Lifelong learning and developing skills are essential for both personal and professional fulfillment. This core domain is about continuous growth, offering tools for adapting to change and achieving success, and at LEARNS.EDU.VN, we will guide you through the process. Dive into strategies, benefits, and real-world examples that highlight the profound impact of ongoing education. Discover the power of perpetual learning and skill enhancement.
1. Understanding the Core Domain of Lifelong Learning
Which Core Domain Includes Lifelong Learning And Developing Skills? Lifelong learning is best described as a continuous, self-motivated, and voluntary pursuit of knowledge for either personal or professional reasons. This core domain emphasizes that education is not limited to the classroom but is a continuous journey of acquiring knowledge, skills, and competencies throughout life. It encompasses various aspects of personal and professional growth, adaptability, and continuous improvement. It is critical to understand this fundamental aspect of lifelong learning to maximize the benefits and remain competitive in today’s rapidly changing world.
1.1. Defining Lifelong Learning
Lifelong learning can be defined as the ongoing, voluntary, and self-motivated pursuit of knowledge for either personal or professional reasons. It is a continuous process that extends beyond formal education and encompasses a wide range of learning experiences. According to a UNESCO report, lifelong learning is “learning that is pursued throughout life with the aim of improving knowledge, skills, and competence within a personal, civic, social, and/or employment-related perspective.” This definition underscores the importance of lifelong learning in various aspects of life.
1.2. The Significance of Skill Development
Skill development is the process of acquiring new skills and enhancing existing ones. It is a critical component of lifelong learning, enabling individuals to adapt to changing circumstances and excel in various roles. Skills can be broadly classified into two categories: hard skills and soft skills. Hard skills are technical abilities specific to a particular job or industry, while soft skills are interpersonal and communication abilities that are valuable in any context. A study by the World Economic Forum found that skills such as critical thinking, creativity, and emotional intelligence will be increasingly important in the future workforce.
1.3. Core Competencies for Lifelong Learners
Several core competencies are essential for lifelong learners. These include:
- Critical Thinking: Analyzing information objectively and making reasoned judgments.
- Problem-Solving: Identifying and resolving complex issues effectively.
- Communication: Expressing ideas clearly and persuasively, both verbally and in writing.
- Collaboration: Working effectively with others to achieve common goals.
- Adaptability: Adjusting to new situations and challenges with flexibility and resilience.
- Digital Literacy: Using technology effectively to access and manage information.
These competencies enable individuals to navigate the complexities of the modern world and continuously grow and develop.
1.4. The Role of Motivation in Lifelong Learning
Motivation is a key driver of lifelong learning. Intrinsic motivation, which comes from within, is particularly effective in sustaining long-term learning efforts. According to research by Carol Dweck at Stanford University, individuals with a growth mindset, who believe that their abilities can be developed through dedication and hard work, are more likely to embrace lifelong learning. Creating a learning environment that fosters curiosity, provides opportunities for exploration, and celebrates achievement can enhance motivation.
1.5. Contextualizing Lifelong Learning
Lifelong learning is not limited to formal education settings. It occurs in various contexts, including workplaces, communities, and online platforms. Workplace learning involves on-the-job training, mentoring, and professional development programs. Community learning encompasses courses, workshops, and events organized by local organizations. Online learning platforms offer a vast array of resources, including courses, tutorials, and webinars. Recognizing and leveraging these diverse learning contexts can enhance lifelong learning outcomes.
1.6. Benefits of Lifelong Learning
The benefits of lifelong learning are numerous and far-reaching. They include:
- Enhanced Employability: Acquiring new skills and knowledge can improve job prospects and career advancement opportunities.
- Personal Growth: Lifelong learning can expand horizons, foster curiosity, and enhance self-esteem.
- Improved Cognitive Function: Engaging in continuous learning can improve memory, attention, and problem-solving abilities.
- Increased Social Engagement: Learning communities and networks provide opportunities for social interaction and collaboration.
- Greater Adaptability: Lifelong learning fosters resilience and the ability to adapt to changing circumstances.
- Economic Benefits: A skilled and knowledgeable workforce can drive economic growth and innovation.
1.7. Challenges to Lifelong Learning
Despite its many benefits, lifelong learning also faces several challenges. These include:
- Time Constraints: Balancing work, family, and other commitments can make it difficult to find time for learning.
- Financial Barriers: The cost of education and training can be a significant obstacle for some individuals.
- Lack of Access: Access to quality learning resources may be limited in certain geographic areas or for certain demographic groups.
- Motivation and Self-Discipline: Sustaining motivation and self-discipline can be challenging, particularly for self-directed learners.
- Relevance and Quality: Ensuring that learning resources are relevant and of high quality is essential for effective lifelong learning.
1.8. Overcoming Barriers to Lifelong Learning
Several strategies can help overcome the barriers to lifelong learning:
- Time Management: Prioritizing learning and incorporating it into daily routines can help overcome time constraints.
- Financial Assistance: Exploring scholarships, grants, and employer-sponsored training programs can reduce financial barriers.
- Online Learning: Leveraging online learning platforms can provide access to affordable and flexible learning resources.
- Setting Goals: Setting clear and achievable learning goals can enhance motivation and self-discipline.
- Seeking Support: Joining learning communities and networks can provide encouragement and support.
1.9. The Future of Lifelong Learning
The future of lifelong learning is bright, with increasing recognition of its importance and growing availability of learning resources. Technology will continue to play a significant role in shaping the future of learning, with the rise of artificial intelligence, virtual reality, and personalized learning platforms. The focus will shift towards skills-based learning, with an emphasis on acquiring competencies that are relevant to the needs of the workforce. Lifelong learning will become increasingly integrated into all aspects of life, from work and education to personal development and community engagement.
1.10. Discover More at LEARNS.EDU.VN
At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing resources and support to help individuals embark on their lifelong learning journey. Visit our website to explore a wide range of courses, articles, and tools that can enhance your skills and knowledge. Join our community of learners and discover the transformative power of lifelong learning. Address: 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States. Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212.
2. Strategies for Fostering Lifelong Learning
Which core domain includes lifelong learning and developing skills? Fostering a culture of lifelong learning involves a multi-faceted approach that encourages curiosity, provides accessible learning opportunities, values learning, and creates supportive learning communities. This section explores effective strategies for promoting lifelong learning at individual, organizational, and societal levels. The goal is to create an environment where learning is not just an activity but a way of life.
2.1. Cultivating a Growth Mindset
A growth mindset, as defined by Carol Dweck, is the belief that abilities and intelligence can be developed through dedication and hard work. Cultivating a growth mindset is essential for fostering lifelong learning. Individuals with a growth mindset embrace challenges, persist in the face of setbacks, and view effort as a path to mastery. To foster a growth mindset:
- Encourage a Love of Learning: Promote curiosity and exploration by providing opportunities for individuals to pursue their interests.
- Emphasize Effort and Progress: Focus on the process of learning rather than just the outcome. Celebrate effort, persistence, and improvement.
- Provide Constructive Feedback: Offer feedback that is specific, actionable, and focused on growth. Help individuals identify areas for improvement and strategies for overcoming challenges.
- Model Lifelong Learning: Demonstrate a commitment to continuous learning by sharing your own learning experiences and challenges.
2.2. Providing Accessible Learning Opportunities
Accessible learning opportunities are essential for promoting lifelong learning. This involves ensuring that learning resources are widely available, affordable, and convenient. Strategies for providing accessible learning opportunities include:
- Online Learning Platforms: Utilize online learning platforms to provide access to a wide range of courses, tutorials, and resources.
- Mobile Learning: Optimize learning content for mobile devices to enable learning on the go.
- Open Educational Resources (OER): Use OER to provide free or low-cost access to high-quality learning materials.
- Flexible Learning Options: Offer flexible learning options, such as self-paced courses and blended learning programs, to accommodate diverse schedules and learning styles.
- Community Learning Centers: Establish community learning centers to provide access to learning resources and support services in local communities.
2.3. Valuing and Recognizing Learning
Valuing and recognizing learning is essential for motivating individuals to engage in lifelong learning. This involves acknowledging and rewarding learning efforts both formally and informally. Strategies for valuing and recognizing learning include:
- Certifications and Credentials: Offer certifications and credentials to recognize the acquisition of new skills and knowledge.
- Badges and Micro-credentials: Use badges and micro-credentials to recognize specific competencies and achievements.
- Performance Reviews: Incorporate learning and development goals into performance reviews and reward employees for achieving them.
- Public Recognition: Celebrate learning achievements through public recognition events and announcements.
- Learning Communities: Create learning communities where individuals can share their learning experiences and celebrate each other’s successes.
2.4. Creating Learning Communities
Learning communities provide a supportive environment where individuals can connect, share knowledge, and engage in collaborative learning experiences. Strategies for creating learning communities include:
- Online Forums: Create online forums and discussion groups where individuals can ask questions, share resources, and engage in peer-to-peer learning.
- Study Groups: Organize study groups where individuals can collaborate on assignments, prepare for exams, and support each other’s learning.
- Mentoring Programs: Establish mentoring programs where experienced individuals can provide guidance and support to newer learners.
- Workshops and Seminars: Host workshops and seminars where individuals can learn from experts and share their own experiences.
- Social Events: Organize social events to foster a sense of community and provide opportunities for informal learning and networking.
2.5. Integrating Technology into Learning
Technology plays a significant role in fostering lifelong learning by providing access to a vast array of learning resources and tools. Strategies for integrating technology into learning include:
- Learning Management Systems (LMS): Use LMS platforms to deliver and manage online courses and learning resources.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): Utilize VR and AR technologies to create immersive and interactive learning experiences.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Leverage AI-powered tools to personalize learning, provide feedback, and automate administrative tasks.
- Social Media: Use social media platforms to share learning resources, engage in discussions, and connect with other learners.
- Mobile Apps: Develop mobile apps to provide access to learning content and tools on mobile devices.
2.6. Promoting Self-Directed Learning
Self-directed learning empowers individuals to take ownership of their learning journey. Strategies for promoting self-directed learning include:
- Goal Setting: Encourage individuals to set clear and achievable learning goals.
- Resource Identification: Provide resources and guidance to help individuals identify relevant learning materials and tools.
- Time Management: Help individuals develop effective time management skills to prioritize learning.
- Reflection and Evaluation: Encourage individuals to reflect on their learning experiences and evaluate their progress.
- Learning Contracts: Use learning contracts to formalize learning goals, activities, and evaluation methods.
2.7. Addressing Learning Styles
Individuals have different learning styles, and effective lifelong learning strategies should address these differences. Common learning styles include visual, auditory, kinesthetic, and reading/writing. Strategies for addressing learning styles include:
- Multimodal Learning: Provide learning materials in various formats, such as videos, podcasts, articles, and interactive exercises.
- Personalized Learning: Tailor learning experiences to individual preferences and needs.
- Active Learning: Incorporate active learning techniques, such as group discussions, case studies, and simulations.
- Feedback and Assessment: Provide regular feedback and assessment to help individuals understand their learning progress and adapt their strategies.
- Learning Style Assessments: Use learning style assessments to help individuals identify their preferred learning styles and strategies.
2.8. Fostering a Culture of Curiosity
Curiosity is a key driver of lifelong learning. Fostering a culture of curiosity involves creating an environment where individuals are encouraged to ask questions, explore new ideas, and challenge assumptions. Strategies for fostering curiosity include:
- Inquiry-Based Learning: Use inquiry-based learning approaches that encourage individuals to investigate questions and explore topics in depth.
- Open-Ended Questions: Ask open-ended questions that stimulate critical thinking and discussion.
- Exploration and Discovery: Provide opportunities for individuals to explore new topics and discover new interests.
- Experimentation and Innovation: Encourage experimentation and innovation by providing resources and support for trying new things.
- Celebrate Curiosity: Recognize and reward curiosity by celebrating questions, ideas, and discoveries.
2.9. Overcoming Fear of Failure
Fear of failure can be a significant barrier to lifelong learning. Creating a supportive and encouraging environment can help individuals overcome this fear. Strategies for overcoming fear of failure include:
- Normalize Failure: Emphasize that failure is a natural part of the learning process.
- Focus on Learning from Mistakes: Encourage individuals to view mistakes as opportunities for learning and growth.
- Provide Support and Encouragement: Offer support and encouragement to help individuals overcome setbacks and persevere.
- Celebrate Resilience: Recognize and reward resilience by celebrating individuals who overcome challenges and achieve their goals.
- Create a Safe Learning Environment: Foster a learning environment where individuals feel safe to take risks and make mistakes.
2.10. Expand Your Horizons with LEARNS.EDU.VN
At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we provide a comprehensive platform for lifelong learning. Explore our resources and tools to enhance your skills and knowledge. Join our community of learners and discover the transformative power of continuous education. Address: 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States. Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212.
3. Core Skills for Lifelong Learning and Development
Which core domain includes lifelong learning and developing skills? Core skills are essential for lifelong learning as they equip individuals with the tools to adapt, innovate, and thrive in various aspects of life. These skills span cognitive, interpersonal, and technological domains, enabling learners to navigate challenges and opportunities effectively. The development of these core skills is a continuous process, aligning with the principles of lifelong learning.
3.1. Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving
Critical thinking involves analyzing information objectively and making reasoned judgments. Problem-solving is the process of identifying and resolving complex issues effectively. These skills are essential for lifelong learners as they enable them to evaluate information, make informed decisions, and overcome challenges. Strategies for developing critical thinking and problem-solving skills include:
- Analyzing Case Studies: Evaluating real-world scenarios to identify problems and propose solutions.
- Engaging in Debates: Participating in discussions to develop arguments and counterarguments.
- Solving Puzzles and Brain Teasers: Engaging in activities that challenge logical reasoning and problem-solving abilities.
- Reflecting on Experiences: Analyzing past experiences to identify lessons learned and areas for improvement.
3.2. Communication Skills
Effective communication involves expressing ideas clearly and persuasively, both verbally and in writing. Communication skills are essential for lifelong learners as they enable them to collaborate with others, share knowledge, and influence outcomes. Strategies for developing communication skills include:
- Practicing Public Speaking: Presenting information to audiences to improve confidence and delivery.
- Writing Regularly: Engaging in writing activities, such as journaling, blogging, and report writing, to improve clarity and coherence.
- Active Listening: Paying attention to and understanding others’ perspectives during conversations.
- Giving and Receiving Feedback: Providing constructive feedback to others and being open to receiving feedback.
3.3. Collaboration and Teamwork
Collaboration and teamwork involve working effectively with others to achieve common goals. These skills are essential for lifelong learners as they enable them to leverage diverse perspectives, share knowledge, and accomplish complex tasks. Strategies for developing collaboration and teamwork skills include:
- Participating in Group Projects: Working with others to complete assignments and achieve shared objectives.
- Joining Teams and Organizations: Engaging in activities that require collaboration and cooperation.
- Practicing Conflict Resolution: Developing skills to manage and resolve conflicts constructively.
- Leading and Facilitating Meetings: Taking on leadership roles to guide discussions and facilitate decision-making.
3.4. Creativity and Innovation
Creativity involves generating original ideas, and innovation involves implementing those ideas to create value. These skills are essential for lifelong learners as they enable them to adapt to changing circumstances, solve problems in novel ways, and drive progress. Strategies for developing creativity and innovation skills include:
- Brainstorming: Generating ideas through collaborative brainstorming sessions.
- Experimenting and Prototyping: Testing new ideas and creating prototypes to validate their feasibility.
- Thinking Outside the Box: Challenging assumptions and exploring unconventional approaches.
- Learning from Failure: Viewing failures as opportunities to learn and improve.
3.5. Digital Literacy
Digital literacy involves using technology effectively to access, manage, and create information. These skills are essential for lifelong learners as they enable them to navigate the digital world, access online resources, and participate in online communities. Strategies for developing digital literacy skills include:
- Taking Online Courses: Learning about technology and digital tools through online courses and tutorials.
- Exploring New Software and Applications: Experimenting with different software and applications to expand technological skills.
- Participating in Online Forums and Communities: Engaging in discussions and sharing knowledge with others in online forums and communities.
- Staying Up-to-Date with Technology Trends: Keeping abreast of the latest technology trends and developments.
3.6. Learning Agility
Learning agility involves adapting to new situations, acquiring new knowledge, and applying it effectively. These skills are essential for lifelong learners as they enable them to navigate change, embrace new challenges, and continuously grow. Strategies for developing learning agility skills include:
- Seeking Out New Experiences: Engaging in activities that challenge existing skills and knowledge.
- Reflecting on Learning Experiences: Analyzing past learning experiences to identify lessons learned and areas for improvement.
- Being Open to Feedback: Seeking and being receptive to feedback from others.
- Experimenting with Different Learning Strategies: Trying different learning strategies to find what works best.
3.7. Self-Direction
Self-direction involves setting goals, managing time, and motivating oneself to learn independently. These skills are essential for lifelong learners as they enable them to take ownership of their learning journey and achieve their goals. Strategies for developing self-direction skills include:
- Setting SMART Goals: Setting specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound goals.
- Creating a Learning Plan: Developing a plan that outlines learning goals, activities, and timelines.
- Managing Time Effectively: Prioritizing tasks and allocating time for learning activities.
- Staying Motivated: Finding ways to stay motivated and engaged in learning.
3.8. Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence involves understanding and managing one’s own emotions, as well as recognizing and influencing the emotions of others. These skills are essential for lifelong learners as they enable them to build relationships, communicate effectively, and navigate challenges. Strategies for developing emotional intelligence skills include:
- Practicing Self-Awareness: Reflecting on one’s own emotions and how they impact behavior.
- Managing Emotions: Developing strategies to manage and regulate emotions effectively.
- Empathizing with Others: Understanding and sharing the feelings of others.
- Building Relationships: Developing and maintaining positive relationships with others.
3.9. Adaptability and Resilience
Adaptability involves adjusting to new situations and challenges with flexibility. Resilience involves bouncing back from setbacks and adversity. These skills are essential for lifelong learners as they enable them to navigate change, overcome challenges, and persist in the face of difficulties. Strategies for developing adaptability and resilience skills include:
- Embracing Change: Viewing change as an opportunity for growth and development.
- Developing Problem-Solving Skills: Learning to identify and resolve problems effectively.
- Building a Support Network: Creating a network of supportive friends, family, and colleagues.
- Practicing Self-Care: Taking care of one’s physical and mental health.
3.10. Enhance Your Skills at LEARNS.EDU.VN
At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we offer a wide range of resources to help you develop these core skills. Explore our courses, articles, and tools to enhance your abilities and achieve your goals. Join our community of learners and unlock your full potential. Address: 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States. Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212.
4. Methods for Skill Development
Which core domain includes lifelong learning and developing skills? Skill development is crucial for personal and professional growth, enabling individuals to adapt to changing circumstances and excel in various roles. Various methods can be employed to develop skills, including formal education, informal learning, experiential learning, and mentoring and coaching. These methods offer different approaches to skill development, catering to diverse learning styles and preferences.
4.1. Formal Education
Formal education involves structured learning experiences, such as courses, workshops, and degree programs. It provides a systematic approach to skill development, offering a comprehensive curriculum and qualified instructors. Formal education is particularly effective for acquiring foundational knowledge and skills. Examples of formal education methods include:
- University Courses: Enrolling in university courses to gain in-depth knowledge and skills in a specific field.
- Vocational Training: Participating in vocational training programs to acquire practical skills for a specific occupation.
- Professional Certifications: Pursuing professional certifications to demonstrate competence in a specific area.
4.2. Informal Learning
Informal learning involves self-directed learning experiences, such as reading, online courses, and self-directed projects. It offers flexibility and personalization, allowing individuals to learn at their own pace and focus on their specific interests and needs. Informal learning is particularly effective for acquiring new skills and knowledge quickly and efficiently. Examples of informal learning methods include:
- Reading Books and Articles: Reading books and articles to gain knowledge and insights on various topics.
- Taking Online Courses: Enrolling in online courses to learn new skills and knowledge from experts.
- Participating in Webinars and Workshops: Attending webinars and workshops to learn from experts and network with peers.
- Self-Directed Projects: Undertaking self-directed projects to apply skills and knowledge in a practical setting.
4.3. Experiential Learning
Experiential learning involves hands-on experiences, such as internships, apprenticeships, and on-the-job training. It provides opportunities to apply skills in a real-world context, enhancing understanding and retention. Experiential learning is particularly effective for developing practical skills and building confidence. Examples of experiential learning methods include:
- Internships: Participating in internships to gain practical experience in a specific field.
- Apprenticeships: Completing apprenticeships to learn a trade or profession through hands-on training.
- On-the-Job Training: Receiving on-the-job training to develop skills and knowledge relevant to a specific job.
- Simulations and Role-Playing: Participating in simulations and role-playing exercises to practice skills in a safe environment.
4.4. Mentoring and Coaching
Mentoring and coaching involve guidance and support from experienced individuals. Mentors and coaches provide valuable insights, feedback, and encouragement, accelerating skill development and enhancing performance. Mentoring and coaching are particularly effective for developing leadership skills and building confidence. Examples of mentoring and coaching methods include:
- One-on-One Mentoring: Receiving guidance and support from an experienced mentor.
- Group Mentoring: Participating in group mentoring sessions with other learners.
- Executive Coaching: Receiving coaching from an executive coach to develop leadership skills.
- Peer Coaching: Engaging in peer coaching with colleagues to provide mutual support and feedback.
4.5. Technology-Enhanced Skill Development
Technology plays a significant role in enhancing skill development, offering access to a vast array of learning resources and tools. Online platforms, simulations, and virtual environments provide immersive and interactive learning experiences. Social media and collaboration tools facilitate peer-to-peer learning and networking. Examples of technology-enhanced skill development methods include:
| Method | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Online Platforms | Access to a wide range of courses, tutorials, and resources. | Flexible learning, personalized content, and access to experts. |
| Simulations | Immersive and interactive learning experiences that simulate real-world scenarios. | Hands-on practice, risk-free environment, and immediate feedback. |
| Virtual Environments | Virtual environments that provide realistic and engaging learning experiences. | Immersive learning, realistic scenarios, and enhanced engagement. |
| Social Media | Platforms for sharing learning resources, engaging in discussions, and connecting with learners. | Peer-to-peer learning, knowledge sharing, and networking opportunities. |


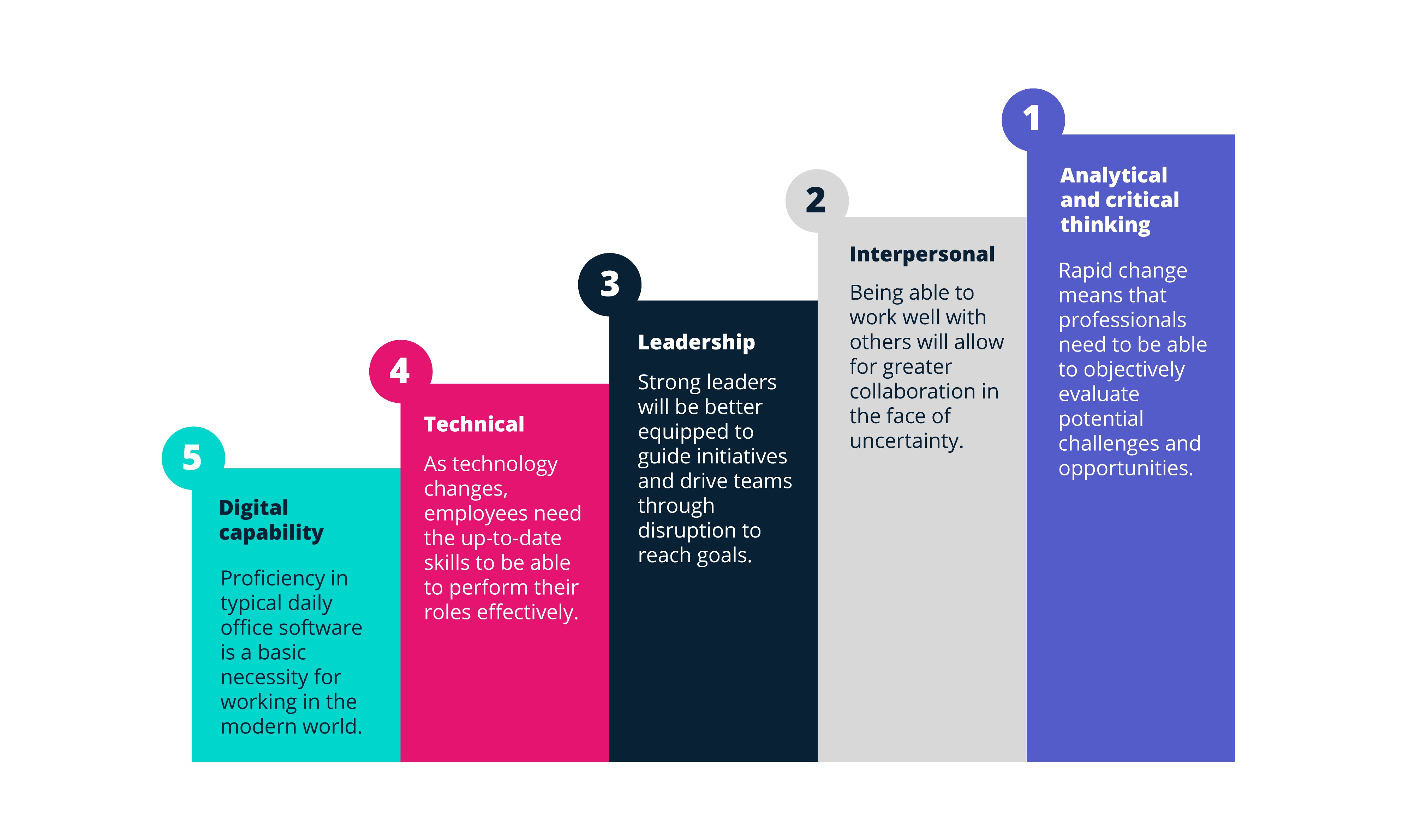

4.6. Blended Learning
Blended learning combines traditional classroom instruction with online learning, offering a flexible and personalized learning experience. It leverages the benefits of both face-to-face interaction and online resources, providing a comprehensive approach to skill development. Blended learning is particularly effective for accommodating diverse learning styles and preferences. Examples of blended learning methods include:
- Flipped Classroom: Students learn content online before class and use class time for discussions and activities.
- Hybrid Courses: Courses that combine online and in-person sessions.
- Technology-Enhanced Instruction: Using technology to enhance traditional classroom instruction.
4.7. Microlearning
Microlearning involves delivering learning content in small, bite-sized chunks. It is designed to be easily digestible and accessible, making it ideal for busy learners. Microlearning is particularly effective for reinforcing knowledge and skills. Examples of microlearning methods include:
- Short Videos: Short videos that explain concepts or demonstrate skills.
- Infographics: Visual representations of information that are easy to understand.
- Quizzes and Assessments: Short quizzes and assessments that test knowledge and skills.
- Mobile Apps: Mobile apps that provide access to learning content and tools on mobile devices.
4.8. Gamification
Gamification involves incorporating game elements into learning activities to increase engagement and motivation. It leverages the principles of game design to make learning more fun and rewarding. Gamification is particularly effective for motivating learners and reinforcing knowledge and skills. Examples of gamification methods include:
- Points and Badges: Earning points and badges for completing learning activities.
- Leaderboards: Competing with other learners on leaderboards.
- Challenges and Quests: Completing challenges and quests to earn rewards.
- Storytelling: Using storytelling to engage learners and make learning more memorable.
4.9. Communities of Practice
Communities of practice are groups of individuals who share a common interest or profession and come together to learn from each other. They provide a supportive environment for knowledge sharing, problem-solving, and skill development. Communities of practice are particularly effective for fostering collaboration and innovation. Examples of communities of practice methods include:
- Online Forums: Participating in online forums to share knowledge and ask questions.
- Workshops and Seminars: Attending workshops and seminars to learn from experts and network with peers.
- Mentoring Programs: Participating in mentoring programs to receive guidance and support.
- Peer Coaching: Engaging in peer coaching with colleagues to provide mutual support and feedback.
4.10. Elevate Your Skills with LEARNS.EDU.VN
At learns.edu.vn, we offer a variety of methods for skill development to help you achieve your goals. Explore our resources and tools to enhance your abilities and unlock your full potential. Join our community of learners and embark on your lifelong learning journey. Address: 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States. Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212.
5. Personal and Professional Growth through Lifelong Learning
Which core domain includes lifelong learning and developing skills? Lifelong learning serves as a catalyst for personal and professional growth, empowering individuals to expand their knowledge, enhance their skills, and refine their perspectives. This continuous pursuit of learning fosters a mindset of curiosity, adaptability, and resilience, which are essential for navigating the complexities of life and the evolving demands of the modern world. In the realm of career advancement and professional success, lifelong learning plays a pivotal role. It enables individuals to stay abreast of industry trends, acquire new skills, and develop specialized knowledge that sets them apart in the competitive job market.
5.1. Enhancing Personal Development
Lifelong learning fosters personal development by expanding knowledge, enhancing skills, and promoting self-awareness. It enables individuals to explore their interests, develop new hobbies, and enhance their overall well-being. Personal development through lifelong learning can lead to:
- Increased Self-Esteem: Acquiring new skills and knowledge can boost confidence and self-esteem.
- Improved Cognitive Function: Engaging in continuous learning can improve memory, attention, and problem-solving abilities.
- Greater Life Satisfaction: Pursuing personal interests and goals can enhance life satisfaction and fulfillment.
- Enhanced Creativity: Exploring new ideas and perspectives can foster creativity and innovation.
- Better Mental Health: Engaging in learning activities can reduce stress and improve mental health.
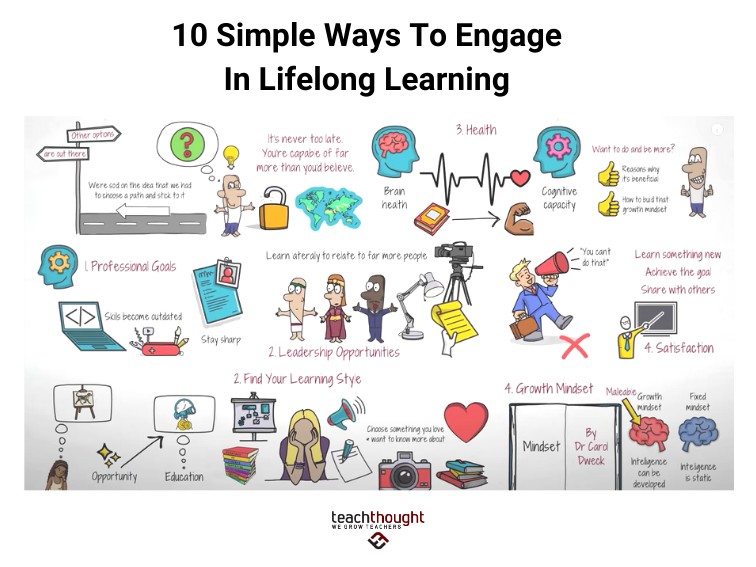
5.2. Advancing Career Opportunities
Lifelong learning plays a crucial role in career advancement and professional success. It enables individuals to stay abreast of industry trends, acquire new skills, and develop specialized knowledge that sets them apart in the competitive job market. Career advancement through lifelong learning can lead to:
- Increased Employability: Acquiring new skills and knowledge can improve job prospects and career advancement opportunities.
- Higher Salaries: Skilled and knowledgeable employees are often rewarded with higher salaries.
- Greater Job Satisfaction: Engaging in meaningful and challenging work can enhance job satisfaction.
- Leadership Opportunities: Developing leadership skills can lead to opportunities to lead and manage teams.
- Career Mobility: Acquiring new skills and knowledge can open doors to new career paths and opportunities.
5.3. Developing Adaptability and Resilience
Lifelong learning fosters adaptability and resilience, which are essential for navigating the complexities of life and the evolving demands of the modern world. Adaptability is the ability to adjust to new situations and challenges with flexibility. Resilience is the ability to bounce back from setbacks and adversity. Developing adaptability and resilience through lifelong learning can lead to:
- Greater Flexibility: The ability to adjust to new situations and challenges with ease.
- Improved Problem-Solving Skills: The ability to identify and resolve problems effectively.
- Enhanced Stress Management: The ability to manage stress and cope with challenging situations.
- Increased Self-Confidence: The confidence to take on new challenges and overcome obstacles.
- Greater Emotional Intelligence: The ability to understand and manage one’s own emotions, as well as recognize and influence the emotions of others.
5.4. Fostering a Growth Mindset
Lifelong learning promotes a growth mindset, which is the belief that abilities and intelligence can be developed through dedication and hard work. Individuals with a growth mindset embrace challenges, persist in the face of setbacks, and view effort as a path to mastery. Fostering a growth mindset through lifelong learning can lead to:
- Increased Motivation: A greater desire to learn and improve.
- Enhanced Resilience: The ability to bounce back from setbacks and challenges.
- Greater Self-Confidence: The confidence to take on new challenges and pursue ambitious goals.
- Improved Problem-Solving Skills: The ability to identify and resolve problems effectively.
- Enhanced Creativity: A greater willingness to experiment and try new things.
5.5. Enhancing Critical Thinking Skills
Lifelong learning enhances critical thinking skills, which are essential for evaluating information, making informed decisions, and solving complex problems. Critical thinking involves analyzing information objectively and making reasoned judgments. Enhancing critical thinking skills through lifelong learning can lead to:
- Improved Decision-Making: The ability to make informed and rational decisions.
- Better Problem-Solving Skills: The ability to identify and resolve complex issues effectively.
- Enhanced Analytical Skills: The ability to analyze information and identify patterns.
- Greater Objectivity: The ability to evaluate information objectively and avoid bias.
- Improved Communication Skills: The ability to express ideas clearly and persuasively.
5.6. Building a Stronger Community
Lifelong learning contributes to building a stronger community by fostering social engagement, promoting civic participation, and enhancing cultural understanding. Engaging in lifelong learning activities can lead to:
- Increased Social Engagement: Opportunities to connect with others and build relationships.
- Greater Civic Participation: A greater awareness of social issues and a desire to contribute to the community.
- Enhanced Cultural Understanding: A greater appreciation for diverse cultures and perspectives.
- Improved Communication Skills: The ability to communicate effectively with others.
- Stronger Social Networks: Building relationships with others who share similar interests and goals.
5.7. Promoting Innovation and Creativity
Lifelong learning promotes innovation and creativity by fostering a culture of curiosity, encouraging experimentation, and providing opportunities to explore new ideas. Engaging in lifelong learning activities can lead to:
- Increased Creativity: The ability to generate original ideas.
- Enhanced Innovation: The ability to implement new ideas and create value.
- Greater Problem-Solving Skills: The ability to identify and resolve complex issues effectively.
- A Greater Willingness to Take Risks: The confidence to experiment and try new things.
- Improved Collaboration Skills: The ability to work effectively with others to achieve common goals.
5.8. Staying Relevant in a Changing World
Lifelong learning is essential for staying relevant in a rapidly changing world. It enables individuals to adapt to new technologies, acquire new skills, and keep abreast of industry trends. Staying relevant through lifelong learning can lead to:
- Increased Employability: A greater likelihood of finding and keeping a job.
- Higher Salaries: The opportunity to earn more money.
- Greater Job Security: A reduced risk of losing one’s job due to obsolescence.
- The Ability to Pursue New Opportunities: The flexibility to change careers and explore new interests.
- A Greater Sense of Purpose: The feeling of contributing to society and making a difference in the world.
5.9. Empowering Personal Growth at Any Age
Lifelong learning is not limited by age or stage of life. It is a continuous process that can empower personal growth and development at any age. Whether you are a student, a working professional, or a retiree, lifelong learning can enhance your skills, expand your knowledge, and enrich your life. At any age, lifelong learning can lead to:
- Increased Self-Esteem: The feeling of accomplishment and confidence that comes from learning new things.
- Improved Cognitive Function: The ability to think clearly and solve problems effectively.
- Greater Life Satisfaction: The feeling of fulfillment that comes from pursuing personal interests and goals.
- Enhanced Social Engagement: The opportunity to connect with others and build relationships.
