The learning ecosystem is a dynamic network that significantly impacts organizational learning, and LEARNS.EDU.VN is here to help you navigate it. This system encompasses people, content, technology, culture, and strategy, shaping both formal and informal learning experiences. By understanding and optimizing your learning ecosystem, you can enhance knowledge acquisition, improve employee engagement, and drive organizational success. Explore learns.edu.vn for more on learning environment, personalized learning, and continuous professional development.
1. What Defines a Learning Ecosystem?
A learning ecosystem is a multifaceted network composed of people, content, technology, culture, and strategy, both within and outside an organization, influencing formal and informal learning. Understanding this definition is crucial for building a robust and effective learning environment.
The concept of an “ecosystem” is vital here. It signifies that this isn’t just a collection of learning resources but a dynamic, interconnected environment. Like a natural ecosystem with interacting species and environments, a learning ecosystem involves various individuals and content pieces, each playing different roles and existing in various learning contexts, all intricately connected.
Just as a thriving ecosystem requires careful nurturing, a healthy learning ecosystem supports continuous growth and development. An organization must understand its ecosystem’s components and the internal and external forces shaping them to achieve its development goals.
1.1 What Are the Key Components of a Learning Ecosystem?
To fully grasp the concept of a learning ecosystem, it’s essential to understand its key components. Each element plays a crucial role in shaping the learning experience and contributing to the overall effectiveness of the system.
- People: This includes learners, instructors, managers, mentors, and external experts.
- Content: Encompasses formal training materials, informal knowledge sharing, and external resources.
- Technology: Involves learning management systems (LMS), mobile devices, and social learning tools.
- Culture: Reflects the organization’s values, beliefs, and attitudes towards learning.
- Strategy: Aligns learning initiatives with organizational goals and objectives.
1.2 How Does a Learning Ecosystem Differ from Traditional Training Methods?
Traditional training methods often focus on formal, structured learning activities, such as classroom sessions or online courses. A learning ecosystem, however, takes a more holistic approach by integrating various learning resources and experiences into a cohesive network.
| Feature | Traditional Training | Learning Ecosystem |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Primarily formal training sessions | Formal and informal learning, internal and external sources |
| Approach | Structured, instructor-led | Flexible, self-directed, collaborative |
| Focus | Knowledge acquisition | Skill development, knowledge sharing, continuous learning |
| Integration | Limited integration with other resources | Seamless integration of resources and experiences |
| Technology | Limited use of technology | Extensive use of technology for access and collaboration |
| Learner Engagement | Passive | Active and engaged |
| Measurement | Limited to course completion and test scores | Comprehensive tracking of learning activities and outcomes |
| Adaptability | Less adaptable to individual needs and preferences | Highly adaptable and personalized |
| Culture | Often lacks emphasis on continuous learning | Promotes a culture of continuous learning and development |
1.3 What Are the Benefits of Implementing a Learning Ecosystem?
Implementing a learning ecosystem can bring numerous benefits to an organization, enhancing its ability to develop and retain talent, improve performance, and achieve its strategic goals.
- Enhanced Learning Experience: A learning ecosystem offers a more engaging, personalized, and effective learning experience.
- Improved Knowledge Retention: By integrating various learning resources and experiences, a learning ecosystem can improve knowledge retention.
- Increased Employee Engagement: A learning ecosystem can increase employee engagement by providing opportunities for self-directed learning.
- Better Alignment with Business Goals: A learning ecosystem can better align learning initiatives with business goals by focusing on developing the skills and knowledge.
- Greater Flexibility and Adaptability: A learning ecosystem is more flexible and adaptable to changing business needs and individual learning preferences.
- Cost Savings: A learning ecosystem can lead to cost savings by reducing the need for expensive formal training programs.
- Competitive Advantage: By creating a culture of continuous learning and development, a learning ecosystem can help an organization gain a competitive advantage.
- Data-Driven Insights: Learning ecosystems provide valuable data and analytics that can be used to optimize learning programs and improve outcomes.
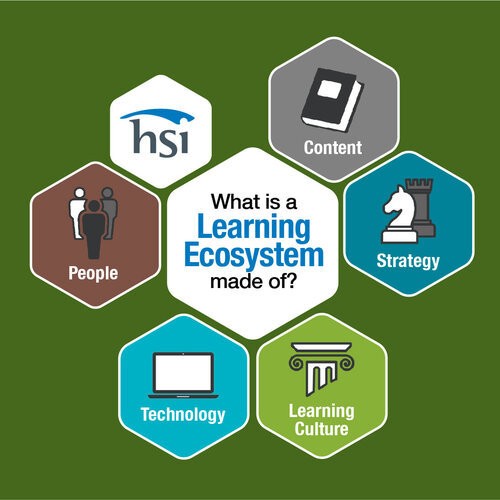 Learning Ecosystem Components
Learning Ecosystem Components
2. Who Are the Key Players in a Learning Ecosystem?
The effectiveness of a learning ecosystem depends on the active participation and collaboration of various stakeholders. These key players contribute to creating a dynamic and supportive learning environment.
2.1 Learners: The Heart of the Ecosystem
Learners are the central focus of any learning ecosystem. Their needs, preferences, and goals should drive the design and implementation of learning initiatives. Active learners engage with content, participate in discussions, and seek out opportunities to expand their knowledge and skills.
How to Engage Learners Effectively:
- Personalize Learning Paths: Tailor learning experiences to individual needs and interests.
- Provide Flexible Learning Options: Offer a variety of learning formats, such as online courses, workshops, and mentoring programs.
- Encourage Self-Directed Learning: Empower learners to take ownership of their development.
- Foster a Collaborative Environment: Create opportunities for learners to connect, share knowledge, and support each other.
- Provide Regular Feedback: Offer constructive feedback to help learners improve and stay motivated.
- Recognize and Reward Achievements: Acknowledge and celebrate learning milestones to reinforce positive behavior.
- Seek Learner Input: Involve learners in the design and evaluation of learning programs to ensure relevance and effectiveness.
2.2 Instructors and Facilitators: Guiding the Learning Journey
Instructors and facilitators play a crucial role in guiding learners through the learning process. They provide expertise, facilitate discussions, and create engaging learning experiences. Effective instructors adapt their teaching methods to meet the needs of diverse learners.
Key Responsibilities of Instructors and Facilitators:
- Content Delivery: Present information in a clear, concise, and engaging manner.
- Facilitation: Guide discussions and activities to promote active learning.
- Assessment: Evaluate learner progress and provide constructive feedback.
- Mentoring: Offer guidance and support to learners as they develop their skills and knowledge.
- Curriculum Development: Design and update learning materials to ensure relevance and effectiveness.
- Technology Integration: Utilize technology to enhance the learning experience and provide access to resources.
- Creating a Positive Learning Environment: Foster a supportive and inclusive atmosphere where learners feel comfortable taking risks and asking questions.
2.3 Managers and Leaders: Championing a Learning Culture
Managers and leaders play a critical role in fostering a learning culture within an organization. They set the tone for learning, provide resources and support, and recognize the value of continuous development. When leaders prioritize learning, employees are more likely to engage in learning activities.
How Managers and Leaders Can Support a Learning Ecosystem:
- Promote a Learning Mindset: Encourage employees to embrace learning as a continuous process.
- Provide Resources and Support: Allocate budget and time for learning initiatives.
- Recognize and Reward Learning: Acknowledge and celebrate learning achievements to reinforce positive behavior.
- Lead by Example: Demonstrate a personal commitment to learning and development.
- Integrate Learning into Performance Management: Link learning goals to performance objectives.
- Foster a Culture of Feedback: Encourage open and honest feedback to promote continuous improvement.
- Support Knowledge Sharing: Create opportunities for employees to share their knowledge and expertise.
2.4 SMEs and Veteran Employees: Internal Knowledge Experts
Subject Matter Experts (SMEs) and veteran employees possess a wealth of knowledge and experience that can be invaluable to a learning ecosystem. They can serve as mentors, provide on-the-job training, and share best practices.
Leveraging SMEs and Veteran Employees:
- Mentoring Programs: Pair experienced employees with newer employees to share knowledge and provide guidance.
- Knowledge Sharing Platforms: Create online forums or communities where employees can ask questions and share insights.
- Training and Development Programs: Involve SMEs in the design and delivery of training programs.
- On-the-Job Training: Provide opportunities for employees to learn from experienced colleagues in real-world settings.
- Communities of Practice: Form groups of employees with shared interests or expertise to collaborate and share knowledge.
- Documentation and Knowledge Capture: Encourage SMEs to document their knowledge and best practices for future reference.
- Recognition and Rewards: Acknowledge and reward SMEs for their contributions to the learning ecosystem.
2.5 External Experts: Enriching Perspectives
External experts can bring fresh perspectives, specialized knowledge, and innovative approaches to a learning ecosystem. They can provide training, consulting, and thought leadership to enhance organizational capabilities.
How to Engage External Experts:
- Training Workshops: Invite external experts to conduct workshops on specialized topics.
- Consulting Services: Engage consultants to provide expertise and guidance on specific projects or initiatives.
- Keynote Speakers: Invite thought leaders to speak at conferences or events.
- Webinars and Online Courses: Offer online learning opportunities led by external experts.
- Partnerships: Collaborate with external organizations to develop and deliver learning programs.
- Advisory Boards: Form advisory boards of external experts to provide strategic guidance on learning initiatives.
- Research and Development: Partner with external experts to conduct research and develop new learning technologies and methodologies.
3. What Types of Content Are Essential in a Learning Ecosystem?
Content is the backbone of any learning ecosystem, providing the information, knowledge, and skills that learners need to succeed. A diverse range of content types can cater to different learning styles and preferences.
3.1 Formal Training Materials: Structured Learning
Formal training materials provide structured learning experiences with defined objectives and assessments. These materials can include:
- Classroom Training: Instructor-led courses conducted in a traditional classroom setting.
- Online Courses: Self-paced learning modules delivered through a learning management system (LMS).
- E-books and Manuals: Comprehensive guides and reference materials.
- Videos and Webinars: Visual learning resources that can be accessed on-demand.
- Assessments and Quizzes: Tools to measure learning progress and knowledge retention.
Creating Effective Formal Training Materials:
- Define Clear Learning Objectives: Specify what learners should know or be able to do after completing the training.
- Structure Content Logically: Organize information in a clear and concise manner.
- Use Engaging Multimedia: Incorporate videos, images, and interactive elements to enhance engagement.
- Provide Opportunities for Practice: Include exercises, simulations, and case studies to reinforce learning.
- Assess Learning Outcomes: Use quizzes, exams, and projects to measure learning progress.
- Provide Feedback: Offer constructive feedback to help learners improve their understanding and skills.
- Ensure Accessibility: Make materials accessible to learners with disabilities.
3.2 Informal Knowledge Sharing: Collaborative Learning
Informal knowledge sharing occurs through conversations, interactions, and collaborations among employees. This type of learning is often spontaneous and organic, driven by the needs and interests of the learners.
Facilitating Informal Knowledge Sharing:
- Create Online Forums and Communities: Provide platforms for employees to connect, ask questions, and share insights.
- Encourage Mentoring and Coaching: Pair experienced employees with newer employees to share knowledge and provide guidance.
- Host Lunch and Learn Sessions: Organize informal gatherings where employees can share their expertise on specific topics.
- Promote Communities of Practice: Form groups of employees with shared interests or expertise to collaborate and share knowledge.
- Utilize Social Media Platforms: Leverage social media tools to facilitate communication and knowledge sharing.
- Create a Culture of Open Communication: Encourage employees to share their ideas and insights freely.
- Recognize and Reward Knowledge Sharing: Acknowledge and celebrate employees who contribute to the knowledge base.
3.3 External Resources: Expanding Horizons
External resources can supplement internal training programs and provide access to specialized knowledge and expertise. These resources can include:
- Industry Publications: Journals, magazines, and websites that provide insights into industry trends and best practices.
- Conferences and Events: Opportunities to learn from experts, network with peers, and stay up-to-date on industry developments.
- Online Courses and Webinars: Learning opportunities offered by external providers.
- Professional Associations: Organizations that provide resources, training, and networking opportunities for professionals in specific fields.
- Research Reports: Studies and analyses that provide insights into specific topics or industries.
- Books and Articles: In-depth explorations of specific topics.
- Open Educational Resources (OER): Freely available educational materials that can be used and adapted for learning purposes.
Integrating External Resources into a Learning Ecosystem:
- Curate Relevant Content: Identify and recommend external resources that align with learning objectives.
- Provide Access to Resources: Make external resources easily accessible through a central portal or learning management system.
- Encourage Learners to Explore: Encourage learners to seek out and share external resources that they find valuable.
- Facilitate Discussions: Create opportunities for learners to discuss and analyze external resources.
- Integrate Resources into Training Programs: Incorporate external resources into formal training programs.
- Evaluate the Quality of Resources: Ensure that external resources are accurate, reliable, and up-to-date.
- Provide Context and Guidance: Help learners understand how external resources relate to their learning goals.
3.4 Performance Support Tools: Just-In-Time Learning
Performance support tools provide learners with access to information and resources at the moment they need it. These tools can include:
- Job Aids: Step-by-step instructions, checklists, and templates that help employees perform specific tasks.
- FAQs: Lists of frequently asked questions and answers.
- Glossaries: Definitions of key terms and concepts.
- Searchable Knowledge Bases: Databases of information that can be accessed on-demand.
- Decision Support Tools: Tools that help employees make informed decisions.
- Expert Systems: Computer programs that provide expert advice and guidance.
- Chatbots: AI-powered virtual assistants that can answer questions and provide support.
Implementing Effective Performance Support Tools:
- Identify Key Performance Gaps: Determine where employees need the most support.
- Create User-Friendly Tools: Design tools that are easy to use and navigate.
- Provide Access at the Point of Need: Make tools accessible when and where employees need them.
- Keep Tools Up-to-Date: Regularly update tools to ensure that they are accurate and relevant.
- Promote Awareness: Make employees aware of the tools and how to use them.
- Provide Training: Offer training on how to use the tools effectively.
- Gather Feedback: Solicit feedback from users to improve the tools.
4. How Does Technology Enhance a Learning Ecosystem?
Technology plays a pivotal role in enhancing a learning ecosystem by providing access to learning resources, facilitating collaboration, and enabling personalized learning experiences.
4.1 Learning Management Systems (LMS): Central Hub
A Learning Management System (LMS) serves as a central hub for managing and delivering learning content. It provides a platform for:
- Content Delivery: Delivering online courses, videos, and other learning materials.
- Tracking Progress: Monitoring learner progress and performance.
- Assessment: Administering quizzes, exams, and other assessments.
- Reporting: Generating reports on learner activity and outcomes.
- Communication: Facilitating communication between learners and instructors.
- Collaboration: Providing tools for learners to collaborate and share knowledge.
- Personalization: Tailoring learning experiences to individual needs and preferences.
Choosing the Right LMS:
- Identify Your Needs: Determine what features and functionality you need in an LMS.
- Consider Your Budget: Evaluate the cost of different LMS options.
- Evaluate User-Friendliness: Choose an LMS that is easy to use for both learners and administrators.
- Assess Integration Capabilities: Ensure that the LMS can integrate with your other systems.
- Check for Mobile Compatibility: Choose an LMS that is accessible on mobile devices.
- Read Reviews: See what other users have to say about different LMS options.
- Request a Demo: Try out the LMS before making a decision.
4.2 Mobile Learning: Anytime, Anywhere Access
Mobile learning provides learners with access to learning resources on their smartphones and tablets. This allows for:
- Anytime, Anywhere Learning: Learners can access content whenever and wherever they have time.
- Just-In-Time Learning: Learners can access information and resources at the moment they need it.
- Personalized Learning: Learners can access content that is relevant to their individual needs and interests.
- Increased Engagement: Mobile learning can be more engaging than traditional learning methods.
- Improved Retention: Mobile learning can improve knowledge retention by providing learners with opportunities to review and reinforce what they have learned.
- Greater Flexibility: Mobile learning provides learners with greater flexibility and control over their learning experience.
Implementing Effective Mobile Learning:
- Design for Mobile: Create content that is optimized for mobile devices.
- Use Microlearning: Break content into small, manageable chunks.
- Incorporate Multimedia: Use videos, images, and interactive elements to enhance engagement.
- Provide Offline Access: Allow learners to access content even when they are not connected to the internet.
- Use Push Notifications: Send reminders and updates to learners.
- Gamify the Experience: Use game mechanics to make learning more engaging.
- Gather Feedback: Solicit feedback from learners to improve the mobile learning experience.
4.3 Social Learning Tools: Collaborative Knowledge Sharing
Social learning tools facilitate collaboration and knowledge sharing among learners. These tools can include:
- Online Forums: Platforms for learners to ask questions, share insights, and discuss topics.
- Social Media Platforms: Tools for learners to connect, communicate, and share resources.
- Wikis: Collaborative websites where learners can create and edit content.
- Blogs: Platforms for learners to share their thoughts and experiences.
- Webinars: Online seminars that allow learners to interact with instructors and peers in real-time.
- Virtual Meeting Tools: Tools for learners to collaborate on projects and assignments.
- Communities of Practice: Groups of learners who share a common interest or expertise.
Fostering Social Learning:
- Create a Culture of Collaboration: Encourage learners to share their knowledge and expertise.
- Provide Opportunities for Interaction: Create activities that require learners to interact with each other.
- Facilitate Discussions: Guide discussions and activities to promote active learning.
- Recognize and Reward Collaboration: Acknowledge and celebrate learners who contribute to the community.
- Model Collaborative Behavior: Demonstrate collaborative behavior as an instructor or facilitator.
- Provide Training on Collaboration Tools: Offer training on how to use social learning tools effectively.
- Gather Feedback: Solicit feedback from learners to improve the social learning experience.
4.4 Analytics and Reporting: Measuring Impact
Analytics and reporting tools provide data on learner activity and outcomes, allowing organizations to measure the impact of their learning initiatives. This data can be used to:
- Track Learner Progress: Monitor learner progress and performance.
- Identify Areas for Improvement: Identify areas where learners are struggling.
- Evaluate the Effectiveness of Training Programs: Determine whether training programs are achieving their objectives.
- Personalize Learning Experiences: Tailor learning experiences to individual needs and preferences.
- Optimize Content: Improve the quality and relevance of learning content.
- Demonstrate ROI: Show the return on investment of learning initiatives.
- Make Data-Driven Decisions: Use data to inform decisions about learning and development.
Leveraging Analytics and Reporting:
- Define Clear Metrics: Determine what you want to measure.
- Collect Data: Gather data on learner activity and outcomes.
- Analyze Data: Identify trends and patterns in the data.
- Interpret Results: Draw conclusions from the data.
- Take Action: Use the data to improve learning initiatives.
- Communicate Results: Share the results with stakeholders.
- Continuously Monitor: Regularly monitor data to track progress and identify new opportunities for improvement.
5. How Does Learning Culture Impact the Ecosystem?
A learning culture is the set of values, beliefs, and attitudes that an organization holds towards learning and development. It significantly impacts the effectiveness of a learning ecosystem.
5.1 Fostering a Growth Mindset
A growth mindset is the belief that abilities and intelligence can be developed through dedication and hard work. Fostering a growth mindset is essential for creating a learning culture.
How to Foster a Growth Mindset:
- Encourage Learning from Mistakes: Create a safe environment where learners feel comfortable taking risks and making mistakes.
- Provide Constructive Feedback: Offer feedback that focuses on effort and progress.
- Emphasize the Process of Learning: Celebrate the journey of learning, not just the outcome.
- Promote a Love of Learning: Encourage learners to explore new topics and challenge themselves.
- Recognize and Reward Effort: Acknowledge and celebrate learners who put in effort and show improvement.
- Model a Growth Mindset: Demonstrate a personal commitment to learning and development.
- Provide Opportunities for Growth: Offer training and development opportunities that allow learners to expand their skills and knowledge.
5.2 Encouraging Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing
Collaboration and knowledge sharing are essential for creating a dynamic and effective learning ecosystem. When learners collaborate and share their knowledge, they can learn from each other and build a stronger sense of community.
How to Encourage Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing:
- Create Online Forums and Communities: Provide platforms for learners to connect, ask questions, and share insights.
- Encourage Mentoring and Coaching: Pair experienced employees with newer employees to share knowledge and provide guidance.
- Host Lunch and Learn Sessions: Organize informal gatherings where employees can share their expertise on specific topics.
- Promote Communities of Practice: Form groups of employees with shared interests or expertise to collaborate and share knowledge.
- Utilize Social Media Platforms: Leverage social media tools to facilitate communication and knowledge sharing.
- Create a Culture of Open Communication: Encourage employees to share their ideas and insights freely.
- Recognize and Reward Knowledge Sharing: Acknowledge and celebrate employees who contribute to the knowledge base.
5.3 Promoting Self-Directed Learning
Self-directed learning is the process of taking the initiative to diagnose your learning needs, formulate learning goals, identify learning resources, implement learning strategies, and evaluate learning outcomes. Promoting self-directed learning empowers learners to take ownership of their development and pursue their interests.
How to Promote Self-Directed Learning:
- Provide Access to Resources: Offer a wide range of learning resources, such as online courses, e-books, and articles.
- Encourage Learners to Set Goals: Help learners identify their learning needs and set clear goals.
- Provide Guidance and Support: Offer guidance and support to learners as they pursue their learning goals.
- Encourage Reflection: Encourage learners to reflect on their learning experiences and identify areas for improvement.
- Provide Feedback: Offer constructive feedback to help learners improve their understanding and skills.
- Recognize and Reward Self-Directed Learning: Acknowledge and celebrate learners who take initiative and pursue their learning goals.
- Create a Culture of Trust: Foster a culture of trust where learners feel comfortable taking risks and experimenting with new ideas.
5.4 Recognizing and Rewarding Learning
Recognizing and rewarding learning reinforces positive behavior and encourages learners to continue to develop their skills and knowledge. Recognition can take many forms, such as:
- Public Acknowledgement: Recognizing learners in team meetings, newsletters, or company-wide events.
- Certificates and Badges: Awarding certificates or badges upon completion of training programs.
- Promotions and Raises: Recognizing learners who demonstrate improved performance and increased value to the organization.
- Opportunities for Advancement: Providing learners with opportunities to take on new challenges and responsibilities.
- Personalized Gifts: Giving learners personalized gifts or experiences that are relevant to their interests.
- Verbal Praise: Offering genuine and specific praise for learners’ accomplishments.
- Letters of Recommendation: Providing letters of recommendation for learners who are seeking new opportunities.
Designing Effective Recognition and Reward Programs:
- Align Rewards with Learning Goals: Ensure that rewards are aligned with the organization’s learning goals.
- Make Rewards Meaningful: Choose rewards that are meaningful and valuable to learners.
- Provide Timely Recognition: Recognize learners as soon as possible after they achieve a learning goal.
- Make Recognition Public: Share learners’ accomplishments with the team or organization.
- Personalize Rewards: Tailor rewards to individual preferences.
- Be Consistent: Consistently recognize and reward learning.
- Evaluate the Program: Regularly evaluate the effectiveness of the recognition and reward program.
6. How to Strategically Align a Learning Ecosystem with Organizational Goals?
To maximize the impact of a learning ecosystem, it must be strategically aligned with organizational goals. This ensures that learning initiatives are focused on developing the skills and knowledge needed to achieve business objectives.
6.1 Identifying Key Competencies
The first step in aligning a learning ecosystem with organizational goals is to identify the key competencies that are critical for success. Competencies are the knowledge, skills, and abilities that employees need to perform their jobs effectively.
How to Identify Key Competencies:
- Analyze Business Goals: Determine what skills and knowledge are needed to achieve business goals.
- Conduct Job Analysis: Analyze job descriptions and tasks to identify required competencies.
- Interview High Performers: Interview employees who are performing well to identify their key competencies.
- Survey Employees: Survey employees to gather feedback on needed competencies.
- Consult with Managers: Consult with managers to identify the competencies that are most important for their teams.
- Review Industry Trends: Stay up-to-date on industry trends to identify emerging competencies.
- Benchmark Against Competitors: Benchmark your organization’s competencies against those of your competitors.
6.2 Designing Targeted Learning Programs
Once key competencies have been identified, the next step is to design targeted learning programs that are focused on developing those competencies. These programs should be:
- Relevant: Aligned with the needs of the organization and the learners.
- Engaging: Designed to capture and maintain learners’ attention.
- Effective: Focused on developing specific skills and knowledge.
- Measurable: Designed to track and measure learning outcomes.
- Accessible: Available to learners when and where they need them.
- Flexible: Adaptable to individual learning styles and preferences.
- Sustainable: Designed to provide ongoing learning and development opportunities.
Elements of Targeted Learning Programs:
- Clear Learning Objectives: Specify what learners should know or be able to do after completing the training.
- Engaging Content: Use videos, images, and interactive elements to enhance engagement.
- Opportunities for Practice: Include exercises, simulations, and case studies to reinforce learning.
- Assessments and Quizzes: Use quizzes, exams, and projects to measure learning progress.
- Feedback and Coaching: Provide constructive feedback to help learners improve their understanding and skills.
- Performance Support Tools: Provide learners with access to information and resources at the moment they need it.
- Social Learning Opportunities: Create opportunities for learners to collaborate and share knowledge.
6.3 Measuring Learning Outcomes and ROI
Measuring learning outcomes and ROI is essential for demonstrating the value of a learning ecosystem and ensuring that it is aligned with organizational goals. Learning outcomes are the changes in knowledge, skills, and attitudes that result from learning. ROI is the return on investment of learning initiatives.
How to Measure Learning Outcomes and ROI:
- Define Clear Metrics: Determine what you want to measure.
- Collect Data: Gather data on learner activity and outcomes.
- Analyze Data: Identify trends and patterns in the data.
- Interpret Results: Draw conclusions from the data.
- Calculate ROI: Determine the return on investment of learning initiatives.
- Communicate Results: Share the results with stakeholders.
- Continuously Monitor: Regularly monitor data to track progress and identify new opportunities for improvement.
Examples of Metrics:
- Knowledge Gain: Measure the increase in knowledge as a result of training.
- Skill Improvement: Measure the improvement in skills as a result of training.
- Performance Improvement: Measure the improvement in job performance as a result of training.
- Employee Engagement: Measure the level of employee engagement as a result of training.
- Customer Satisfaction: Measure the level of customer satisfaction as a result of training.
- Revenue Growth: Measure the increase in revenue as a result of training.
- Cost Savings: Measure the cost savings as a result of training.
7. What Are the Latest Trends in Learning Ecosystems?
The field of learning ecosystems is constantly evolving, with new technologies, methodologies, and best practices emerging all the time. Staying up-to-date on the latest trends is essential for creating a dynamic and effective learning ecosystem.
7.1 Personalized Learning Paths
Personalized learning paths tailor learning experiences to individual needs, preferences, and goals. This approach recognizes that learners have different learning styles, paces, and interests, and that a one-size-fits-all approach is not always effective.
How to Implement Personalized Learning Paths:
- Assess Learner Needs: Use assessments and surveys to determine learners’ knowledge, skills, and interests.
- Provide a Variety of Learning Resources: Offer a wide range of learning resources, such as online courses, e-books, and videos.
- Allow Learners to Choose Their Own Path: Empower learners to choose the learning resources and activities that are most relevant to their needs.
- Provide Guidance and Support: Offer guidance and support to learners as they navigate their learning paths.
- Track Learner Progress: Monitor learner progress and provide feedback.
- Adapt Learning Paths as Needed: Adjust learning paths based on learner progress and feedback.
- Use Adaptive Learning Technologies: Implement adaptive learning technologies that automatically adjust the difficulty and content of learning based on learner performance.
7.2 Microlearning
Microlearning delivers content in small, bite-sized chunks that can be easily consumed and applied. This approach is particularly effective for busy learners who have limited time for training.
Benefits of Microlearning:
- Increased Engagement: Microlearning is more engaging than traditional learning methods.
- Improved Retention: Microlearning improves knowledge retention by providing learners with opportunities to review and reinforce what they have learned.
- Greater Flexibility: Microlearning provides learners with greater flexibility and control over their learning experience.
- Just-In-Time Learning: Microlearning provides learners with access to information and resources at the moment they need it.
- Cost-Effective: Microlearning is more cost-effective than traditional learning methods.
- Easy to Update: Microlearning content is easy to update and revise.
- Mobile-Friendly: Microlearning content is optimized for mobile devices.
7.3 Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming the field of learning by providing personalized learning experiences, automating administrative tasks, and providing insights into learner behavior.
AI Applications in Learning:
- Personalized Learning: AI can be used to personalize learning experiences based on learners’ knowledge, skills, and interests.
- Adaptive Learning: AI can be used to create adaptive learning systems that automatically adjust the difficulty and content of learning based on learner performance.
- Chatbots: AI-powered chatbots can be used to answer learner questions and provide support.
- Automated Grading: AI can be used to automate the grading of quizzes, exams, and assignments.
- Content Curation: AI can be used to curate relevant learning content from a variety of sources.
- Learning Analytics: AI can be used to analyze learner data to identify trends and patterns.
- Predictive Analytics: AI can be used to predict learner performance and identify learners who are at risk of falling behind.
7.4 Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR) in Training
Virtual and Augmented Reality (VR/AR) provide immersive and interactive learning experiences that can enhance engagement and improve knowledge retention.
VR/AR Applications in Training:
- Simulations: VR/AR can be used to create realistic simulations of real-world scenarios.
- Virtual Tours: VR/AR can be used to provide virtual tours of facilities or locations.
- Interactive Training: VR/AR can be used to create interactive training modules that allow learners to practice skills in a safe and controlled environment.
- Product Demonstrations: VR/AR can be used to demonstrate how products work.
- Safety Training: VR/AR can be used to provide safety training in a safe and realistic environment.
- Onboarding: VR/AR can be used to provide new employees with an immersive and engaging onboarding experience.
- Skills Development: VR/AR can be used to develop a wide range of skills, such as communication, teamwork, and problem-solving.
8. Common Challenges in Building a Learning Ecosystem
Building a learning ecosystem can be a complex undertaking, and organizations often face a number of challenges along the way. Being aware of these challenges and developing strategies to overcome them is essential for success.
8.1 Lack of Buy-In from Stakeholders
One of the most common challenges in building a learning ecosystem is a lack of buy-in from stakeholders. Stakeholders may not understand the value of a learning ecosystem or may be resistant to change.
Strategies for Gaining Buy-In:
- Communicate the Value: Clearly communicate the value of a learning ecosystem to stakeholders.
- Involve Stakeholders in the Process: Involve stakeholders in the design and implementation of the learning ecosystem.
- Address Concerns: Address stakeholders’ concerns and answer their questions.
- Demonstrate Success: Demonstrate the success of the learning ecosystem through data and metrics.
- Start Small: Start with a small pilot project to demonstrate the value of a learning ecosystem.
- Celebrate Successes: Celebrate successes and recognize the contributions of stakeholders.
- Build a Coalition: Build a coalition of supporters who can advocate for the learning ecosystem.
8.2 Resistance to Change
Resistance to change is a common human reaction, and it can be a major obstacle in building a learning ecosystem. Employees may be comfortable with the way things are and may be reluctant to adopt new technologies, methodologies, or processes.
Strategies for Overcoming Resistance to Change:
- Communicate the Need for Change: Clearly communicate the need for change and explain why a learning ecosystem is necessary.
- Involve Employees in the Process: Involve employees in the design and implementation of the learning ecosystem.
- Provide Training and Support: Provide employees with the training and support they need to use new technologies and methodologies.
- Address Concerns: Address employees’ concerns and answer their questions.
- Celebrate Successes: Celebrate successes and recognize the contributions of employees.
- Lead by Example: Demonstrate a personal commitment to the learning ecosystem.
- Create a Culture of Trust: Foster a culture of trust where employees feel comfortable taking risks and experimenting with new ideas.
8.3 Technology Overload
With so many learning technologies available, it can be easy to get overwhelmed and implement too many tools. This can lead to confusion, frustration, and low adoption rates.
Strategies for Avoiding Technology Overload:
- Start with a Clear Strategy: Develop a clear strategy for how technology will be used to support learning.
- Focus on User Needs: Choose technologies that meet the needs of learners and instructors.
- Integrate Technologies: Integrate technologies with existing systems.
- Provide Training and Support: Provide users with the training and support they need to use the technologies effectively.
- Avoid Over-Complication: Keep the technology ecosystem simple and easy to use.
- Gather Feedback: Solicit feedback from users to improve the technology ecosystem.
- Continuously Evaluate: Regularly evaluate the effectiveness of the technology ecosystem.
8.4 Lack of Resources
Building a learning ecosystem
