E-learning in education is revolutionizing how we acquire knowledge and skills, offering a dynamic alternative to traditional learning methods. Discover with LEARNS.EDU.VN how digital education resources provide flexible, accessible, and personalized educational experiences for everyone. Explore the future of education with online learning platforms, virtual classrooms, and digital literacy tools.
1. Defining E-Learning: A Modern Approach to Education
E-learning, short for electronic learning, represents a transformative shift in education, leveraging technology to deliver educational content and facilitate learning experiences. Unlike traditional classroom settings, e-learning transcends geographical boundaries and time constraints, offering unparalleled flexibility and accessibility. It encompasses a wide range of digital resources and methodologies, including online courses, virtual classrooms, interactive simulations, and multimedia content, all designed to engage learners and enhance knowledge acquisition.
1.1 The Evolution of E-Learning
Initially, e-learning primarily involved the digital distribution of learning materials from instructors to students. Today, it has evolved into a dynamic and interactive ecosystem that fosters multidirectional communication and collaboration. Learners now have the freedom to choose how they access and interact with content, engaging with peers and educators in meaningful ways.
1.2 Key Characteristics of E-Learning
- Flexibility: Learners can access educational materials and participate in learning activities at their own pace and convenience, fitting studies into their schedules.
- Accessibility: E-learning removes geographical barriers, making education available to anyone with an internet connection, regardless of location.
- Personalization: Adaptive learning technologies and personalized learning paths cater to individual needs and learning styles, optimizing the educational experience.
- Interactivity: E-learning platforms incorporate interactive elements such as quizzes, simulations, and discussion forums to enhance engagement and knowledge retention.
1.3 Types of E-Learning
E-learning encompasses various formats and delivery methods to cater to diverse learning preferences and pedagogical goals:
- Online Courses: Structured learning experiences delivered through online platforms, covering a wide range of subjects and skill sets.
- Virtual Classrooms: Real-time interactive sessions conducted online, simulating the traditional classroom environment with live lectures, discussions, and collaborative activities.
- Mobile Learning (M-Learning): Educational content delivered through mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets, enabling learning on the go.
- Blended Learning: A hybrid approach that combines online learning with traditional face-to-face instruction, leveraging the benefits of both methods.
2. The Importance of E-Learning in Today’s World
E-learning has emerged as a critical component of modern education and professional development. It addresses the evolving needs of learners and organizations in a rapidly changing world.
2.1 Bridging the Skills Gap
The rapid pace of technological advancement necessitates continuous learning and upskilling. E-learning provides a flexible and accessible means for individuals to acquire new skills and stay relevant in the workforce. As industries evolve, e-learning plays a vital role in retraining and reskilling workers, ensuring they possess the competencies needed to thrive in emerging roles.
2.2 Corporate Training and Development
Companies increasingly rely on e-learning to deliver ongoing training and development programs to their employees. Learning Management Systems (LMS) are widely used in corporate settings to manage and track employee learning, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and enhancing job performance. E-learning offers a cost-effective and scalable solution for organizations to invest in their workforce and drive business outcomes.
2.3 Higher Education Transformation
Higher education institutions are integrating e-learning methods to enhance the learning experience for students both inside and outside the classroom. Online learning platforms and digital resources provide students with greater flexibility and access to course materials, fostering a more personalized and engaging learning environment. According to a 2022 McKinsey & Company survey, 65% of higher education students want schools to retain aspects of online learning in the post-pandemic world.
3. Advantages of E-Learning: Why Choose Digital Education?
E-learning offers numerous advantages over traditional learning methods, making it an attractive option for learners of all ages and backgrounds.
3.1 Unparalleled Flexibility and Convenience
E-learning provides learners with the flexibility to study at their own pace and on their own schedule. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with busy lifestyles or those who need to balance education with work and family responsibilities. Learners can access course materials and complete assignments anytime, anywhere, as long as they have an internet connection.
3.2 Cost-Effectiveness and Affordability
E-learning can be more cost-effective than traditional education, as it eliminates the need for physical classrooms, transportation, and printed materials. Online courses and digital resources often come at a lower cost than traditional tuition fees, making education more accessible to a wider range of learners.
3.3 Personalized Learning Experiences
E-learning platforms often incorporate adaptive learning technologies that tailor the learning experience to individual needs and learning styles. Personalized learning paths, customized feedback, and targeted resources help learners optimize their learning and achieve their goals more effectively.
3.4 Enhanced Engagement and Interactivity
E-learning incorporates interactive elements such as quizzes, simulations, videos, and discussion forums to enhance engagement and knowledge retention. Multimedia content and gamified learning experiences make learning more enjoyable and effective.
3.5 Scalability and Accessibility
E-learning can reach a global audience, making education accessible to learners in remote or underserved areas. Online courses and digital resources can be easily scaled to accommodate large numbers of students, without the limitations of physical classroom space.
4. Disadvantages of E-Learning: Addressing the Challenges
While e-learning offers numerous advantages, it also presents certain challenges that need to be addressed to ensure its effectiveness and accessibility.
4.1 The Need for Self-Discipline and Motivation
E-learning requires learners to be self-disciplined and motivated, as they are responsible for managing their own learning and staying on track with course assignments. Without the structure and supervision of a traditional classroom, some learners may struggle to stay focused and engaged.
4.2 Technical Issues and Digital Divide
Access to technology and reliable internet connectivity is essential for e-learning. However, not all learners have equal access to these resources, creating a digital divide that can limit participation in online education. Technical issues such as software glitches, hardware malfunctions, and network outages can also disrupt the learning experience.
4.3 Lack of Face-to-Face Interaction
E-learning can sometimes lack the personal interaction and social connection that are inherent in traditional classroom settings. The absence of face-to-face communication can make it difficult for learners to build relationships with peers and instructors, potentially leading to feelings of isolation and detachment.
4.4 Credibility and Quality Concerns
The quality and credibility of online courses and e-learning resources can vary widely. Learners need to be discerning when selecting online programs and materials, ensuring that they are reputable and aligned with their learning goals.
5. Exploring E-Learning Platforms and Tools
A wide variety of e-learning platforms and tools are available to support digital learning and online training. These resources cater to diverse needs and preferences, offering features such as course management, content creation, communication tools, and assessment capabilities.
5.1 Learning Management Systems (LMS)
LMS platforms provide a centralized hub for managing and delivering e-learning content, tracking learner progress, and assessing performance. Popular LMS platforms include:
- Canvas: A widely used LMS in higher education, offering a robust suite of tools for course management, communication, and collaboration.
- Moodle: An open-source LMS known for its flexibility and customization options, suitable for both academic and corporate settings.
- Sakai: A collaborative learning environment designed for higher education, offering tools for course management, content sharing, and assessment.
- Schoology: A K-12 LMS that provides a platform for creating and delivering engaging digital learning experiences.
5.2 Social Media Platforms for E-Learning
Social media platforms can be leveraged to facilitate e-learning by creating communities of learners and enabling content sharing and discussion.
- Facebook: Users can create groups to share information and ideas, fostering communication and collaboration among group members.
- LinkedIn: Enables professional networking and knowledge sharing, with a dedicated e-learning platform called LinkedIn Learning offering over 4,000 business courses.
- X (formerly known as Twitter): Connects learners through hashtags for specific topics or events, facilitating real-time discussions and knowledge sharing.
- YouTube: Provides a platform for posting and accessing educational content for free, allowing users to comment on and rate videos.
5.3 Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs)
MOOCs offer free or low-cost online courses to large numbers of learners, often modeled on courses taught by top-tier universities. Popular MOOC platforms include:
- Coursera: Partners with universities and organizations to offer a wide range of courses, specializations, and degrees.
- edX: Founded by Harvard and MIT, offering courses and programs from leading universities and institutions worldwide.
- Udemy: Provides a marketplace for instructors to create and sell online courses on a variety of topics.
- Skillshare: Focuses on creative skills and practical learning, offering courses in design, photography, and other creative fields.
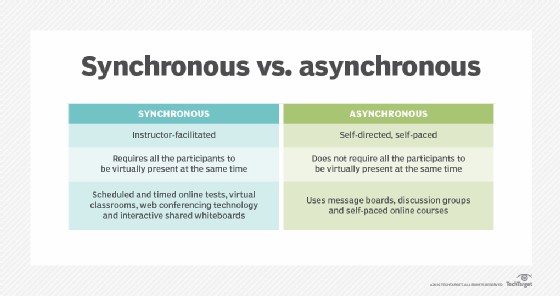
6. Synchronous vs. Asynchronous E-Learning: Choosing the Right Approach
E-learning can be delivered through synchronous or asynchronous methods, each offering unique advantages and catering to different learning preferences.
6.1 Synchronous E-Learning
Synchronous e-learning requires participants to be present at the same time, albeit virtually. This approach fosters real-time interaction and collaboration among learners and instructors. Examples of synchronous e-learning methods include:
- Virtual Classrooms: Live online sessions where instructors deliver lectures, facilitate discussions, and conduct interactive activities.
- Web Conferencing: Tools like Zoom and Microsoft Teams enable real-time communication and collaboration through video conferencing, screen sharing, and chat features.
- Interactive Whiteboards: Shared digital whiteboards allow learners to collaborate on visual projects and brainstorm ideas in real-time.
6.2 Asynchronous E-Learning
Asynchronous e-learning does not require participants to be present at the same time. This approach offers greater flexibility and allows learners to access materials and complete assignments at their own pace. Examples of asynchronous e-learning methods include:
- Online Courses: Self-paced learning modules that learners can access and complete at their own convenience.
- Discussion Boards: Online forums where learners can post questions, share ideas, and engage in discussions with peers and instructors.
- Pre-recorded Videos: Lectures and demonstrations that learners can watch at their own pace, pausing, rewinding, and rewatching as needed.
7. The Future of E-Learning: Trends and Innovations
E-learning is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing learning preferences. Several key trends and innovations are shaping the future of e-learning:
| Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Personalized Learning | Adaptive learning technologies and AI-powered tools that tailor the learning experience to individual needs and learning styles. |
| Mobile Learning | Increased use of mobile devices for learning, with educational content optimized for smartphones and tablets. |
| Microlearning | Bite-sized learning modules that deliver focused content in short bursts, ideal for busy learners and just-in-time training. |
| Gamification | Incorporating game elements such as points, badges, and leaderboards to enhance engagement and motivation. |
| Virtual and Augmented Reality | Immersive learning experiences that simulate real-world scenarios, providing hands-on training in a safe and engaging environment. |
| AI-Powered Learning | Artificial intelligence is used to personalize learning paths, provide intelligent tutoring, and automate administrative tasks. |
| Data Analytics | Learning analytics tools that track learner progress and identify areas for improvement, enabling instructors to optimize their teaching strategies and course content. |
| Accessibility | Focus on creating inclusive learning experiences for learners with disabilities, ensuring that e-learning resources are accessible to everyone. |
| Blockchain in Education | Secure and transparent management of educational credentials and records, enabling learners to easily share their achievements with employers and institutions. |
| Emphasis on Soft Skills | E-learning programs increasingly focus on developing soft skills such as communication, collaboration, and critical thinking, which are essential for success in the modern workplace. |

8. E-Learning and the Learner: Who Benefits Most?
E-learning benefits a wide range of learners, across different age groups, educational backgrounds, and professional fields. Its adaptability makes it a powerful tool for:
8.1 Students of All Ages
From elementary school students to university undergraduates, e-learning provides supplementary resources, advanced courses, and alternative learning environments. It can help struggling students catch up or enable advanced learners to explore subjects beyond the standard curriculum.
8.2 Professionals Seeking Career Advancement
Working professionals often turn to e-learning to gain new skills, earn certifications, or pursue advanced degrees without interrupting their careers. The flexibility of online programs allows them to balance work, family, and education.
8.3 Individuals Seeking Personal Enrichment
E-learning is not just for academic or professional advancement. Many individuals use online courses to explore new hobbies, learn new languages, or delve into subjects that interest them, purely for personal enrichment.
8.4 Remote Learners
For individuals living in remote areas or with limited access to traditional educational institutions, e-learning provides a vital connection to knowledge and learning opportunities.
8.5 Lifelong Learners
E-learning supports the concept of lifelong learning, enabling individuals to continuously update their skills and knowledge throughout their lives.
9. Practical Tips for Effective E-Learning
To maximize the benefits of e-learning, consider these practical tips:
- Set Clear Goals: Define what you want to achieve through e-learning.
- Create a Study Schedule: Treat your online courses like regular classes.
- Eliminate Distractions: Find a quiet place to study.
- Engage Actively: Participate in discussions and ask questions.
- Utilize Available Resources: Make use of all course materials and support services.
- Take Breaks: Prevent burnout by scheduling regular breaks.
- Stay Organized: Keep track of assignments and deadlines.
- Network with Peers: Connect with other learners for support and collaboration.
- Seek Feedback: Ask for feedback on your work to improve.
- Apply What You Learn: Put your new knowledge and skills into practice.
10. The E-Learning Revolution: A Historical Perspective
The concept of e-learning has a rich history, evolving significantly over time.
10.1 Early Beginnings
The roots of e-learning can be traced back to the 19th century with the advent of correspondence courses. These courses allowed students to learn remotely through printed materials delivered by mail.
10.2 The Electronic University Network
In 1983, Ron Gordon launched the Electronic University Network (EUN), an early online educational network aimed at providing online courses through universities and colleges.
10.3 The Rise of the World Wide Web
The creation of the World Wide Web in 1989 marked a turning point for e-learning, providing a platform for sharing information and educational resources more rapidly and easily.
10.4 The Term “E-Learning” is Coined
The term “e-learning” was first coined in 1999, coinciding with the launch of various online course implementations.
10.5 The Emergence of MOOCs
In the late 2000s, Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) emerged, offering free or low-cost online courses to large numbers of learners.
10.6 The COVID-19 Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of e-learning, with many companies and educational institutions embracing online learning to continue operations during lockdowns and social distancing measures.
11. Integrating E-Learning with Traditional Education
E-learning doesn’t have to replace traditional education; instead, it can enhance it. Blended learning models combine the best aspects of both approaches, offering a balanced and effective educational experience.
11.1 The Benefits of Blended Learning
Blended learning allows for personalized instruction, greater flexibility, and increased student engagement. It also helps students develop digital literacy skills and prepares them for the tech-driven world.
11.2 Strategies for Effective Integration
To successfully integrate e-learning with traditional education, educators should:
- Align Online and Offline Activities: Ensure that online and offline activities complement each other.
- Provide Clear Instructions: Give students clear instructions on how to navigate the online components of the course.
- Offer Support and Guidance: Provide ongoing support and guidance to students as they transition between online and offline learning.
- Use Technology Effectively: Select and use technology tools that enhance the learning experience.
- Assess Learning Outcomes: Evaluate student learning outcomes using a variety of assessment methods.
12. E-Learning in Specific Fields: Tailoring Education to Industries
E-learning can be tailored to meet the specific needs of various industries. Here are some examples:
12.1 Healthcare
E-learning is used to train healthcare professionals, provide continuing education, and educate patients. Online courses can cover topics such as medical procedures, patient care, and healthcare regulations.
12.2 Business
E-learning is used to train employees, develop leadership skills, and improve business performance. Online courses can cover topics such as management, marketing, finance, and human resources.
12.3 Technology
E-learning is used to train IT professionals, develop software skills, and stay up-to-date with the latest technologies. Online courses can cover topics such as programming, web development, and cybersecurity.
12.4 Education
E-learning is used to train teachers, develop curriculum, and improve teaching methods. Online courses can cover topics such as pedagogy, classroom management, and instructional design.
13. Addressing Common Misconceptions About E-Learning
There are several misconceptions about e-learning that need to be addressed:
- E-Learning is Only for Tech-Savvy Individuals: E-learning is designed to be user-friendly and accessible to individuals of all technical abilities.
- E-Learning is Inferior to Traditional Education: E-learning can be just as effective as traditional education, and in some cases, even more so.
- E-Learning is Isolating: E-learning can be a social and collaborative experience, with opportunities for interaction with peers and instructors.
- E-Learning is Easy: E-learning requires discipline, motivation, and effort.
- E-Learning is Expensive: E-learning can be more cost-effective than traditional education.
14. The Role of Governments and Organizations in Promoting E-Learning
Governments and organizations play a crucial role in promoting e-learning by:
- Investing in Infrastructure: Providing funding for technology and internet access.
- Developing Standards: Creating quality standards for online courses and programs.
- Providing Training: Offering training and support for educators and learners.
- Promoting Access: Ensuring that e-learning is accessible to all individuals, regardless of their location or socioeconomic status.
- Supporting Research: Funding research on the effectiveness of e-learning.
15. E-Learning and Accessibility: Ensuring Inclusivity
Accessibility is a critical consideration in e-learning. E-learning materials should be designed to be accessible to individuals with disabilities.
15.1 Best Practices for Accessibility
- Provide Alternative Text for Images: Use alternative text to describe images for visually impaired users.
- Use Captions and Transcripts for Videos: Provide captions and transcripts for videos to make them accessible to hearing-impaired users.
- Use Clear and Simple Language: Use clear and simple language to make the content easier to understand.
- Provide Keyboard Navigation: Ensure that the website or platform can be navigated using a keyboard.
- Use Sufficient Color Contrast: Use sufficient color contrast to make the content easier to read.
16. Resources for Getting Started with E-Learning
Ready to dive into the world of e-learning? Here are some resources to help you get started:
- Online Course Platforms: Explore platforms like Coursera, edX, Udemy, and Skillshare.
- Learning Management Systems: Check out LMS platforms like Canvas, Moodle, Sakai, and Schoology.
- Educational Websites: Visit educational websites like Khan Academy and MIT OpenCourseWare.
- Libraries: Access e-books, online courses, and other resources through your local library.
- Professional Organizations: Join professional organizations in your field to access training and networking opportunities.
17. What Is E-Learning in Education? FAQs Answered
1. What exactly is e-learning?
E-learning is education delivered electronically, using computers, tablets, and smartphones via the internet. It encompasses online courses, virtual classrooms, and digital learning resources.
2. How does e-learning differ from traditional learning?
Traditional learning typically occurs in a physical classroom with face-to-face interaction, while e-learning offers flexibility, accessibility, and often personalized learning paths.
3. What are the main benefits of e-learning?
Benefits include flexibility, cost-effectiveness, accessibility, personalized learning, and enhanced engagement through interactive elements.
4. Are there any drawbacks to e-learning?
Drawbacks can include the need for self-discipline, technical issues, lack of face-to-face interaction, and concerns about the quality and credibility of online resources.
5. Is e-learning suitable for all age groups?
Yes, e-learning can be adapted for all age groups, from young children to adults, with appropriate content and delivery methods.
6. How can I ensure that an e-learning course is credible?
Check the credentials of the instructors, the reputation of the institution or platform offering the course, and read reviews from other learners.
7. What types of technology are needed for e-learning?
You’ll need a computer or mobile device, internet access, and often software such as a web browser, video conferencing tool, and word processor.
8. How can I stay motivated in an e-learning environment?
Set clear goals, create a study schedule, eliminate distractions, engage actively, and connect with other learners for support.
9. Can e-learning replace traditional education entirely?
While e-learning offers many benefits, a blended approach that combines online and offline learning can be the most effective for many learners.
10. Where can I find reliable e-learning resources?
Explore reputable online course platforms like Coursera, edX, Udemy, and Skillshare, as well as educational websites and libraries.
18. Conclusion: Embrace the Potential of E-Learning
E-learning is transforming education, offering unparalleled flexibility, accessibility, and personalization. By understanding its benefits and challenges, and by leveraging the available resources and technologies, learners of all ages and backgrounds can embrace the potential of e-learning to achieve their educational and professional goals.
Ready to explore the world of e-learning? Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today to discover a wide range of courses and resources designed to help you succeed. Whether you’re looking to acquire new skills, advance your career, or simply pursue your passion for learning, LEARNS.EDU.VN has something for everyone. Unlock your potential with digital education at LEARNS.EDU.VN.
Contact us:
- Address: 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 555-555-1212
- Website: learns.edu.vn
Start your e-learning journey today and unlock a world of knowledge and opportunity.
