Self-regulated learning is a powerful approach to education, empowering you to take control of your learning journey; at LEARNS.EDU.VN, we believe understanding self-regulated learning is crucial for academic and professional success, by mastering this skill, you unlock your full potential and achieve your goals. Discover effective study habits and learning strategies to enhance your educational journey.
1. Understanding Self-Regulated Learning
Self-regulated learning (SRL) is a proactive, cyclical process where learners take ownership of their learning journey. It involves planning, monitoring, and evaluating one’s learning strategies and outcomes. This approach enables students to adapt and improve their learning process continually. Self-regulated learners are more likely to succeed academically and professionally because they are equipped with the skills to learn effectively in any environment. According to research, SRL significantly enhances academic performance and lifelong learning skills.
1.1. Definition of Self-Regulated Learning
Self-regulated learning refers to the ability of learners to understand and control their learning environment. It involves setting goals, selecting and implementing appropriate learning strategies, monitoring progress, and self-evaluating outcomes. Self-regulated learners are active participants in their education, taking responsibility for their learning process.
1.2. Key Components of Self-Regulated Learning
The key components of self-regulated learning include:
- Goal Setting: Setting specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals.
- Strategy Selection: Choosing effective learning strategies based on the task and individual learning style.
- Self-Monitoring: Tracking progress and making adjustments as needed.
- Self-Evaluation: Reflecting on performance and identifying areas for improvement.
- Self-Efficacy: Belief in one’s ability to succeed in learning tasks.
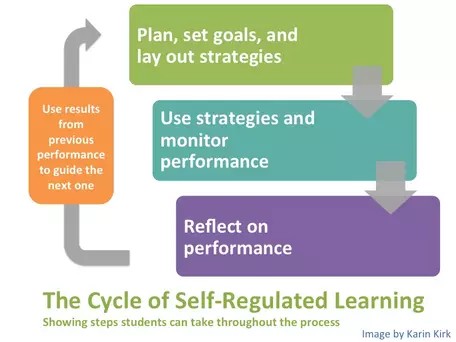
1.3. The Cyclical Process of Self-Regulated Learning
The self-regulated learning process is cyclical, involving three main phases:
- Forethought Phase: Planning and setting goals before starting a learning task.
- Performance Phase: Implementing strategies and monitoring progress during the task.
- Self-Reflection Phase: Evaluating outcomes and reflecting on the effectiveness of the strategies used.
1.4. Importance of Self-Regulated Learning
Self-regulated learning is crucial for several reasons:
- Improved Academic Performance: SRL strategies lead to better understanding and retention of information.
- Enhanced Motivation: Taking control of learning increases intrinsic motivation.
- Development of Lifelong Learning Skills: SRL equips learners with the skills to adapt and learn continuously.
- Increased Self-Efficacy: Successfully applying SRL strategies boosts confidence in one’s learning abilities.
2. The Forethought Phase: Planning and Goal Setting
The forethought phase is the initial step in the self-regulated learning cycle, focusing on planning and goal setting. This phase is critical because it sets the foundation for effective learning. By analyzing the task, setting specific goals, and planning strategies, learners can approach their studies with a clear direction and purpose. This proactive approach can significantly enhance learning outcomes and efficiency.
2.1. Analyzing the Learning Task
Before diving into a learning task, it’s essential to analyze its requirements. Ask yourself:
- What are the specific objectives of the task?
- What knowledge and skills are required to complete it successfully?
- How does this task relate to previous learning experiences?
- What are the potential challenges and obstacles?
2.2. Setting SMART Goals
Setting SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) goals is a cornerstone of self-regulated learning. Here’s how to apply the SMART framework:
- Specific: Clearly define what you want to achieve.
- Measurable: Establish criteria for measuring progress.
- Achievable: Set goals that are realistic and attainable.
- Relevant: Ensure goals align with your overall learning objectives.
- Time-bound: Set a deadline for achieving your goals.
2.3. Planning Effective Learning Strategies
Planning effective learning strategies involves selecting techniques that match the task and your learning style. Consider the following:
- Identify Resources: Determine what resources you will need, such as textbooks, online materials, or study groups.
- Choose Study Methods: Select appropriate study methods, such as summarizing, mind mapping, or practice testing.
- Create a Study Schedule: Develop a realistic schedule that allocates time for each task.
- Anticipate Obstacles: Identify potential obstacles and plan how to overcome them.
2.4. Setting Expectations for Outcomes
Setting realistic expectations for outcomes is important for maintaining motivation. Consider:
- Assess Current Standing: Evaluate your current knowledge and skills in relation to the task.
- Determine Desired Outcome: Decide what level of performance you want to achieve (e.g., mastery, competence, or completion).
- Adjust Expectations: Adjust your expectations based on the time and resources available.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Analyzing Learning Task | Understanding the task requirements, objectives, and challenges. |
| Setting SMART Goals | Defining specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound goals. |
| Planning Strategies | Selecting appropriate study methods, identifying resources, and creating a study schedule. |
| Setting Expectations | Establishing realistic expectations for learning outcomes based on available resources and current standing. |
| Example | For a history exam: (1) Understand the exam format and topics, (2) Aim to score 80%, (3) Use flashcards and practice questions, study 2 hours daily, (4) Expect to improve from a previous 70% by focusing on weak areas. Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN for detailed guides and courses to master self-regulated learning and achieve your academic goals. Contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States or Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212. |


3. The Performance Phase: Implementing Strategies and Monitoring Progress
The performance phase is where the planned strategies are put into action. It involves implementing chosen learning techniques, monitoring progress, and making necessary adjustments along the way. This phase requires active engagement and self-awareness to ensure that the learning process remains effective and aligned with the set goals.
3.1. Implementing Chosen Learning Strategies
During the performance phase, it’s crucial to actively engage with the selected learning strategies. This might involve:
- Active Reading: Engaging with the text by highlighting key points and taking notes.
- Practice Testing: Regularly testing yourself on the material to reinforce learning.
- Concept Mapping: Creating visual representations of concepts and their relationships.
- Collaborative Learning: Participating in group discussions and study sessions.
3.2. Self-Observation Techniques
Self-observation involves reflecting on your actions and their effectiveness. Key techniques include:
- Journaling: Keeping a learning journal to track progress and reflect on study habits.
- Time Tracking: Monitoring how time is spent on different tasks to identify inefficiencies.
- Self-Questioning: Asking yourself questions about your understanding and engagement with the material.
3.3. Overcoming Obstacles and Challenges
Obstacles are inevitable in the learning process. Planning for potential challenges can help mitigate their impact. Strategies include:
- Identifying Potential Obstacles: Anticipating challenges such as distractions, lack of resources, or difficult concepts.
- Developing Contingency Plans: Creating backup plans to address potential obstacles.
- Seeking Support: Reaching out to teachers, peers, or mentors for help when needed.
3.4. Monitoring Progress and Making Adjustments
Regularly monitoring progress is essential for staying on track. This involves:
- Tracking Intermediate Goals: Monitoring progress towards sub-goals and adjusting strategies as needed.
- Seeking Feedback: Actively seeking feedback from instructors or peers to identify areas for improvement.
- Adapting Strategies: Being flexible and willing to adjust learning strategies based on feedback and progress.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Implementing Strategies | Actively engaging with chosen learning techniques such as active reading, practice testing, and concept mapping. |
| Self-Observation | Reflecting on actions and their effectiveness through journaling, time tracking, and self-questioning. |
| Overcoming Obstacles | Planning for potential challenges by identifying obstacles, developing contingency plans, and seeking support. |
| Monitoring Progress | Regularly tracking progress towards intermediate goals, seeking feedback, and adapting strategies based on progress and feedback. |
| Example | While studying, if distracted, try studying in a quiet space. If struggling with a concept, revisit the material, ask for help from a friend, or contact your professor. For additional resources and personalized learning strategies, visit LEARNS.EDU.VN. Reach out to us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States or Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212 for assistance. |
4. The Self-Reflection Phase: Evaluating Performance and Outcomes
The self-reflection phase is the final step in the self-regulated learning cycle, focusing on evaluating performance and outcomes. This phase involves reflecting on the effectiveness of the strategies used, analyzing the results, and planning for future learning tasks. It is a critical step for continuous improvement and enhancing self-regulated learning skills.
4.1. Evaluating Performance and Results
Evaluating performance involves comparing the actual results with the initial goals. Key steps include:
- Comparing Outcomes: Assessing whether the desired outcomes were achieved.
- Analyzing Performance: Identifying strengths and weaknesses in the learning process.
- Seeking External Feedback: Gathering feedback from instructors, peers, or mentors to gain additional insights.
4.2. Reflecting on the Effectiveness of Strategies
Reflecting on the strategies used helps in understanding what worked well and what didn’t. Consider the following:
- Assessing Strategy Appropriateness: Evaluating whether the chosen strategies were suitable for the task.
- Analyzing Implementation: Examining how the strategies were implemented and identifying areas for improvement.
- Identifying Key Factors: Determining which factors contributed to the success or failure of the strategies.
4.3. Attributing Outcomes to Effort and Strategy
Attributing outcomes to effort and strategy helps in developing a growth mindset. Key principles include:
- Focusing on Controllable Factors: Attributing success or failure to factors that can be controlled, such as effort, strategy, and time management.
- Avoiding Fixed Mindsets: Avoiding attributing outcomes to fixed traits, such as intelligence or ability.
- Encouraging a Growth Mindset: Believing that abilities can be developed through dedication and hard work.
4.4. Planning for Future Learning Tasks
Planning for future learning tasks involves using the insights gained from the self-reflection phase to improve future learning experiences. This includes:
- Adjusting Goals: Modifying goals based on previous outcomes and experiences.
- Refining Strategies: Selecting and implementing more effective strategies for future tasks.
- Improving Time Management: Optimizing time management skills to enhance efficiency.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Evaluating Performance | Comparing actual results with initial goals, analyzing performance, and seeking external feedback. |
| Reflecting on Strategies | Assessing the appropriateness of strategies, analyzing implementation, and identifying key factors contributing to success or failure. |
| Attributing Outcomes | Focusing on controllable factors such as effort and strategy, avoiding fixed mindsets, and encouraging a growth mindset. |
| Planning for Future Tasks | Adjusting goals, refining strategies, and improving time management based on insights gained from the self-reflection phase. |
| Example | After a test, review your performance and identify any areas where you need to improve. Adjust your study habits accordingly. For expert guidance and resources, explore LEARNS.EDU.VN. Contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States or Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212 for assistance. |
5. Practical Strategies for Enhancing Self-Regulated Learning
Enhancing self-regulated learning involves implementing practical strategies that can be integrated into daily study habits. These strategies help learners take control of their learning process, improve their academic performance, and develop lifelong learning skills.
5.1. Time Management Techniques
Effective time management is crucial for self-regulated learning. Techniques include:
- Creating a Study Schedule: Developing a structured schedule that allocates specific times for studying, breaks, and other activities.
- Prioritizing Tasks: Identifying and prioritizing the most important tasks to focus on.
- Using Time Management Tools: Utilizing tools such as calendars, planners, and apps to track and manage time effectively.
5.2. Effective Note-Taking Methods
Effective note-taking can enhance understanding and retention of information. Methods include:
- Cornell Method: Dividing notes into cues, notes, and summary sections for better organization.
- Mind Mapping: Creating visual representations of concepts and their relationships.
- Active Listening: Focusing on key points and summarizing information in your own words.
5.3. Creating a Conducive Study Environment
A conducive study environment can significantly impact learning outcomes. Factors to consider include:
- Minimizing Distractions: Choosing a quiet and comfortable study space free from distractions.
- Optimizing Lighting and Temperature: Ensuring adequate lighting and a comfortable temperature to enhance focus.
- Organizing Study Materials: Keeping study materials organized and easily accessible.
5.4. Utilizing Learning Resources and Tools
Utilizing available learning resources and tools can enhance the learning experience. These include:
- Online Resources: Accessing online articles, videos, and tutorials to supplement learning.
- Library Resources: Utilizing library resources such as books, journals, and databases for research.
- Educational Apps: Using educational apps to enhance learning and track progress.
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Time Management | Creating a study schedule, prioritizing tasks, and using time management tools such as calendars and apps. |
| Note-Taking | Employing effective note-taking methods such as the Cornell Method, mind mapping, and active listening. |
| Study Environment | Creating a conducive study environment by minimizing distractions, optimizing lighting and temperature, and organizing study materials. |
| Learning Resources | Utilizing online resources, library materials, and educational apps to enhance learning and track progress. |
| Example | To effectively manage your time, create a study schedule and set clear goals for each study session. Minimize distractions by studying in a quiet environment. Utilize online resources and educational apps to support your learning. For more strategies and personalized support, visit LEARNS.EDU.VN. Contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States or Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212 for assistance. |
6. Self-Regulated Learning in Different Learning Environments
Self-regulated learning is adaptable to various learning environments, including traditional classrooms, online courses, and self-directed study. Understanding how to apply SRL in each of these settings can significantly enhance the learning experience.
6.1. Traditional Classroom Settings
In traditional classroom settings, SRL involves:
- Active Participation: Engaging actively in class discussions and activities.
- Note-Taking: Taking effective notes and reviewing them regularly.
- Seeking Clarification: Asking questions and seeking clarification on unclear concepts.
- Utilizing Office Hours: Attending office hours to get additional help and support from the instructor.
6.2. Online Learning Environments
In online learning environments, SRL requires:
- Time Management: Managing time effectively to complete assignments and stay on track.
- Self-Discipline: Maintaining self-discipline to stay focused and motivated.
- Utilizing Online Resources: Taking advantage of online resources such as discussion forums, virtual office hours, and online tutorials.
- Seeking Technical Support: Seeking technical support when encountering technical issues.
6.3. Self-Directed Learning
In self-directed learning, SRL is essential for:
- Setting Learning Goals: Defining clear learning goals and objectives.
- Selecting Learning Resources: Choosing appropriate learning resources and materials.
- Monitoring Progress: Tracking progress and making adjustments as needed.
- Evaluating Outcomes: Evaluating learning outcomes and reflecting on the learning process.
| Learning Environment | Self-Regulated Learning Strategies |
|---|---|
| Traditional Classroom | Active participation, effective note-taking, seeking clarification, and utilizing office hours. |
| Online Learning | Time management, self-discipline, utilizing online resources, and seeking technical support. |
| Self-Directed Learning | Setting learning goals, selecting learning resources, monitoring progress, and evaluating outcomes. |
| Example | Adapt your self-regulated learning strategies to suit each environment. Whether you are in a classroom, taking online courses, or learning independently, focus on being proactive and taking responsibility for your learning. Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN for more strategies and resources. Contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States or Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212. |
7. Overcoming Common Challenges in Self-Regulated Learning
While self-regulated learning offers numerous benefits, learners often face challenges that can hinder their progress. Identifying and addressing these challenges is essential for maximizing the effectiveness of SRL strategies.
7.1. Procrastination
Procrastination is a common obstacle in self-regulated learning. Strategies to overcome procrastination include:
- Breaking Down Tasks: Dividing large tasks into smaller, more manageable steps.
- Setting Deadlines: Setting specific deadlines for each task to stay on track.
- Using Time Management Techniques: Employing time management techniques such as the Pomodoro Technique to improve focus.
7.2. Lack of Motivation
Lack of motivation can significantly impact learning outcomes. Strategies to enhance motivation include:
- Setting Meaningful Goals: Setting goals that are personally meaningful and aligned with interests.
- Rewarding Progress: Rewarding yourself for achieving milestones to stay motivated.
- Seeking Support: Seeking support from peers, mentors, or instructors to stay encouraged.
7.3. Difficulty with Self-Assessment
Difficulty with self-assessment can hinder the self-reflection phase of SRL. Strategies to improve self-assessment skills include:
- Seeking External Feedback: Actively seeking feedback from instructors, peers, or mentors.
- Using Rubrics: Utilizing rubrics or assessment criteria to evaluate performance objectively.
- Reflecting on Past Experiences: Reflecting on past learning experiences to identify areas for improvement.
7.4. Managing Distractions
Managing distractions is crucial for maintaining focus and concentration. Strategies to minimize distractions include:
- Creating a Quiet Study Environment: Choosing a quiet and comfortable study space free from distractions.
- Using Technology Wisely: Utilizing technology tools to block distracting websites and apps.
- Taking Breaks: Taking regular breaks to refresh your mind and avoid burnout.
| Challenge | Strategies to Overcome |
|---|---|
| Procrastination | Breaking down tasks, setting deadlines, and using time management techniques like the Pomodoro Technique. |
| Lack of Motivation | Setting meaningful goals, rewarding progress, and seeking support from peers, mentors, or instructors. |
| Difficulty with Self-Assessment | Seeking external feedback, using rubrics, and reflecting on past experiences. |
| Managing Distractions | Creating a quiet study environment, using technology wisely to block distractions, and taking regular breaks. |
| Example | Recognize the challenges and implement these strategies to overcome them. Whether you’re struggling with procrastination, lack of motivation, or managing distractions, consistent effort and the right approach can enhance your self-regulated learning skills. Explore LEARNS.EDU.VN for more tips and resources. Contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States or Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212. |
8. The Role of Educators in Fostering Self-Regulated Learning
Educators play a crucial role in fostering self-regulated learning among students. By implementing strategies that promote SRL, educators can empower students to take ownership of their learning and achieve academic success.
8.1. Creating a Supportive Learning Environment
Creating a supportive learning environment involves:
- Providing Clear Expectations: Communicating clear expectations and learning objectives.
- Offering Constructive Feedback: Providing constructive feedback that helps students understand their strengths and weaknesses.
- Encouraging Collaboration: Encouraging collaboration and peer support among students.
8.2. Teaching Self-Regulated Learning Strategies
Educators can teach SRL strategies by:
- Explicit Instruction: Providing explicit instruction on SRL strategies such as goal setting, time management, and self-assessment.
- Modeling: Modeling SRL behaviors and strategies in their own teaching practices.
- Providing Opportunities for Practice: Providing opportunities for students to practice SRL strategies in various learning tasks.
8.3. Providing Feedback and Support
Providing feedback and support involves:
- Offering Timely Feedback: Providing timely feedback that helps students monitor their progress and make adjustments.
- Providing Individualized Support: Offering individualized support based on students’ needs and learning styles.
- Encouraging Self-Reflection: Encouraging students to reflect on their learning experiences and identify areas for improvement.
8.4. Assessing Self-Regulated Learning Skills
Assessing SRL skills involves:
- Using Self-Assessment Tools: Utilizing self-assessment tools such as questionnaires and rubrics to assess students’ SRL skills.
- Observing Student Behavior: Observing students’ behavior and strategies during learning tasks.
- Collecting Student Work Samples: Collecting student work samples to evaluate their application of SRL strategies.
| Role of Educators | Strategies |
|---|---|
| Creating a Supportive Environment | Providing clear expectations, offering constructive feedback, and encouraging collaboration. |
| Teaching SRL Strategies | Providing explicit instruction, modeling SRL behaviors, and providing opportunities for practice. |
| Providing Feedback and Support | Offering timely feedback, providing individualized support, and encouraging self-reflection. |
| Assessing SRL Skills | Using self-assessment tools, observing student behavior, and collecting student work samples. |
| Example | Educators can empower students by creating a supportive learning environment and teaching self-regulated learning strategies. Providing feedback and assessing SRL skills helps students take ownership of their learning journey. Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN for educational resources. Contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States or Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212. |
9. The Benefits of Self-Regulated Learning for Lifelong Learning
Self-regulated learning is not only beneficial for academic success but also crucial for lifelong learning. By developing SRL skills, individuals can adapt to new challenges, acquire new knowledge, and continuously improve their abilities throughout their lives.
9.1. Adaptability to Change
SRL promotes adaptability to change by:
- Developing Problem-Solving Skills: Enhancing problem-solving skills that enable individuals to address new challenges effectively.
- Fostering a Growth Mindset: Encouraging a growth mindset that embraces learning and improvement.
- Promoting Flexibility: Promoting flexibility in learning strategies and approaches.
9.2. Continuous Improvement
SRL supports continuous improvement by:
- Encouraging Self-Reflection: Encouraging self-reflection to identify areas for improvement.
- Promoting Goal Setting: Promoting goal setting to guide learning and development.
- Fostering a Learning Orientation: Fostering a learning orientation that values continuous growth and development.
9.3. Enhanced Problem-Solving Skills
SRL enhances problem-solving skills by:
- Encouraging Critical Thinking: Encouraging critical thinking and analysis to identify and address problems effectively.
- Promoting Creativity: Promoting creativity and innovation in problem-solving approaches.
- Fostering Resilience: Fostering resilience in the face of challenges and setbacks.
9.4. Increased Self-Efficacy
SRL increases self-efficacy by:
- Promoting Self-Confidence: Promoting self-confidence in one’s ability to learn and achieve goals.
- Fostering a Sense of Control: Fostering a sense of control over the learning process.
- Encouraging Persistence: Encouraging persistence in the face of challenges and obstacles.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Adaptability to Change | Developing problem-solving skills, fostering a growth mindset, and promoting flexibility. |
| Continuous Improvement | Encouraging self-reflection, promoting goal setting, and fostering a learning orientation. |
| Enhanced Problem-Solving | Encouraging critical thinking, promoting creativity, and fostering resilience. |
| Increased Self-Efficacy | Promoting self-confidence, fostering a sense of control, and encouraging persistence. |
| Example | Embrace self-regulated learning to enhance your ability to adapt, improve, and solve problems. Increased self-efficacy leads to greater confidence and persistence in lifelong learning. Explore LEARNS.EDU.VN for lifelong learning resources. Contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States or Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212. |
10. Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Self-Regulated Learning
Examining case studies of successful SRL implementation can provide valuable insights and inspiration for educators and learners alike. These examples demonstrate how SRL strategies can be effectively applied in various settings to enhance learning outcomes.
10.1. Case Study 1: Enhancing Academic Performance in College Students
A study at a large university implemented SRL strategies among undergraduate students. The results showed:
- Improved Grades: Students who used SRL strategies had significantly higher grades compared to those who did not.
- Increased Motivation: Students reported increased motivation and engagement in their studies.
- Better Time Management: Students demonstrated improved time management skills and study habits.
10.2. Case Study 2: Promoting Self-Directed Learning in Online Courses
An online learning platform implemented SRL strategies to promote self-directed learning. The findings included:
- Higher Completion Rates: Students who used SRL strategies had higher completion rates in online courses.
- Increased Engagement: Students showed increased engagement in online discussions and activities.
- Improved Self-Assessment: Students demonstrated improved self-assessment skills and learning outcomes.
10.3. Case Study 3: Fostering Lifelong Learning in Professional Development
A professional development program incorporated SRL strategies to foster lifelong learning among participants. The outcomes revealed:
- Enhanced Skill Development: Participants demonstrated enhanced skill development and knowledge acquisition.
- Increased Self-Efficacy: Participants reported increased self-efficacy and confidence in their abilities.
- Better Career Advancement: Participants experienced better career advancement opportunities.
| Case Study | Results |
|---|---|
| Enhancing Academic Performance in College Students | Improved grades, increased motivation, and better time management. |
| Promoting Self-Directed Learning in Online Courses | Higher completion rates, increased engagement, and improved self-assessment. |
| Fostering Lifelong Learning in Professional Development | Enhanced skill development, increased self-efficacy, and better career advancement. |
| Example | These case studies illustrate the effectiveness of self-regulated learning strategies in various contexts. Implement SRL in your own learning journey and experience the benefits firsthand. Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN for more information. Contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States or Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212. |
Ready to take control of your learning journey? Explore the comprehensive resources and courses at learns.edu.vn to master self-regulated learning skills. Contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States, or reach out via WhatsApp at +1 555-555-1212. Start your path to academic and professional success today!
FAQ About Self-Regulated Learning
1. What is self-regulated learning?
Self-regulated learning (SRL) is a proactive process where learners take control of their learning by setting goals, selecting strategies, monitoring progress, and reflecting on outcomes.
2. Why is self-regulated learning important?
SRL enhances academic performance, increases motivation, develops lifelong learning skills, and boosts self-efficacy.
3. What are the key components of self-regulated learning?
Key components include goal setting, strategy selection, self-monitoring, self-evaluation, and self-efficacy.
4. What are the phases of the self-regulated learning cycle?
The phases are forethought (planning), performance (implementation), and self-reflection (evaluation).
5. How can I improve my time management skills for self-regulated learning?
Create a study schedule, prioritize tasks, and use time management tools like calendars and apps.
6. What are effective note-taking methods for self-regulated learning?
Use the Cornell Method, mind mapping, and active listening to take effective notes.
7. How can I create a conducive study environment?
Minimize distractions, optimize lighting and temperature, and organize study materials.
8. What are some common challenges in self-regulated learning?
Common challenges include procrastination, lack of motivation, difficulty with self-assessment, and managing distractions.
9. How can educators foster self-regulated learning among students?
Educators can create a supportive learning environment, teach SRL strategies, provide feedback and support, and assess SRL skills.
10. What are the benefits of self-regulated learning for lifelong learning?
SRL promotes adaptability to change, continuous improvement, enhanced problem-solving skills, and increased self-efficacy, making it essential for lifelong learning.