The value of learning the four levels of the Kirkpatrick Model lies in its ability to provide a comprehensive evaluation of training programs, and at LEARNS.EDU.VN, we help you master this framework. By understanding the reaction, learning, behavior, and results, organizations can justify costs, improve programs, and ensure training aligns with business goals. Unlock the full potential of your training initiatives with in-depth knowledge and skills development, and discover effective training strategies, performance improvement techniques, and business outcome analysis on LEARNS.EDU.VN.
1. Understanding the Kirkpatrick Model
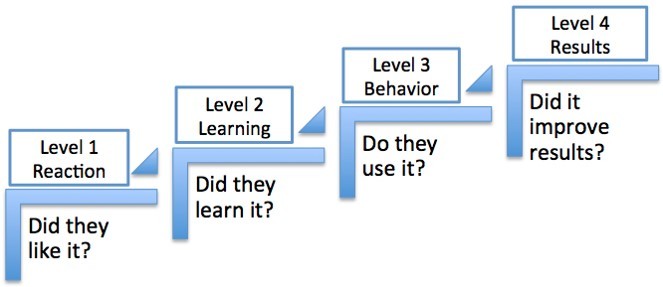
The Kirkpatrick Model, a cornerstone of training evaluation, offers a structured approach to assessing the effectiveness of training programs. Developed by Donald Kirkpatrick in 1959 and refined over the years, this model provides a four-level framework for evaluating training initiatives. Each level focuses on a different aspect of the training, from initial reactions to tangible business results. Let’s explore what each level entails:
-
Level 1: Reaction
This level gauges the immediate response of participants to the training. It seeks to answer the question: Did the learners like the training? Assessments often involve feedback forms or “happy sheets” distributed at the end of a program. While easy to collect, this data provides limited insight into actual learning or behavioral changes.
-
Level 2: Learning
Focusing on knowledge transfer, Level 2 assesses how much the participants learned from the training. This is typically measured through pre- and post-tests. In e-learning environments, multiple-choice questions tracked by a Learning Management System (LMS) are commonly used.
-
Level 3: Behavior
This level evaluates whether the training led to changes in the participants’ on-the-job behavior. Evaluators look for evidence that learners are applying new knowledge and skills in their daily tasks. Data collection often involves surveying supervisors and colleagues to observe changes in performance.
-
Level 4: Results
Level 4 examines the tangible outcomes of the training on business performance. This might include improvements in productivity, sales, employee retention, or customer satisfaction. While it offers the most valuable insights, linking training directly to specific business results can be challenging due to various influencing factors.
 Kirkpatrick model levels
Kirkpatrick model levels
Understanding each level of the Kirkpatrick Model is essential for a comprehensive training evaluation strategy. It helps organizations to justify the costs of training, determine the effectiveness of their programs, and continuously improve future training initiatives.
2. The Significance of Reaction (Level 1)
Level 1 of the Kirkpatrick Model focuses on the immediate reactions of learners to the training program. While often dismissed as superficial, gauging learner reaction is a crucial initial step. It involves gathering feedback on various aspects of the training, such as the facilitator’s delivery, the venue, and the overall learning environment.
Why Measure Reaction?
- Immediate Feedback: Provides quick insights into what learners liked or disliked about the training.
- Identifies Issues: Highlights potential problems with the program content, delivery, or logistics.
- Enhances Engagement: Positive reactions can boost learner morale and encourage active participation.
Methods for Measuring Reaction
- Feedback Forms: Distribute questionnaires at the end of the training session.
- Verbal Feedback: Encourage learners to share their thoughts and suggestions openly.
- Online Surveys: Use digital platforms to collect feedback efficiently.
Example Questions for Level 1 Evaluation
- Did you find the training content relevant to your job?
- Was the facilitator knowledgeable and engaging?
- Was the venue comfortable and conducive to learning?
- Did the training meet your expectations?
- Would you recommend this training to others?
Measuring reaction helps training managers identify areas for improvement and ensure that future training programs are well-received. However, it is essential to remember that positive reactions do not guarantee learning or behavioral changes. As such, Level 1 evaluation should be complemented by assessments at higher levels to provide a more comprehensive picture of training effectiveness. For more in-depth resources and tools, visit LEARNS.EDU.VN.
3. Deep Dive into Learning (Level 2)
Level 2 of the Kirkpatrick Model delves into the extent to which participants have acquired the intended knowledge and skills from the training program. This level is critical for determining whether the training objectives have been met and whether learners have absorbed the information presented. Effective measurement at Level 2 ensures that the training content has been successfully transferred to the participants.
Assessing Knowledge and Skills
- Pre- and Post-Tests: Administering tests before and after the training helps to measure the knowledge gained.
- Quizzes: Incorporating quizzes throughout the training reinforces learning and assesses comprehension.
- Practical Exercises: Engaging learners in hands-on activities allows them to apply new skills and demonstrate their abilities.
Tools for Measuring Learning
- Learning Management Systems (LMS): Track learner progress, scores, and engagement.
- Online Assessment Platforms: Utilize platforms with various question types and automated grading.
- Classroom Assessments: Conduct traditional paper-based tests and exercises.
Examples of Level 2 Evaluation Methods
| Method | Description | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre- and Post-Tests | Tests administered before and after training to measure knowledge gain. | Quantifiable results, clear measurement of learning. | May not reflect real-world application, can be stressful for learners. |
| Quizzes | Short assessments during training to reinforce learning. | Immediate feedback, reinforces key concepts. | May disrupt the flow of training, limited depth. |
| Practical Exercises | Hands-on activities to apply learned skills. | Demonstrates practical application, enhances engagement. | Can be time-consuming, requires resources and careful planning. |
| LMS Tracking | Monitoring learner progress and scores on a learning management system. | Comprehensive data, automated tracking, personalized learning paths. | Requires investment in LMS, depends on the quality of the LMS content. |
| Online Assessments | Using online platforms for tests and quizzes. | Efficient, automated grading, various question types. | Requires internet access, may lack personal interaction. |
| Classroom Assessments | Traditional tests and exercises conducted in a classroom setting. | Direct interaction, immediate feedback. | Time-consuming, requires manual grading. |
Level 2 evaluation provides valuable data on the effectiveness of the training content and delivery methods. By thoroughly assessing what learners have gained, organizations can make informed decisions about program improvements and future training initiatives. Discover more strategies and tools for effective learning assessment at LEARNS.EDU.VN.
4. Analyzing Behavior (Level 3)
Level 3 of the Kirkpatrick Model focuses on evaluating whether the training has led to changes in the learners’ behavior on the job. This level goes beyond knowledge acquisition and assesses if participants are applying what they have learned in their daily tasks. Measuring behavioral changes provides valuable insights into the practical impact of the training program.
Key Aspects of Behavior Evaluation
- Application of Knowledge: Are learners using the new information and skills in their work?
- Performance Improvement: Has the training resulted in improved job performance?
- Consistency: Are the behavioral changes consistent over time?
Methods for Measuring Behavior
- Observation: Directly observe learners in their work environment to assess behavioral changes.
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Gather feedback from learners, supervisors, and colleagues.
- Performance Reviews: Review performance metrics to identify improvements related to the training.
Challenges in Measuring Behavior
- Attribution: Determining whether behavioral changes are solely due to the training.
- Time Lag: Changes in behavior may take time to manifest.
- Subjectivity: Assessments can be influenced by personal biases.
Strategies for Effective Behavior Evaluation
| Strategy | Description | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| 360-Degree Feedback | Gather feedback from multiple sources (learners, supervisors, colleagues). | Provides a comprehensive view of behavioral changes, reduces bias. | Can be time-consuming, requires careful coordination. |
| Performance Monitoring | Track key performance indicators (KPIs) before and after the training. | Quantifiable data, clear measurement of performance improvements. | Difficult to attribute changes solely to the training. |
| Follow-Up Interviews | Conduct interviews with learners to discuss their experiences and challenges in applying new skills. | Provides qualitative insights, identifies barriers to behavior change. | Subjective, requires skilled interviewers. |
| On-the-Job Observation | Observe learners in their work environment to assess behavioral changes directly. | Provides firsthand evidence of behavioral changes, realistic assessment. | Can be intrusive, requires trained observers. |
| Action Plans and Goal Setting | Encourage learners to create action plans and set goals for applying new skills. | Enhances accountability, promotes behavior change. | Requires follow-up and support. |
Evaluating behavior effectively requires a combination of methods and a clear understanding of the challenges involved. By implementing these strategies, organizations can gain valuable insights into the real-world impact of their training programs. Find additional resources and best practices for behavior evaluation at LEARNS.EDU.VN.
5. Assessing Results (Level 4)
Level 4 of the Kirkpatrick Model assesses the tangible business results achieved as a direct consequence of the training program. This level provides the most compelling evidence of training effectiveness by linking it to organizational goals. Evaluating results helps organizations determine the return on investment (ROI) of their training initiatives.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Level 4
- Increased Productivity: Measure improvements in output, efficiency, and quality.
- Higher Sales: Track revenue growth and sales performance.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: Monitor customer feedback, retention, and loyalty.
- Reduced Costs: Identify cost savings through process improvements and waste reduction.
- Employee Retention: Assess employee turnover and retention rates.
Methods for Measuring Results
- Financial Analysis: Calculate the financial benefits of the training program.
- Statistical Analysis: Use data to identify correlations between training and business outcomes.
- Case Studies: Document specific examples of how training has led to positive results.
Challenges in Measuring Results
- Attribution: Isolating the impact of training from other factors influencing business results.
- Time Frame: Results may take time to materialize.
- Data Availability: Accessing accurate and relevant data can be difficult.
Strategies for Effective Results Evaluation
| Strategy | Description | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Establish Clear Objectives | Define specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives for the training program. | Provides a clear focus for the evaluation, ensures alignment with business goals. | Requires careful planning and analysis. |
| Use Control Groups | Compare the results of trained employees with a control group that did not receive the training. | Helps to isolate the impact of the training program. | Can be difficult to implement, may not be feasible in all situations. |
| Calculate Return on Investment (ROI) | Measure the financial benefits of the training program against the costs. | Provides a clear indication of the financial value of the training. | Requires accurate data and analysis. |
| Conduct Longitudinal Studies | Track the results over an extended period to assess the long-term impact of the training program. | Provides a more comprehensive understanding of the training’s effectiveness. | Time-consuming, requires ongoing data collection and analysis. |
| Integrate with Business Intelligence (BI) Tools | Use BI tools to analyze data from multiple sources and identify correlations between training and business outcomes. | Provides a more holistic view of the training’s impact, enables data-driven decision-making. | Requires investment in BI tools and expertise. |
By implementing these strategies, organizations can effectively measure the results of their training programs and demonstrate their value. Discover more insights and tools for results evaluation at LEARNS.EDU.VN.
6. Benefits of Mastering All Four Levels
Mastering all four levels of the Kirkpatrick Model provides organizations with a comprehensive and holistic approach to training evaluation. This mastery not only ensures that training programs are effective but also aligns them strategically with the overall business goals. Understanding the benefits of each level and how they interconnect is crucial for maximizing the impact of training initiatives.
Comprehensive Evaluation
By assessing reaction, learning, behavior, and results, organizations gain a complete picture of the training program’s effectiveness. This comprehensive evaluation helps identify strengths and weaknesses, enabling continuous improvement.
Strategic Alignment
Mastering all four levels ensures that training programs are aligned with the organization’s strategic goals. By linking training outcomes to business results, organizations can demonstrate the value of their investment in employee development.
Data-Driven Decision-Making
The data collected at each level provides valuable insights for decision-making. Organizations can use this information to optimize training content, delivery methods, and evaluation strategies.
Improved ROI
By measuring the impact of training on business results, organizations can calculate the return on investment (ROI) of their training initiatives. This helps justify training expenses and secure funding for future programs.
Enhanced Accountability
Mastering all four levels promotes accountability at all stages of the training process. From instructional designers to trainers and learners, everyone is responsible for achieving the desired outcomes.
Benefits of Mastering Each Level
| Level | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Reaction | Provides immediate feedback for improving the training experience. |
| Learning | Assesses knowledge and skill acquisition, ensuring that training objectives are met. |
| Behavior | Evaluates the application of learned skills on the job, demonstrating practical impact. |
| Results | Measures the tangible business outcomes of training, justifying the investment. |
Mastering all four levels of the Kirkpatrick Model empowers organizations to create training programs that are not only engaging and informative but also aligned with business objectives and deliver measurable results. Enhance your expertise in training evaluation and strategic alignment with resources available at LEARNS.EDU.VN.
7. Real-World Applications and Case Studies
The Kirkpatrick Model is not just a theoretical framework; it has practical applications across various industries and organizations. Examining real-world case studies can provide valuable insights into how the model can be effectively implemented to enhance training programs and achieve tangible business results.
Case Study 1: Healthcare Industry
A large hospital implemented a training program to improve patient care and reduce medical errors. Using the Kirkpatrick Model, they evaluated the program at all four levels:
- Reaction: Participants reported high satisfaction with the training content and delivery.
- Learning: Post-training assessments showed a significant improvement in knowledge of patient safety protocols.
- Behavior: Observations indicated that healthcare professionals were consistently applying new protocols in their daily tasks.
- Results: The hospital saw a reduction in medical errors and an improvement in patient satisfaction scores.
Case Study 2: Technology Company
A tech company launched a training program to enhance the sales skills of its employees. The evaluation process included:
- Reaction: Sales representatives appreciated the interactive nature of the training and the practical tips provided.
- Learning: Sales simulations and quizzes demonstrated that participants had acquired new sales techniques.
- Behavior: Sales managers observed that employees were using the new techniques in their interactions with customers.
- Results: The company experienced a significant increase in sales revenue and customer retention rates.
Case Study 3: Manufacturing Sector
A manufacturing company implemented a training program to improve the efficiency of its production processes. The evaluation involved:
- Reaction: Employees found the training relevant to their jobs and appreciated the opportunity to learn new skills.
- Learning: Assessments showed that participants had gained a better understanding of lean manufacturing principles.
- Behavior: Observations indicated that employees were implementing lean techniques in their daily tasks.
- Results: The company experienced a reduction in production costs and an improvement in product quality.
Key Takeaways from Case Studies
- Comprehensive Evaluation: Evaluating training at all four levels provides a holistic view of its effectiveness.
- Strategic Alignment: Aligning training objectives with business goals is crucial for achieving tangible results.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: Using data to inform decisions about training content, delivery methods, and evaluation strategies.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly evaluating training programs and making adjustments based on feedback and results.
These real-world examples demonstrate the value of the Kirkpatrick Model in enhancing training programs and achieving tangible business results. Discover more case studies and practical insights at LEARNS.EDU.VN.
8. Common Pitfalls to Avoid in Kirkpatrick’s Model Implementation
While the Kirkpatrick Model provides a robust framework for training evaluation, organizations often encounter pitfalls that can undermine its effectiveness. Recognizing and avoiding these common mistakes is crucial for ensuring accurate and meaningful evaluation results.
Focusing Solely on Level 1 (Reaction)
Many organizations limit their evaluation efforts to Level 1, collecting feedback on learner satisfaction without measuring actual learning or behavioral changes. This provides a superficial understanding of training effectiveness.
Neglecting Level 3 (Behavior) and Level 4 (Results)
Skipping Levels 3 and 4 deprives organizations of valuable insights into the practical impact of training on job performance and business outcomes. This can lead to misguided decisions about training investments.
Failing to Establish Clear Objectives
Without clear and measurable objectives, it is difficult to assess whether the training program has achieved its intended goals. Objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
Inadequate Data Collection
Poor data collection methods can result in inaccurate or incomplete evaluation results. Organizations should use a variety of data collection techniques and ensure that data is collected consistently.
Lack of Follow-Up
Failing to follow up with learners and stakeholders after the training program can limit the ability to assess long-term behavioral changes and business results.
Overlooking External Factors
External factors, such as changes in the market or organizational structure, can influence training outcomes. Organizations should consider these factors when interpreting evaluation results.
Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
| Pitfall | How to Avoid |
|---|---|
| Focusing solely on Level 1 | Implement evaluation methods at all four levels of the Kirkpatrick Model. |
| Neglecting Levels 3 and 4 | Allocate resources for measuring behavioral changes and business results. |
| Failing to establish clear objectives | Define SMART objectives for each training program. |
| Inadequate data collection | Use a variety of data collection techniques and ensure data accuracy. |
| Lack of follow-up | Implement follow-up surveys and interviews to assess long-term impact. |
| Overlooking external factors | Consider external factors when interpreting evaluation results. |
By avoiding these common pitfalls, organizations can ensure that their training evaluations are accurate, meaningful, and contribute to continuous improvement. Enhance your training evaluation strategies and avoid common mistakes with resources available at LEARNS.EDU.VN.
9. Future Trends in Training Evaluation
As technology advances and the learning landscape evolves, training evaluation is also undergoing significant changes. Staying abreast of these future trends is essential for organizations looking to optimize their training programs and achieve maximum impact.
AI-Powered Evaluation
Artificial intelligence (AI) is being used to automate and enhance various aspects of training evaluation. AI-powered tools can analyze learner data, provide personalized feedback, and predict training outcomes.
Learning Analytics
Learning analytics involves the collection and analysis of data related to learner behavior and performance. This data can be used to identify patterns, personalize learning experiences, and measure the effectiveness of training programs.
Microlearning Evaluation
With the rise of microlearning, new evaluation methods are needed to assess the impact of short, focused learning modules. This may involve measuring knowledge retention, skill application, and learner engagement.
Gamification and Simulation
Gamification and simulation are increasingly being used in training programs to enhance engagement and provide realistic learning experiences. Evaluation methods should assess the effectiveness of these techniques in achieving learning objectives.
Personalized Learning Paths
Personalized learning paths tailor training content and delivery methods to individual learner needs and preferences. Evaluation methods should assess the effectiveness of personalized learning in improving learner outcomes.
Future Trends in Training Evaluation
| Trend | Description | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI-Powered Evaluation | Using artificial intelligence to automate and enhance training evaluation processes. | Improved efficiency, personalized feedback, predictive analytics. | Data privacy concerns, bias in algorithms, need for skilled data scientists. |
| Learning Analytics | Collecting and analyzing data related to learner behavior and performance. | Data-driven decision-making, personalized learning experiences, improved learner outcomes. | Data security concerns, need for data analysis skills, ethical considerations. |
| Microlearning Evaluation | Assessing the impact of short, focused learning modules. | Improved knowledge retention, skill application, learner engagement. | Difficulty in measuring long-term impact, need for creative evaluation methods. |
| Gamification and Simulation | Using game-like elements and realistic simulations in training programs. | Enhanced engagement, improved knowledge retention, realistic learning experiences. | Difficulty in measuring learning outcomes, need for careful design and implementation. |
| Personalized Learning Paths | Tailoring training content and delivery methods to individual learner needs and preferences. | Improved learner outcomes, increased engagement, personalized learning experiences. | Difficulty in scaling, need for adaptive learning platforms, data privacy concerns. |
By embracing these future trends, organizations can create more effective and impactful training programs. Stay ahead of the curve with the latest insights and tools for training evaluation at LEARNS.EDU.VN.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the Kirkpatrick Model?
The Kirkpatrick Model is a four-level framework for evaluating the effectiveness of training programs, focusing on reaction, learning, behavior, and results.
Why is training evaluation important?
Training evaluation helps organizations justify costs, improve programs, and ensure alignment with business goals.
What are the four levels of the Kirkpatrick Model?
The four levels are Reaction, Learning, Behavior, and Results.
How do you measure reaction (Level 1)?
Reaction is typically measured using feedback forms and surveys to assess learner satisfaction.
How do you measure learning (Level 2)?
Learning is measured using pre- and post-tests, quizzes, and practical exercises to assess knowledge gain.
How do you measure behavior (Level 3)?
Behavior is measured through observation, surveys, and performance reviews to assess changes in on-the-job performance.
How do you measure results (Level 4)?
Results are measured using financial analysis, statistical analysis, and case studies to assess the impact on business outcomes.
What are some common pitfalls in implementing the Kirkpatrick Model?
Common pitfalls include focusing solely on Level 1, neglecting Levels 3 and 4, and failing to establish clear objectives.
How can AI enhance training evaluation?
AI can automate data analysis, provide personalized feedback, and predict training outcomes.
Where can I learn more about the Kirkpatrick Model and training evaluation?
You can find more information and resources at LEARNS.EDU.VN, including detailed guides, case studies, and expert insights.
By addressing these frequently asked questions, organizations can gain a better understanding of the Kirkpatrick Model and its applications in training evaluation. For more detailed information and expert guidance, visit LEARNS.EDU.VN.
Learning the four levels of the Kirkpatrick Model equips you with the tools to transform your training programs. Ready to take the next step? Visit learns.edu.vn today to explore our comprehensive resources and unlock the full potential of your learning initiatives. Contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States or WhatsApp: +1 555-555-1212.