Are you wondering Why Learn Python in today’s tech-driven world? Python is a versatile and widely-used programming language that empowers individuals across various domains. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we believe understanding Python’s value is the first step toward unlocking your potential in technology. From data science to web development and beyond, Python offers a gateway to exciting career opportunities and innovative problem-solving, making it an essential skill for the modern learner. Explore the immense possibilities with Python, master core programming concepts, and discover ways to enhance creativity and innovation through data analysis and web application development.
1. What is Python Programming Language?
Python is a high-level, interpreted, general-purpose programming language. Created by Guido van Rossum and first released in 1991, Python’s design philosophy emphasizes code readability with its use of significant indentation. Its language constructs as well as its object-oriented approach aim to help programmers write clear, logical code for small and large-scale projects. Python is dynamically typed and garbage-collected. It supports multiple programming paradigms, including structured (particularly procedural), object-oriented, and functional programming. Python is often described as a “batteries included” language due to its comprehensive standard library.
1.1 Key Features of Python
Python is known for its several key features that contribute to its popularity and usability. Here’s a detailed look at some of the most important ones:
- Easy to Read and Learn: Python has a simple, readable syntax that closely resembles English, making it easier for beginners to learn and understand.
- Versatile: Python supports multiple programming paradigms, including object-oriented, imperative, and functional programming styles, allowing developers to choose the best approach for their projects.
- Extensive Libraries: Python has a vast standard library and supports numerous third-party libraries and frameworks that extend its capabilities for various tasks, such as web development, data analysis, and machine learning.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Python is compatible with many operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux, making it a portable language for developing applications that can run on different platforms.
- Large Community: Python has a large and active community of developers who contribute to its growth and provide support to fellow programmers. This community ensures that Python remains up-to-date and well-supported.
- Dynamically Typed: Python is a dynamically typed language, which means that the type checking is done at runtime. This allows for faster development and easier prototyping.
- Interpreted Language: Python is an interpreted language, meaning that the source code is executed line by line, making debugging easier.
1.2 Why Python is Popular
Python has gained significant popularity over the years, becoming one of the most widely used programming languages in the world. There are several reasons for its widespread adoption:
- Beginner-Friendly: Python’s straightforward syntax makes it an excellent choice for individuals new to programming. Its readability reduces the learning curve, enabling beginners to grasp programming concepts quickly.
- Versatile Applications: Python is used in diverse fields such as web development, data science, machine learning, artificial intelligence, and automation. This versatility makes it a valuable skill for professionals in various industries.
- Strong Community Support: Python boasts a large and active community that provides extensive documentation, tutorials, and support forums. This robust community support helps developers resolve issues and learn new techniques effectively.
- Rich Ecosystem of Libraries: Python offers a wealth of libraries and frameworks, such as NumPy, pandas, Django, and Flask, which simplify complex tasks and accelerate development. These tools enable developers to focus on solving problems rather than writing code from scratch.
- High Demand in the Job Market: Python skills are highly sought after by employers across various industries. Proficiency in Python can lead to numerous job opportunities with competitive salaries.
According to a survey conducted by the Python Software Foundation, Python’s simplicity and versatility are the primary reasons developers choose to use it.
2. Top 10 Reasons Why You Should Learn Python
Here are the top 10 compelling reasons why learning Python can be a game-changer for your career and personal growth.
2.1 Career Opportunities and High Salary
Python programming language offers several job opportunities and promises high growth with excellent salary prospects. Here are some of the roles available for Python developers:
- Python Developer: Develops and maintains Python-based applications.
- Data Scientist: Uses Python to analyze data, create models, and derive insights.
- Machine Learning Engineer: Develops machine learning models and algorithms using Python.
- Web Developer: Uses Python frameworks like Django and Flask to build web applications.
- Software Engineer: Develops software solutions using Python.
- Automation Engineer: Uses Python to automate tasks and processes.
Average Salary of a Python Developer
The average salary of a Python developer varies based on experience, location, and company size. According to Glassdoor, the average salary for a Python developer in the United States is around $120,000 per year.
| Location | Average Salary |
|---|---|
| United States | $120,000 |
| United Kingdom | £55,000 |
| Canada | CAD 90,000 |
| Germany | €65,000 |
| Australia | AUD 110,000 |
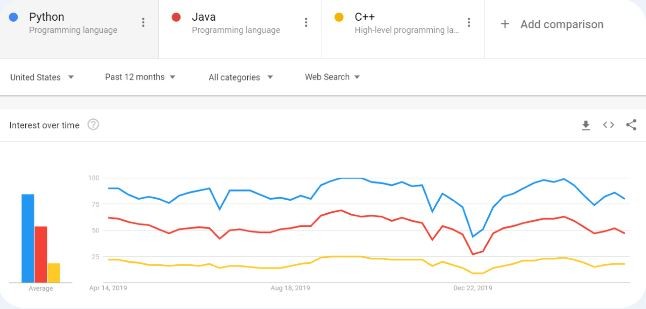
According to a study by Indeed, Python developer roles are among the fastest-growing job categories in the tech industry.
2.2 Python for Data Science
Python is widely used in data science due to its robust, scalable nature and extensible visualization and graphics options. It supports several popular libraries, making it a preferred choice for data analysis and manipulation.
Popular Data Science Libraries in Python:
- NumPy: Provides support for large, multi-dimensional arrays and matrices, along with a collection of mathematical functions to operate on these arrays.
- pandas: Offers data structures and functions for efficient data analysis and manipulation, including data alignment, missing data handling, and data reshaping.
- Matplotlib: A plotting library for creating static, interactive, and animated visualizations in Python.
- Seaborn: A high-level interface for creating informative and aesthetically pleasing statistical graphics based on Matplotlib.
- Scikit-learn: A simple and efficient tool for data mining and data analysis, built on NumPy, SciPy, and Matplotlib.
- Statsmodels: Provides classes and functions for the estimation of many different statistical models, as well as tools for statistical testing and data exploration.
2.3 Machine Learning with Python
Python is one of the most preferred programming languages for machine learning because of its simple syntax and support for several machine learning libraries.
Popular Machine Learning Libraries in Python:
- TensorFlow: An open-source machine learning framework developed by Google, widely used for building and training deep learning models.
- Keras: A high-level neural networks API written in Python, which runs on top of TensorFlow, Theano, and CNTK.
- PyTorch: An open-source machine learning framework developed by Facebook, known for its flexibility and ease of use in building dynamic computational graphs.
- Scikit-learn: Provides simple and efficient tools for data mining and data analysis, including classification, regression, clustering, and dimensionality reduction.
According to a report by O’Reilly, Python is the most popular language for machine learning, with TensorFlow and Scikit-learn being the most widely used libraries.
2.4 Python for Web Development
Python provides a vast collection of frameworks that makes it much easier for developers to develop web applications.
Popular Web Development Frameworks in Python:
- Django: A high-level Python web framework that encourages rapid development and clean, pragmatic design. Django takes care of much of the hassle of web development, so you can focus on writing your app without needing to reinvent the wheel.
- Flask: A lightweight WSGI web application framework. Flask is designed to make getting started quick and easy, with the ability to scale up to complex applications.
- Pyramid: A general-purpose Python web framework. It makes it easy to write web applications, whether they’re small or big, simple or complex.
- Tornado: A Python web framework and asynchronous networking library. Tornado uses a non-blocking network I/O, which can scale to tens of thousands of open connections.
2.5 Scripting and Automation with Python
Python can be used for writing scripts and automating workflows without human intervention, making it very convenient for various tasks.
Examples of Scripting and Automation with Python:
- System Administration: Automating tasks such as file management, user management, and system monitoring.
- Web Scraping: Extracting data from websites using libraries like Beautiful Soup and Scrapy.
- Task Scheduling: Automating the execution of tasks at specific times using libraries like
schedule. - Data Processing: Automating data cleaning, transformation, and loading (ETL) processes.
2.6 Extensive Libraries and Packages
Python has a range of libraries, packages, frameworks, and modules for data manipulation, statistical calculations, web development, machine learning, and data science.
Examples of Popular Python Libraries and Packages:
- Data Manipulation: NumPy, pandas
- Statistical Calculations: SciPy, Statsmodels
- Web Development: Django, Flask, Pyramid
- Machine Learning: TensorFlow, Keras, PyTorch, Scikit-learn
- Data Science: Matplotlib, Seaborn
These libraries and packages provide a wealth of functionality, enabling developers to tackle a wide range of tasks efficiently.
2.7 Python Testing Frameworks
Python supports several built-in testing frameworks that help in debugging and speeding up workflows.
Popular Testing Frameworks in Python:
- unittest: Python’s built-in testing framework, which provides a standard way to write and run tests.
- pytest: A popular third-party testing framework that offers a simple and flexible way to write tests.
- doctest: A module that allows you to embed test cases directly in your docstrings.
- nose: An extension to unittest that makes testing easier.
These testing frameworks help ensure that your code is reliable and bug-free.
2.8 Portable and Extensible Nature of Python
A code developed in Python is often compatible with most non-native platforms. It can be integrated with Java, .NET components, or C/C++ libraries.
Advantages of Python’s Portability and Extensibility:
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Python code can run on various operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- Integration with Other Languages: Python can be integrated with other programming languages, such as Java, C, and C++, allowing you to leverage existing codebases and libraries.
- Wide Range of Applications: Python can be used to develop a wide range of applications, from web applications to scientific simulations.
2.9 An Active and Supportive Community
Python has a massive community that can help you with programming errors or issues with the software. You can post your queries in community forums, and community members will address them in real quick time.
Benefits of Python’s Active Community:
- Extensive Documentation: Python has comprehensive documentation that covers all aspects of the language and its libraries.
- Online Forums: There are numerous online forums and communities where you can ask questions and get help from other Python developers.
- Open Source: Python is an open-source language, which means that anyone can contribute to its development and improvement.
2.10 Simplicity and Ease of Use
Python has a simple syntax and is easy to understand and learn, making it a popular pick when it comes to programming languages.
Key Aspects of Python’s Simplicity and Ease of Use:
- Readable Syntax: Python’s syntax is clear and readable, making it easier to understand and maintain code.
- Concise Code: Python allows you to write the same code using fewer lines compared to other languages like Java or C++.
- Beginner-Friendly: Python’s simplicity makes it an excellent choice for individuals new to programming.
| Feature | Java | Python |
|---|---|---|
| Syntax | Verbose, requires more code to achieve the same functionality | Concise, requires less code |
| Readability | Can be complex due to its structure and syntax | Highly readable, easy to understand |
| Boilerplate Code | Requires more boilerplate code, such as class declarations and main methods | Minimal boilerplate code required |
| Learning Curve | Steeper learning curve, especially for beginners | Gentler learning curve, beginner-friendly |
| Example Code | java public class Welcome { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("Welcome to LEARNS.EDU.VN"); } } | print('Welcome to LEARNS.EDU.VN') |
3. Understanding the Intent Behind Learning Python
To truly appreciate the value of learning Python, it’s essential to understand the various motivations and intentions that drive individuals to embark on this journey. By recognizing these underlying needs and desires, you can better tailor your learning approach and maximize the benefits of acquiring Python skills.
Here are five key intentions that commonly motivate people to learn Python:
- Career Advancement: Many individuals seek to learn Python to enhance their career prospects and unlock new job opportunities. Python’s widespread use in various industries makes it a valuable skill for professionals looking to advance their careers or transition into the tech sector.
- Skill Development: Some people learn Python to expand their skill set and acquire new technical abilities. Python’s versatility allows individuals to apply it to a wide range of tasks, from data analysis to web development, making it a valuable addition to their repertoire.
- Problem-Solving: Python’s expressive syntax and extensive libraries make it an ideal language for solving complex problems. Individuals may learn Python to develop custom solutions for challenges they face in their work or personal lives.
- Personal Projects: Many individuals learn Python to pursue personal projects and hobbies. Python’s ease of use and availability of resources make it an excellent choice for developing side projects, such as automating tasks, building websites, or analyzing data.
- Educational Purposes: Python is often used in educational settings to teach programming concepts and introduce students to computer science. Learning Python can provide a solid foundation for further studies in technology and related fields.
3.1 Matching User Intent with Python Learning
Understanding the intent behind learning Python helps tailor the learning experience to meet specific goals. Here’s how different intents can shape the learning path:
- For Career Advancement: Focus on industry-relevant skills such as web development with Django or data analysis with pandas. Networking and portfolio building are also crucial.
- For Skill Development: Explore a broad range of Python libraries and frameworks to gain a versatile skill set. Experiment with different types of projects to apply new knowledge.
- For Problem-Solving: Identify specific problems and learn the Python tools needed to solve them. Focus on practical application and building custom solutions.
- For Personal Projects: Choose projects that align with personal interests and use Python to bring ideas to life. This hands-on approach reinforces learning and builds confidence.
- For Educational Purposes: Follow structured courses and tutorials that cover fundamental programming concepts. Engage in coding exercises and assignments to solidify understanding.
By aligning the learning approach with the underlying intent, individuals can maximize their learning outcomes and achieve their goals more effectively. Whether it’s landing a dream job, building a personal project, or solving a complex problem, Python provides the tools and resources needed to succeed.
4. Addressing the Challenges of Learners
Learning Python, like any new skill, comes with its own set of challenges. Recognizing and addressing these challenges is crucial for a successful learning journey. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing resources and support to help learners overcome these obstacles and achieve their goals.
4.1 Common Challenges Faced by Python Learners
- Finding Quality Learning Resources: One of the primary challenges is finding reliable and up-to-date learning materials. The abundance of online resources can be overwhelming, and it’s not always easy to distinguish between high-quality and subpar content.
- Maintaining Motivation: Learning a new programming language requires time and effort, and it’s common for learners to lose motivation along the way. The initial excitement can fade as learners encounter complex concepts and challenging exercises.
- Understanding Complex Concepts: Python involves various complex concepts, such as object-oriented programming, data structures, and algorithms. Grasping these concepts can be difficult, especially for beginners without prior programming experience.
- Applying Knowledge to Real-World Projects: Many learners struggle to transition from theoretical knowledge to practical application. Knowing the syntax and concepts is not enough; being able to apply them to real-world projects is essential.
- Keeping Up with the Evolving Landscape: Python is a constantly evolving language, with new libraries, frameworks, and best practices emerging regularly. Keeping up with these changes can be challenging, especially for those who are new to the language.
4.2 How LEARNS.EDU.VN Helps Overcome These Challenges
At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we understand these challenges and offer a range of services and resources to help learners overcome them. Our goal is to provide a supportive and effective learning environment that empowers individuals to succeed in their Python journey.
- Curated Learning Resources: We provide a carefully curated selection of high-quality learning resources, including tutorials, articles, and documentation. Our resources are designed to be accurate, up-to-date, and easy to understand, ensuring that learners have access to the best possible materials.
- Structured Learning Paths: We offer structured learning paths that guide learners through the essential concepts and skills they need to master Python. Our learning paths are designed to be progressive, building on foundational knowledge and gradually introducing more advanced topics.
- Hands-On Projects: We provide hands-on projects and exercises that allow learners to apply their knowledge to real-world scenarios. Our projects are designed to be challenging yet achievable, helping learners build confidence and practical skills.
- Community Support: We foster a supportive community where learners can connect with each other, ask questions, and share their experiences. Our community forums provide a space for learners to collaborate, learn from each other, and receive guidance from experienced mentors.
- Expert Guidance: We offer access to expert instructors and mentors who can provide personalized guidance and support. Our experts are available to answer questions, provide feedback, and help learners overcome challenges they encounter along the way.
4.3 Empowering Learners Through Education
At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we believe that education is the key to empowering individuals and transforming lives. By providing high-quality learning resources, structured learning paths, and personalized support, we aim to help learners unlock their full potential and achieve their goals in the field of Python programming.
5. Structuring Your Learning Journey with a Defined Roadmap
Embarking on a learning journey without a clear roadmap can be daunting. A well-defined learning path provides structure, clarity, and direction, helping you stay focused and motivated as you progress toward your goals. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we emphasize the importance of creating a roadmap to guide your Python learning experience.
5.1 Creating a Python Learning Roadmap
- Define Your Goals: Start by defining your goals and objectives. What do you want to achieve by learning Python? Are you looking to pursue a career in data science, web development, or automation? Clearly defining your goals will help you tailor your learning path to your specific needs.
- Assess Your Current Knowledge: Assess your current knowledge and experience with programming. Are you a complete beginner, or do you have some prior programming experience? Understanding your starting point will help you choose the appropriate learning resources and pace yourself accordingly.
- Choose a Learning Path: Select a learning path that aligns with your goals and skill level. There are numerous learning paths available, ranging from beginner-friendly introductions to advanced specializations. Choose a path that suits your needs and interests.
- Gather Learning Resources: Gather the learning resources you’ll need to follow your chosen learning path. This may include online tutorials, books, documentation, and coding exercises. Ensure that your resources are reliable, up-to-date, and aligned with your learning goals.
- Set a Schedule: Set a realistic schedule for your learning activities. How much time can you dedicate to learning Python each day or week? Setting a schedule will help you stay on track and make consistent progress toward your goals.
- Track Your Progress: Track your progress and celebrate your achievements along the way. Use a journal, spreadsheet, or project management tool to track your learning activities, milestones, and accomplishments. Celebrating your progress will help you stay motivated and engaged.
- Seek Feedback: Seek feedback from mentors, peers, or instructors. Ask for their insights and suggestions on how you can improve your learning approach and overcome challenges. Constructive feedback can be invaluable in helping you refine your skills and achieve your goals.
- Stay Flexible: Stay flexible and adapt your roadmap as needed. Learning is an iterative process, and you may need to adjust your goals, resources, or schedule as you gain experience and insights. Be open to new opportunities and willing to adapt to changing circumstances.
5.2 Sample Python Learning Roadmap
Here’s a sample Python learning roadmap for beginners:
- Introduction to Python:
- Learn the basics of Python syntax, data types, and control structures.
- Install Python and set up your development environment.
- Write and run simple Python programs.
- Data Structures and Algorithms:
- Explore fundamental data structures such as lists, dictionaries, and sets.
- Learn basic algorithms for sorting, searching, and manipulating data.
- Practice implementing data structures and algorithms in Python.
- Object-Oriented Programming (OOP):
- Understand the principles of object-oriented programming, including classes, objects, and inheritance.
- Learn how to design and implement object-oriented programs in Python.
- Practice building reusable and maintainable code using OOP principles.
- Web Development with Flask or Django:
- Choose a web framework such as Flask or Django.
- Learn the basics of web development, including HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
- Build simple web applications using your chosen framework.
- Data Analysis with pandas and NumPy:
- Learn how to use pandas and NumPy to analyze and manipulate data.
- Explore common data analysis tasks such as cleaning, transforming, and visualizing data.
- Practice analyzing real-world datasets using Python.
- Machine Learning with Scikit-learn:
- Learn the basics of machine learning, including classification, regression, and clustering.
- Explore common machine learning algorithms using Scikit-learn.
- Practice building machine learning models and evaluating their performance.
6. Maximizing Learning with Effective Study Techniques
To make the most of your Python learning journey, it’s essential to adopt effective study techniques that enhance comprehension, retention, and application of knowledge. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we emphasize the importance of using proven study strategies to maximize your learning outcomes.
6.1 Proven Study Techniques for Python Learners
- Active Learning: Engage actively with the material by asking questions, summarizing concepts, and explaining them in your own words. Active learning promotes deeper understanding and retention compared to passive reading or listening.
- Spaced Repetition: Review material at increasing intervals to reinforce memory and prevent forgetting. Use flashcards or spaced repetition software to schedule reviews and optimize retention.
- Interleaving: Mix up different topics or concepts during study sessions to improve learning and problem-solving skills. Interleaving helps you differentiate between concepts and apply them in different contexts.
- Practice Coding: Practice coding regularly to reinforce your understanding of Python syntax and concepts. Write small programs, solve coding challenges, and work on real-world projects to build your skills and confidence.
- Seek Feedback: Seek feedback from mentors, peers, or instructors to identify areas for improvement and refine your skills. Constructive feedback can help you correct mistakes, improve your understanding, and accelerate your learning progress.
- Use Visual Aids: Use visual aids such as diagrams, charts, and mind maps to organize information and visualize complex concepts. Visual aids can help you understand relationships between concepts and improve your ability to recall information.
- Teach Others: Teach others what you’ve learned to reinforce your understanding and identify gaps in your knowledge. Teaching requires you to organize your thoughts, explain concepts clearly, and answer questions, which can deepen your understanding and retention.
- Take Breaks: Take regular breaks to avoid burnout and maintain focus. Short breaks can help you refresh your mind, improve your concentration, and enhance your ability to learn and retain information.
6.2 Implementing Effective Study Habits
- Set Realistic Goals: Set realistic goals for your study sessions and break down complex tasks into smaller, manageable steps. Setting achievable goals can help you stay motivated and track your progress.
- Create a Study Schedule: Create a study schedule that allocates specific times for learning Python. Stick to your schedule as much as possible to establish a routine and make consistent progress.
- Minimize Distractions: Minimize distractions during your study sessions by turning off notifications, closing unnecessary tabs, and finding a quiet study environment. Eliminating distractions can help you focus and concentrate on the material.
- Use a Variety of Resources: Use a variety of resources to learn Python, including online tutorials, books, documentation, and coding exercises. Using multiple resources can provide different perspectives and reinforce your understanding.
- Stay Organized: Stay organized by keeping your code, notes, and resources in a structured and accessible manner. Use version control systems, note-taking apps, or project management tools to stay organized and efficient.
7. Leveraging Online Resources and Communities for Support
In today’s digital age, online resources and communities offer invaluable support for Python learners. From tutorials and documentation to forums and social media groups, the internet provides a wealth of information and opportunities to connect with fellow learners and experts. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we encourage learners to leverage these resources to enhance their learning experience.
7.1 Top Online Resources for Python Learners
- Official Python Documentation: The official Python documentation is a comprehensive and authoritative source of information on the Python language and its standard library. It includes tutorials, reference manuals, and how-to guides for learners of all levels.
- Website: https://docs.python.org/3/
- Stack Overflow: Stack Overflow is a popular question-and-answer website for programmers. It’s an excellent resource for finding solutions to common coding problems, getting feedback on your code, and learning from experienced developers.
- Website: https://stackoverflow.com/
- Reddit: Reddit is a social media platform that hosts numerous communities (subreddits) dedicated to Python programming. These subreddits are great places to ask questions, share resources, and connect with other learners.
- Website: https://www.reddit.com/
- Relevant Subreddits: r/python, r/learnpython, r/datascience
- GitHub: GitHub is a web-based platform for version control and collaboration. It’s a great place to find open-source Python projects, contribute to existing projects, and showcase your code to potential employers.
- Website: https://github.com/
- Online Learning Platforms: Online learning platforms such as Coursera, edX, and Udacity offer a wide range of Python courses taught by experts from top universities and institutions. These courses often include video lectures, coding exercises, and hands-on projects.
- Websites:
- Coursera: https://www.coursera.org/
- edX: https://www.edx.org/
- Udacity: https://www.udacity.com/
- Websites:
- TutorialsPoint: TutorialsPoint is a comprehensive website that offers tutorials on various programming languages and technologies, including Python. It provides step-by-step instructions, examples, and exercises for learners of all levels.
- Website: https://www.tutorialspoint.com/
- Real Python: Real Python is a website that offers high-quality tutorials, articles, and resources for Python learners. It covers a wide range of topics, from basic syntax to advanced concepts, and provides practical examples and projects to help you apply your knowledge.
- Website: https://realpython.com/
7.2 Participating in Online Communities
- Join Forums and Groups: Join online forums and social media groups dedicated to Python programming. These communities provide a supportive environment where you can ask questions, share resources, and connect with other learners.
- Ask Questions: Don’t hesitate to ask questions when you’re stuck or confused. Online communities are full of knowledgeable and experienced developers who are willing to help you learn.
- Answer Questions: Share your knowledge and expertise by answering questions from other learners. Helping others can reinforce your understanding of Python concepts and improve your communication skills.
- Contribute to Open Source Projects: Contribute to open-source Python projects on GitHub. Contributing to open-source projects can give you valuable experience working on real-world codebases and collaborating with other developers.
- Attend Meetups and Conferences: Attend local Python meetups and conferences to network with other developers and learn about the latest trends and technologies. Meetups and conferences are great opportunities to meet people in the Python community and expand your knowledge.
8. The Role of Hands-On Projects in Solidifying Learning
While theoretical knowledge is essential, hands-on projects play a crucial role in solidifying your understanding of Python and developing practical skills. By working on real-world projects, you can apply what you’ve learned, solve problems, and build a portfolio that showcases your abilities to potential employers. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we emphasize the importance of hands-on projects in the Python learning journey.
8.1 Benefits of Hands-On Projects
- Reinforce Learning: Hands-on projects provide an opportunity to apply what you’ve learned in a practical context. By working on projects, you can reinforce your understanding of Python syntax, concepts, and best practices.
- Develop Problem-Solving Skills: Projects often involve solving complex problems and overcoming challenges. Working on projects can help you develop your problem-solving skills and learn how to approach new and unfamiliar tasks.
- Build a Portfolio: Projects can serve as valuable additions to your portfolio, showcasing your skills and abilities to potential employers. A well-curated portfolio can demonstrate your proficiency in Python and increase your chances of landing a job or internship.
- Gain Real-World Experience: Projects can simulate real-world scenarios and give you experience working on tasks that are similar to those you might encounter in a professional setting. This experience can be invaluable in preparing you for a career in Python programming.
- Boost Confidence: Completing a project can be a rewarding experience that boosts your confidence and motivates you to continue learning. Successfully building something from scratch can give you a sense of accomplishment and inspire you to tackle more challenging tasks.
8.2 Project Ideas for Python Learners
- Web Scraper: Build a web scraper that extracts data from a website and saves it to a file or database. This project can help you learn about HTML parsing, web requests, and data extraction techniques.
- To-Do List App: Create a to-do list app that allows users to add, edit, and delete tasks. This project can help you learn about GUI programming, event handling, and data persistence.
- Simple Calculator: Develop a simple calculator that performs basic arithmetic operations. This project can help you learn about user input, conditional statements, and mathematical functions.
- Text-Based Game: Design a text-based game such as a guessing game, a maze game, or a trivia game. This project can help you learn about game logic, user interaction, and random number generation.
- Data Visualization: Create a data visualization that displays data from a file or database in a chart or graph. This project can help you learn about data analysis, plotting libraries, and data presentation techniques.
- Automation Script: Write an automation script that automates a repetitive task such as renaming files, sending emails, or backing up data. This project can help you learn about file system operations, email protocols, and task scheduling.
- Simple Web Application: Build a simple web application using a framework such as Flask or Django. This project can help you learn about web development, routing, templating, and database integration.
9. How Python Skills Can Open Doors to Various Industries
Python’s versatility and widespread adoption make it a valuable skill that can open doors to various industries. From technology and finance to healthcare and education, Python is used in a wide range of applications and roles. At learns.edu.vn, we emphasize the importance of understanding how Python skills can translate into career opportunities across different sectors.
9.1 Industries Where Python is Widely Used
- Technology: Python is a staple in the technology industry, where it is used for web development, software engineering, data science, and machine learning. Companies like Google, Facebook, and Amazon rely heavily on Python for various tasks and projects.
- Finance: Python is increasingly used in the finance industry for tasks such as quantitative analysis, algorithmic trading, risk management, and fraud detection. Financial institutions like banks, hedge funds, and investment firms use Python to automate processes and make data-driven decisions.
- Healthcare: Python is used in the healthcare industry for tasks such as medical image analysis, bioinformatics, drug discovery, and patient data management. Healthcare organizations use Python to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance patient care.
- Education: Python is used in the education industry for teaching programming concepts, building educational software, and conducting research. Universities, schools, and online learning platforms use Python to provide students with valuable programming skills and knowledge.
- Marketing: Python is used in the marketing industry for tasks such as data analysis, marketing automation, and customer relationship management (CRM). Marketing agencies and companies use Python to analyze customer data, personalize marketing campaigns, and improve customer engagement.
- Science and Research: Python is widely used in science and research for tasks such as data analysis, scientific computing, and simulation. Researchers use Python to process large datasets, build models, and analyze results in various fields, including physics, astronomy, and biology.
9.2 Career Paths for Python Professionals
- Data Scientist: Data scientists use Python to analyze data, build models, and extract insights to help organizations make better decisions.
- Machine Learning Engineer: Machine learning engineers use Python to develop and deploy machine learning models for various applications, such as image recognition, natural language processing, and recommendation systems.
- Web Developer: Web developers use Python to build web applications and websites using frameworks such as Django and Flask.
- Software Engineer: Software engineers use Python to develop software applications and tools for various platforms, including desktop, web, and mobile.
- Automation Engineer: Automation engineers use Python to automate tasks and processes in various industries, such as manufacturing, healthcare, and finance.
- Quantitative Analyst: Quantitative analysts use Python to develop mathematical models and algorithms for financial analysis and trading.
- Bioinformatician: Bioinformatic
