shape of each letter changes depending on its position in a word (initial, medial, final, or isolated). This means you need to learn multiple forms for each letter.
2.2. Pronunciation
Arabic has sounds that do not exist in English, such as emphatic consonants and guttural sounds. These sounds can be difficult for English speakers to produce and distinguish.
2.3. Grammar
Arabic grammar is highly complex, with a system of verb conjugations and noun declensions that can be challenging to master. Arabic also uses a system of “broken plurals,” where the plural form of a noun is not predictable and must be memorized.
2.4. Dialects
Arabic has numerous dialects, which can vary significantly from one region to another. Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) is used in formal settings and media, but everyday conversation often involves regional dialects. This means that learning MSA may not be sufficient for communicating with native speakers in different parts of the Arab world.
2.5. Cultural Context
Understanding Arabic culture is essential for effective communication. Arabic-speaking cultures often place a high value on politeness and indirectness, which can affect how language is used in social interactions.
2.6. Resources for Learning Arabic
To tackle these challenges, consider these resources:
- Online Courses: Platforms like Madinah Arabic and Bayna Yadayk offer structured Arabic courses.
- Language Exchange Partners: Websites like Speaky and italki can help you find native Arabic speakers for practice.
- Textbooks: Alif Baa and Arabic for Dummies are popular textbooks for beginners.
- Media: Watching Arabic movies, TV shows, and news can help you improve your listening comprehension and vocabulary.
- Immersion: Spending time in an Arabic-speaking country is invaluable for language learning.
3. Japanese
Japanese is known for its complex writing system, honorific language, and unique grammatical structure. These factors make it a challenging language for English speakers to learn.
3.1. Writing System
Japanese uses three different writing systems:
- Hiragana: A phonetic script used for native Japanese words and grammatical particles.
- Katakana: A phonetic script used for foreign loanwords and onomatopoeia.
- Kanji: Logographic characters borrowed from Chinese, each representing a word or concept.
You need to learn all three writing systems to read and write Japanese fluently. Kanji, in particular, can be daunting due to the large number of characters and their varying readings.
3.2. Grammar
Japanese grammar differs significantly from English grammar. The word order is subject-object-verb, which can be confusing for English speakers. Japanese also uses particles to indicate the grammatical function of words in a sentence.
3.3. Honorific Language
Japanese has a complex system of honorific language (Keigo), which is used to show respect to superiors, elders, and guests. Using the correct level of politeness is essential in Japanese culture, and mistakes can be seen as rude.
3.4. Pronunciation
While Japanese pronunciation is relatively straightforward, there are some sounds that do not exist in English. Additionally, Japanese uses pitch accent, where the meaning of a word can change depending on the pitch of the syllables.
3.5. Cultural Context
Understanding Japanese culture is crucial for effective communication. Japanese culture values indirectness and politeness, which can affect how language is used in social interactions.
3.6. Resources for Learning Japanese
To master Japanese, consider these resources:
- Textbooks: Genki and Minna no Nihongo are popular textbook series for learning Japanese.
- Online Courses: Platforms like WaniKani and Tofugu offer resources for learning Kanji and grammar.
- Language Exchange Partners: Websites like italki and HelloTalk can connect you with native Japanese speakers.
- Anime and Manga: Watching anime and reading manga can be a fun way to improve your vocabulary and listening comprehension.
- Immersion: Spending time in Japan is highly beneficial for language learning.
4. Hungarian
Hungarian is a Uralic language that is known for its complex grammar, unique vocabulary, and agglutinative structure. These features make it a challenging language for English speakers to learn.
4.1. Grammar
Hungarian grammar is highly complex, with a large number of cases and verb conjugations. Hungarian has 18 cases, which are used to indicate the grammatical function of nouns and adjectives. Additionally, Hungarian verbs are conjugated based on tense, mood, and person.
4.2. Vocabulary
Hungarian vocabulary is largely unrelated to English vocabulary, which means that you need to learn a completely new set of words. Hungarian also uses a lot of suffixes to create new words, which can be confusing for English speakers.
4.3. Agglutinative Structure
Hungarian is an agglutinative language, which means that words are formed by adding multiple suffixes to a base word. This can result in very long words with complex meanings.
4.4. Pronunciation
Hungarian pronunciation includes sounds that are not found in English, such as long vowels and palatalized consonants. These sounds can be difficult for English speakers to produce and distinguish.
4.5. Resources for Learning Hungarian
To tackle these challenges, consider these resources:
- Textbooks: Teach Yourself Hungarian and Colloquial Hungarian are popular textbooks for learning Hungarian.
- Online Courses: Platforms like Memrise and Duolingo offer Hungarian courses.
- Language Exchange Partners: Websites like italki and Tandem can connect you with native Hungarian speakers.
- Media: Watching Hungarian movies and TV shows can help you improve your listening comprehension and vocabulary.
- Immersion: Spending time in Hungary is highly beneficial for language learning.
4.6. Unique Idioms
Subtle cultural elements within Hungarian make it uniquely difficult to learn: It heavily relies on idioms, which can act as a real barrier to language learning. For example, Annyit ér, mint halottnak a csók which means “It’s worth as much as a kiss is to a dead person” implying something is pointless and won’t be appreciated.
5. Korean
Korean is a language isolate that is known for its unique writing system, complex grammar, and honorific language. These features make it a challenging language for English speakers to learn.
5.1. Writing System
Korean uses Hangul, a phonetic alphabet that was invented in the 15th century. While Hangul is relatively easy to learn, it is different from the Latin alphabet used in English. Additionally, Korean is often written with Chinese characters (Hanja), which adds another layer of complexity.
5.2. Grammar
Korean grammar differs significantly from English grammar. The word order is subject-object-verb, and Korean uses particles to indicate the grammatical function of words in a sentence. Korean also has a complex system of verb endings that indicate tense, mood, and politeness level.
5.3. Honorific Language
Korean has a complex system of honorific language, which is used to show respect to superiors, elders, and guests. Using the correct level of politeness is essential in Korean culture, and mistakes can be seen as rude.
5.4. Pronunciation
Korean pronunciation includes sounds that are not found in English, such as aspirated consonants and tense vowels. These sounds can be difficult for English speakers to produce and distinguish.
5.5. Resources for Learning Korean
To master Korean, consider these resources:
- Textbooks: Korean From Zero! and Talk To Me In Korean are popular textbook series for learning Korean.
- Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera and edX offer comprehensive Korean courses.
- Language Exchange Partners: Websites like HelloTalk and Tandem can connect you with native Korean speakers.
- K-Dramas and K-Pop: Watching K-dramas and listening to K-pop can be a fun way to improve your vocabulary and listening comprehension.
- Immersion: Spending time in Korea is highly beneficial for language learning.
5.6. Sentence Structure
When describing an action in Korean, the word order is subject + object + action. English speakers can also trip up over the formality levels: Very informal, informal, and formal. The language hierarchy is usually split by age, seniority, and your familiarity with the person.
Why Are These Languages Considered Difficult?
Several factors contribute to the difficulty of these languages for English speakers:
- Linguistic Distance: The greater the differences in grammar, vocabulary, and pronunciation between English and another language, the harder it will be to learn.
- Writing System: Languages with non-Latin scripts can be particularly challenging for English speakers, as they require learning a completely new writing system.
- Cultural Differences: Understanding the cultural context in which a language is used is essential for effective communication. Languages that reflect very different cultural values and norms can be more difficult to master.
- Pronunciation: Languages with sounds that do not exist in English can be challenging to pronounce and distinguish.
- Grammar Complexity: Languages with complex grammatical structures, such as numerous cases or verb conjugations, can be difficult to learn.
Tips for Learning Difficult Languages
Despite the challenges, it is possible to learn these languages with dedication and the right approach. Here are some tips for success:
- Set Realistic Goals: Learning a difficult language takes time and effort. Set achievable goals and celebrate your progress along the way.
- Find a Good Teacher or Tutor: A qualified teacher can provide guidance and support, helping you to overcome challenges and stay motivated.
- Use a Variety of Resources: Combine textbooks, online courses, language exchange partners, and media to create a well-rounded learning experience.
- Practice Regularly: Consistent practice is essential for language learning. Try to spend some time each day working on your language skills.
- Immerse Yourself in the Language: Surround yourself with the language as much as possible. Listen to music, watch movies, and read books in your target language.
- Don’t Be Afraid to Make Mistakes: Everyone makes mistakes when learning a new language. Don’t let fear of making mistakes hold you back.
- Stay Motivated: Learning a difficult language can be frustrating at times. Find ways to stay motivated, such as setting goals, rewarding yourself for progress, and connecting with other learners.
- Focus on Communication: Ultimately, the goal of language learning is to communicate with others. Focus on developing your ability to express yourself and understand others, even if you make mistakes along the way.
- Utilize LEARNS.EDU.VN: Explore the wealth of resources available at LEARNS.EDU.VN, tailored to support language learners at all levels.
The Benefits of Learning a Difficult Language
While learning a difficult language can be challenging, it also offers numerous benefits:
- Cognitive Benefits: Learning a new language can improve cognitive skills such as memory, problem-solving, and multitasking.
- Cultural Understanding: Learning a difficult language can provide deeper insights into the culture and worldview of its speakers.
- Career Opportunities: In today’s globalized world, being able to speak a difficult language can open up career opportunities in fields such as translation, interpretation, and international business.
- Personal Growth: Overcoming the challenges of learning a difficult language can be a rewarding experience that boosts confidence and self-esteem.
- Travel Experiences: Being able to speak a difficult language can enhance your travel experiences, allowing you to connect with locals and gain a deeper understanding of the places you visit.
Language Difficulty Ranking and Factors
The Foreign Service Institute (FSI) has categorized languages by difficulty for native English speakers. The FSI rankings are based on the amount of time it takes for a student to achieve “professional working proficiency” in the language.
| Category | Language | Approximate Time to Achieve Proficiency |
|---|---|---|
| I | French | 24-30 weeks (600-750 hours) |
| I | Spanish | 24-30 weeks (600-750 hours) |
| II | German | 36 weeks (900 hours) |
| III | Indonesian | 44 weeks (1100 hours) |
| III | Russian | 44 weeks (1100 hours) |
| IV | Hindi | 88 weeks (2200 hours) |
| IV | Arabic | 88 weeks (2200 hours) |
| IV | Mandarin | 88 weeks (2200 hours) |
| IV | Japanese | 88 weeks (2200 hours) |
| IV | Korean | 88 weeks (2200 hours) |


Factors Affecting Language Difficulty
Several factors influence how difficult a language is to learn for a particular individual:
- Native Language: The similarity between your native language and the target language is a significant factor. Languages that share a common linguistic ancestor or have borrowed vocabulary from each other will generally be easier to learn.
- Learning Style: Some people are better at learning languages through visual methods, while others prefer auditory or kinesthetic approaches. Finding a learning style that works for you can make the process more efficient.
- Motivation: Your level of motivation is a crucial factor in language learning. If you are genuinely interested in the language and culture, you will be more likely to persevere through the challenges.
- Time Commitment: The amount of time you are willing to dedicate to language learning will also affect your progress. Consistent practice is essential for success.
- Resources: Access to quality resources, such as textbooks, online courses, and language exchange partners, can make the learning process easier and more enjoyable.
New Trends in Language Learning
The field of language learning is constantly evolving, with new technologies and methodologies emerging all the time. Here are some of the latest trends:
- Gamification: Many language learning apps and platforms are incorporating game-like elements to make the process more engaging and fun.
- Personalization: Adaptive learning technologies are being used to tailor language lessons to individual learners’ needs and preferences.
- Virtual Reality (VR): VR is being used to create immersive language learning environments, allowing learners to practice their skills in realistic scenarios.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered chatbots and virtual tutors are providing learners with personalized feedback and support.
- Microlearning: Short, focused lessons are becoming increasingly popular, as they can be easily integrated into busy schedules.
The Role of LEARNS.EDU.VN in Language Education
LEARNS.EDU.VN is committed to providing high-quality language education resources to learners around the world. Our website offers a wide range of articles, tutorials, and courses designed to help you achieve your language learning goals. Whether you are a beginner or an advanced learner, you will find valuable resources to support your journey.
Benefits of Using LEARNS.EDU.VN
- Expert Guidance: Our content is created by experienced language teachers and linguists who are passionate about helping you succeed.
- Comprehensive Resources: We offer a wide range of resources, including articles, tutorials, courses, and language learning tools.
- Personalized Learning: Our platform allows you to track your progress, set goals, and customize your learning experience.
- Community Support: Connect with other learners from around the world and share your experiences, tips, and challenges.
- Affordable Options: We offer a variety of free and affordable resources to make language learning accessible to everyone.
Conclusion
While Mandarin Chinese, Arabic, Japanese, Hungarian, and Korean are considered among the hardest languages for English speakers to learn, they are also incredibly rewarding to master. Each language opens a door to a rich culture, a unique history, and a new way of seeing the world. With dedication, the right resources, and a willingness to embrace the challenges, you can successfully navigate the complexities of these languages and achieve fluency. And remember, LEARNS.EDU.VN is here to support you every step of the way with expert guidance, comprehensive resources, and a vibrant community of learners. So, take the leap, embark on your language learning journey, and discover the incredible rewards that await you.
Are you ready to start your language learning adventure? Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today and explore our extensive collection of resources, tailored to help you conquer any language challenge. From expert-led courses to interactive tutorials and a supportive community, LEARNS.EDU.VN is your ultimate destination for unlocking your linguistic potential. Don’t wait—begin your journey now and transform your world!
For more information, visit our website at LEARNS.EDU.VN or contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States, or Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212.
FAQ
1. Which language is the hardest to learn for English speakers?
Generally, Mandarin Chinese, Arabic, Japanese, Hungarian, and Korean are considered the hardest languages for English speakers due to their tonal qualities, complex writing systems, and grammatical structures.
2. Why is Mandarin Chinese so difficult to learn?
Mandarin Chinese is difficult because it is a tonal language, has a complex writing system with thousands of characters, and makes extensive use of idioms and proverbs.
3. What makes Arabic challenging for English speakers?
Arabic is challenging due to its right-to-left writing system, complex grammar, unique sounds, and the existence of numerous regional dialects.
4. Why is Japanese considered a difficult language to learn?
Japanese is difficult because it uses three different writing systems (Hiragana, Katakana, and Kanji), has a subject-object-verb word order, and employs a complex system of honorific language.
5. What are the main challenges in learning Hungarian?
Hungarian is challenging due to its complex grammar with 18 cases, unique vocabulary unrelated to English, and agglutinative structure that creates long, complex words.
6. Why is Korean hard for English speakers to learn?
Korean is difficult because it is a language isolate with a unique writing system (Hangul), a subject-object-verb word order, and a complex system of honorific language.
7. How long does it take to learn one of these difficult languages?
According to the Foreign Service Institute (FSI), it can take approximately 88 weeks (2200 hours) of study to achieve “professional working proficiency” in languages like Arabic, Mandarin, Japanese, and Korean.
8. What are some tips for learning a difficult language?
Some tips include setting realistic goals, finding a good teacher or tutor, using a variety of resources, practicing regularly, immersing yourself in the language, and not being afraid to make mistakes.
9. What are the benefits of learning a difficult language?
The benefits include improved cognitive skills, deeper cultural understanding, expanded career opportunities, personal growth, and enhanced travel experiences.
10. Where can I find resources to help me learn these languages?
You can find resources at learns.edu.vn, which offers expert guidance, comprehensive materials, personalized learning options, and community support. Other resources include online courses, textbooks, language exchange partners, and media in your target language.
