Why Is It Important To Learn About Minerals? It’s crucial to understand minerals because they are fundamental building blocks of our modern world, impacting everything from our homes and technology to our health and the global economy, insights which LEARNS.EDU.VN explores in depth. Understanding their formation, uses, and environmental impact is vital for informed decision-making and a sustainable future. Explore mineral resources, their importance, and resource management at LEARNS.EDU.VN.
1. What Are Minerals And Why Should You Care?
Minerals are naturally occurring, inorganic solids with a definite chemical composition and a crystalline structure, and understanding them is essential for informed decision-making in our daily lives and for a sustainable future. They form through various geological processes, and their unique properties make them essential components in countless products and technologies that we rely on daily. From the construction of our homes to the devices we use for communication, minerals are integral to modern society. Let’s delve deeper into why studying minerals is crucial:
- Ubiquitous Presence: Minerals are everywhere, forming the foundation of our built environment, from the gypsum in drywall to the limestone in concrete.
- Technological Advancements: They are the key components in smartphones, computers, and other electronic devices, making our digital world possible.
- Economic Significance: Mineral resources drive industries, contributing significantly to national economies through mining, processing, and manufacturing sectors.
- Environmental Impact: Understanding minerals helps us manage resources sustainably and mitigate the environmental effects of mining and industrial activities.
LEARNS.EDU.VN provides a comprehensive exploration of the fascinating world of minerals, offering detailed insights into their formation, properties, and the critical roles they play in our daily lives and global economy.
2. How Do Minerals Impact Our Daily Lives?
Minerals are so deeply integrated into our daily lives that we often overlook their importance, yet they are essential for everything from the houses we live in to the food we eat and the technologies we use. Examining the specific ways minerals affect our everyday routines highlights just how crucial they are:
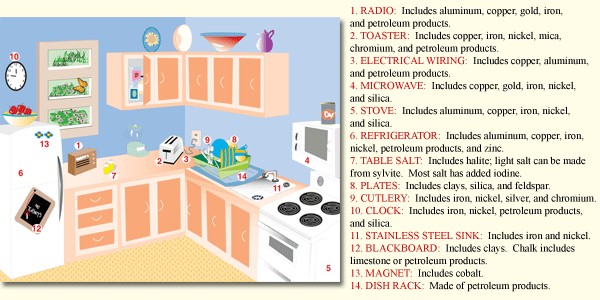
2.1 In Our Homes And Buildings
Our homes and office buildings are constructed using numerous mineral materials that provide structural integrity and functionality. Consider these examples:
- Gypsum: Used in drywall, providing smooth interior walls.
- Limestone: An ingredient in concrete, essential for foundations and structural support.
- Clay: Used to make bricks, forming the walls of many buildings.
- Titanium Oxide: Employed in paint to enhance its opacity and brightness.
- Silica: Used in the production of glass for windows, allowing natural light into our buildings.
- Copper: Used for electrical wiring, ensuring we have power for lights and appliances.
- Iron, Chromium, Nickel, Molybdenum: Combined to make stainless steel for plumbing fixtures, providing durability and corrosion resistance.
2.2 In Our Food And Agriculture
Minerals play a significant role in food production, from the fertilizers used to grow crops to the tools and appliances we use to prepare and store our meals. Examples include:
- Phosphate and Potash: Used in fertilizers to promote plant growth, ensuring high crop yields.
- Selenium, Phosphorus, and Zinc: Supplement animal fodder, contributing to the health and productivity of livestock.
- Mineral Commodities: Used in modern appliances like refrigerators and stoves, preserving food and enabling cooking.
- Salt: Used for seasoning food, enhancing flavors.
- Stainless Steel: Used for cutlery, providing hygiene and durability.
- Clay: Used for making plates and dishes.
- Silica: Used for making glassware, offering safe and attractive ways to serve beverages.
2.3 In Our Hobbies And Recreation
Advances in materials science have transformed sports and recreational equipment, making them stronger, lighter, and more durable. Mineral materials are now essential in various hobbies and recreational activities:
- Aluminum, Carbon Fiber, Magnesium, and Titanium: Used in bicycles for lighter, more durable frames and components.
- Aluminum, Fiberglass, Graphite, Titanium, Zirconium, Beryllium, Copper, Tungsten, and Steel: Used in baseball bats, tennis racquets, and golf clubs for enhanced performance.
- Clay, Sand, and Silt: Used in race tracks and playing surfaces for baseball and tennis, providing optimal playing conditions.
- Calcined Clay: Used to dry wet spots on fields and reduce soil compaction, ensuring safe and consistent playing surfaces.
2.4 In Our Technology
Modern technology relies heavily on minerals, with devices like smartphones incorporating a vast array of elements from the periodic table. Examples include:
- Smartphones: Utilize almost 75% of the elements from the periodic table, including rare earth elements, for various functions.
- Electronics: Rely on minerals like gold, silver, and copper for conductivity and durability.
- Batteries: Use lithium, nickel, and cobalt to store and provide power to devices.
LEARNS.EDU.VN offers detailed courses and resources that explore these connections, providing insights into how minerals impact your daily life and the broader implications for society.
3. What Role Do Minerals Play In The Environment?
Minerals significantly influence our environment, affecting both ecological health and human well-being. Understanding these environmental interactions is crucial for sustainable resource management and mitigating potential risks.
3.1 Minerals And Health
Many minerals are essential for human health, such as calcium, magnesium, iron, potassium, and zinc, which we obtain from our diet. However, exposure to certain minerals or elevated levels of essential minerals can have negative health consequences. These exposures can occur through:
- Air, Water, and Soil: Everyday contact with our surroundings can expose us to both beneficial and harmful minerals.
- Man-Made Disturbances: Activities like mining and industrial processes can release minerals into the environment, leading to contamination.
- Natural Disasters: Events such as volcanic eruptions and earthquakes can redistribute minerals, affecting local ecosystems and human populations.
3.2 Environmental Impact Of Mining
Mining activities can have substantial environmental consequences, including:
- Habitat Destruction: Mining operations often require clearing large areas of land, destroying natural habitats.
- Water Contamination: Mining can release harmful substances into water sources, affecting aquatic life and human water supplies.
- Soil Degradation: Removal of topsoil and exposure of subsurface materials can lead to soil erosion and loss of fertility.
3.3 Managing Environmental Risks
Effective management of mineral resources is essential to minimize environmental risks and ensure sustainable practices. This includes:
- Land Management Plans: Developing and implementing plans to minimize the effects of mineral-borne contaminants on human and ecosystem health.
- Reclamation Activities: Rehabilitating old mining areas to reduce environmental impacts and promote ecosystem recovery.
- Investigation and Analysis: Conducting thorough investigations and analyses of mineral-related environmental issues to inform effective cleanup strategies.
3.4 Case Study: Animas River Watershed
Studies of old mining areas in the Animas River watershed in southwestern Colorado provide valuable insights into the environmental impacts of mining and the effectiveness of reclamation activities. These studies have helped agencies plan and carry out effective cleanup strategies, reducing the long-term environmental effects of mining.
LEARNS.EDU.VN offers resources and courses that delve into these environmental aspects, promoting a deeper understanding of the complex relationship between minerals and the environment.
4. Why Is Securing Future Mineral Supplies Important?
As global living standards rise and emerging economies grow, the demand for mineral resources is increasing rapidly. This escalating demand necessitates a strategic approach to securing future mineral supplies to sustain economic growth and national security.
4.1 Rising Global Demand
Emerging economies like China and India are increasing their participation in the global economy, leading to a surge in demand for durable goods and products manufactured from mineral materials. This growth is depleting known mineral deposits at an accelerated rate, requiring the discovery and development of new resources.
4.2 Mineral Consumption In The U.S.
Each person in the U.S. requires more than 25,000 pounds of new nonfuel minerals annually to produce the items we use daily. This high consumption rate underscores the importance of securing reliable mineral supplies for the future.
The following table illustrates the estimated lifetime mineral requirements for an American born in 2008, highlighting the vast quantities of minerals needed for necessities, lifestyles, and health:
| Mineral Commodity | Amount Required Over A Lifetime |
|---|---|
| Aluminum (Bauxite) | 5,677 pounds |
| Cement | 65,480 pounds |
| Clays | 19,245 pounds |
| Copper | 1,309 pounds |
| Gold | 1,576 ounces |
| Iron Ore | 29,608 pounds |
| Lead | 928 pounds |
| Phosphate Rock | 19,815 pounds |
| Stone, Sand, Gravel | 1.61 million pounds |
| Zinc | 671 pounds |

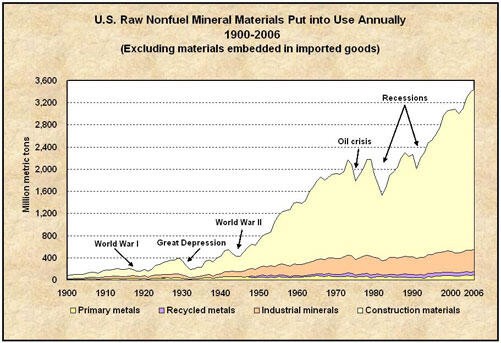
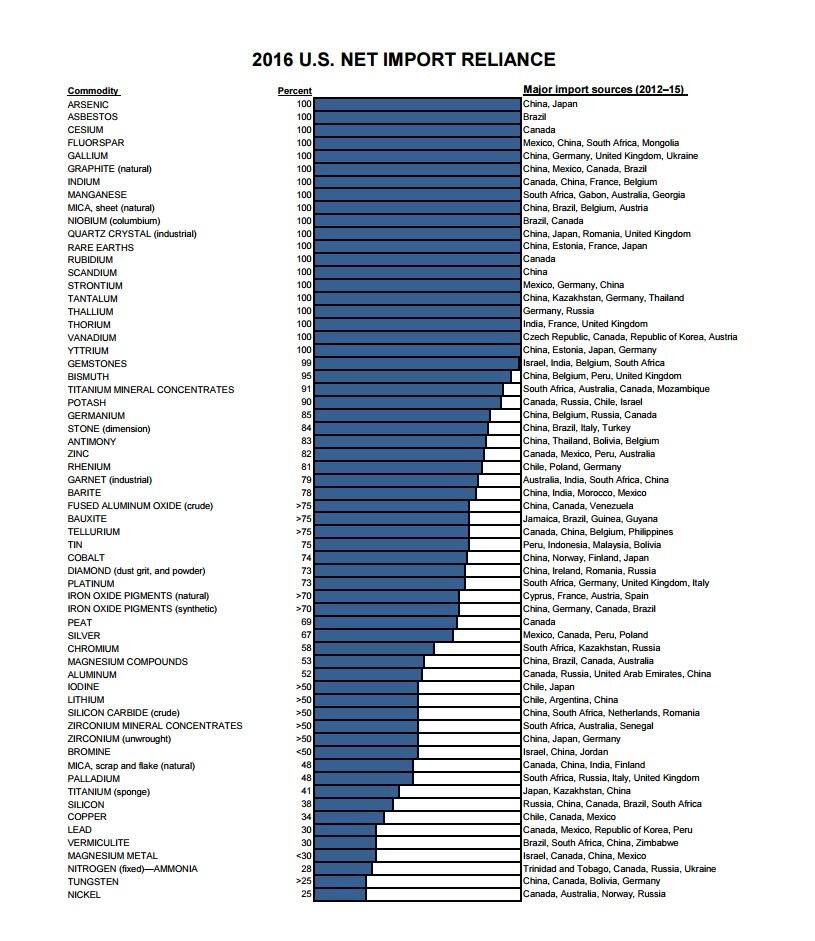
4.3 USGS Assessments Of Mineral Resources
The USGS Mineral Resources Program (MRP) conducts assessments of global and U.S. mineral resources to identify potential future supplies. For example, a recent assessment of copper resources in the Andes of South America revealed that there are likely more copper reserves in undiscovered deposits than have already been produced and exist in known deposits.
4.4 Preparing For Future Assessments
The MRP is preparing for a new national assessment of mineral resources in the United States. This assessment requires state-of-the-art methodologies and up-to-date background information to:
- Identify mineral materials that will be important for emerging technologies and the future U.S. and global economy.
- Refine techniques to decrease uncertainty in estimates of the location, quantity, and quality of undiscovered mineral resources.
- Improve methods to identify resources not directly exposed at the Earth’s surface.
- Enhance our ability to identify potential environmental consequences of developing mineral resources.
4.5 International Cooperation
The MRP’s expertise in mineral resource and mineral environmental assessments is recognized internationally. The MRP provides assistance to developing countries, aiding in the economic development and environmental management of mineral resources in regions such as Afghanistan and the Philippines.
5. How Do Minerals Impact The Economy?
Minerals are fundamental to the U.S. and global economies, influencing various sectors and driving technological advancements. Understanding their economic significance is essential for informed policy-making and strategic resource management.
5.1 Critical Minerals And The Economy
A recent study by the National Research Council (NRC) of the National Academies highlights the importance of minerals to the U.S. economy. The study characterizes the criticality of a mineral commodity by assessing:
- Economic Importance: How vital a particular commodity is to the economy.
- Supply Risk: The risk that the supply of an important commodity might be interrupted.
Commodities identified as being among the most critical include platinum-group metals and rare-earth elements.
5.2 Key Commodities
- Platinum-Group Metals: Essential components of pollution control systems (catalytic converters) in gasoline- and diesel-powered vehicles. These metals facilitate the reduction of carbon monoxide, hydrocarbon, and nitrogen oxide emissions.
- Rare-Earth Elements: Used in the manufacture of high-strength magnets, lasers, high-temperature metal alloys, and refractory ceramics, which are strategic to the defense industry.
5.3 U.S. Reliance On Foreign Sources
The U.S. increasingly relies on foreign sources for many mineral commodities that are vital to the economy. This dependence underscores the need for continuous, unbiased mineral information provided through a federally funded system of information collection and dissemination.
5.4 The Role Of The USGS MRP
The USGS MRP is the sole Federal provider of objective mineral resource science and information. Its research on mineral resource potential and mineral environmental issues, along with the collection, analysis, and dissemination of domestic and international mineral commodity information, provides a one-stop access point for public and private users.
5.5 Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies require mineral commodities on a greater scale and in a larger number of applications than ever before. Advances in alternative energy technologies, nanotechnology, telecommunications, and the aerospace and defense industries are all made possible by incorporating new applications of mineral materials.
5.6 Scarce Commodities
Some mineral commodities used in emerging technologies are rare and their known resources limited. The USGS MRP is conducting research to better understand the character of known resources for these rare and scarce commodities and is developing criteria to assess the possibility of undiscovered resources required to sustain emerging technology industries.
6. FAQ: Your Questions About Minerals Answered
6.1 Why are minerals important to study?
Minerals are essential because they form the foundation of our modern world, influencing technology, construction, health, and the economy. Studying minerals helps us understand their uses, manage resources sustainably, and mitigate environmental impacts.
6.2 What are the main uses of minerals in everyday life?
Minerals are used in construction materials (like gypsum and limestone), electronics (like copper and gold), agriculture (in fertilizers), and household items (like stainless steel cutlery and glass).
6.3 How do minerals affect our health?
Some minerals like calcium, iron, and zinc are vital for our health, while exposure to others, such as asbestos or lead, can be harmful. Understanding mineral content in food and the environment is crucial for maintaining health.
6.4 What is the environmental impact of mining minerals?
Mining can lead to habitat destruction, water contamination, and soil degradation. Sustainable mining practices and reclamation efforts are essential to minimize these negative impacts.
6.5 What are rare earth elements, and why are they important?
Rare earth elements are a group of seventeen chemical elements crucial for various technologies, including smartphones, electric vehicles, and defense systems. They are essential for technological advancement and economic competitiveness.
6.6 How does the USGS Mineral Resources Program contribute to our understanding of minerals?
The USGS MRP provides objective science and unbiased information about mineral resources, conducting research, assessments, and data collection to inform policy decisions and promote sustainable resource management.
6.7 Why is it important to secure future mineral supplies?
As global demand for minerals increases, securing future supplies is essential for sustaining economic growth, supporting technological innovation, and ensuring national security.
6.8 What are some critical minerals for the U.S. economy?
Critical minerals include platinum-group metals (used in catalytic converters) and rare-earth elements (used in high-strength magnets and defense applications). These minerals are vital for various industries and national security.
6.9 How can individuals contribute to sustainable mineral use?
Individuals can support sustainable mineral use by recycling electronics, reducing consumption, and advocating for responsible mining practices.
6.10 Where can I learn more about minerals and their importance?
LEARNS.EDU.VN provides comprehensive resources and courses on minerals, their properties, uses, and environmental impacts, offering in-depth knowledge for students, professionals, and anyone interested in this vital field.
7. Want To Learn More About Minerals?
The next time you use your cell phone, drive a car, or turn on a light, consider the minerals that make these everyday activities possible. Understanding the importance of minerals is essential for informed decision-making, sustainable resource management, and a better future.
Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN to explore our extensive resources and courses on mineral science. Discover how minerals impact our lives, the economy, and the environment, and gain the knowledge you need to make a difference.
Address: 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States
Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212
Website: learns.edu.vn
