Social emotional learning (SEL) is essential for fostering a positive and safe learning environment, and LEARNS.EDU.VN is here to guide you through it. By enhancing the ability to succeed academically, professionally, and personally, SEL equips individuals with crucial skills for navigating life’s challenges and building strong relationships. Discover how improving emotional intelligence and cultivating essential skills can lead to a more fulfilling and successful life.
1. What Is Social Emotional Learning (SEL) and Why Is It Important?
Social Emotional Learning (SEL) is the process through which individuals develop self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, relationship skills, and responsible decision-making. SEL is important because it equips individuals with the skills necessary to navigate emotions, build healthy relationships, and make responsible decisions, leading to improved mental health, academic success, and overall well-being.
SEL encompasses a range of competencies that are vital for success in school, the workplace, and life. These competencies enable individuals to understand and manage their emotions, show empathy for others, build positive relationships, and make informed decisions. By integrating SEL into education and other settings, we can foster a more supportive and inclusive environment where everyone has the opportunity to thrive.
1.1. Defining Social Emotional Learning
SEL is defined as the process through which children and adults acquire and effectively apply the knowledge, attitudes, and skills necessary to:
- Understand and manage emotions
- Set and achieve positive goals
- Feel and show empathy for others
- Establish and maintain positive relationships
- Make responsible decisions
These five core competencies are interconnected and essential for personal and social development.
1.2. The Significance of SEL
The significance of SEL lies in its ability to enhance various aspects of life. Research consistently shows that SEL leads to:
- Improved Academic Performance: Students with strong SEL skills tend to perform better academically, demonstrating higher grades and test scores.
- Enhanced Social Skills: SEL promotes positive social behaviors, such as kindness, empathy, and cooperation, leading to better relationships with peers and adults.
- Reduced Behavioral Problems: SEL helps reduce conduct problems, bullying, and other risky behaviors by teaching self-regulation and responsible decision-making.
- Greater Emotional Well-being: Individuals with well-developed SEL skills experience less stress, anxiety, and depression, leading to improved mental health.
- Long-Term Success: SEL skills are crucial for success in college, careers, and personal relationships, contributing to a more fulfilling and productive life.
A study by the Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning (CASEL) found that students participating in SEL programs showed an 11-percentile-point gain in academic achievement compared to those who did not participate. This highlights the direct impact of SEL on academic success.
1.3. The Role of LEARNS.EDU.VN in Promoting SEL
LEARNS.EDU.VN plays a crucial role in promoting SEL by providing resources, guidance, and support for educators, parents, and students. The platform offers a wide range of articles, tools, and courses designed to help individuals develop and enhance their social and emotional skills. Whether you’re looking for tips on improving self-awareness or strategies for fostering positive relationships, LEARNS.EDU.VN has something for everyone.
Table 1: Key Components of Social Emotional Learning
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Self-Awareness | Understanding one’s own emotions, strengths, weaknesses, values, and goals, and recognizing how they impact others. |
| Self-Management | Managing one’s emotions, thoughts, and behaviors effectively in different situations, including regulating stress, controlling impulses, and persevering through challenges. |
| Social Awareness | Understanding the perspectives of others, empathizing with them, and recognizing social norms and ethical standards. |
| Relationship Skills | Establishing and maintaining healthy and rewarding relationships with diverse individuals and groups, including communicating clearly, listening actively, and resolving conflicts constructively. |
| Responsible Decision-Making | Making ethical, constructive, and safe choices about personal behavior and social interactions, considering the well-being of oneself and others. |
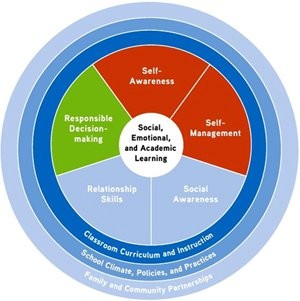 Wheel chart illustrating Social, Emotional, and Academic Learning, encompassing Self-Awareness, Self-Management, Social Awareness, Relationship Skills, and Responsible Decision-Making.
Wheel chart illustrating Social, Emotional, and Academic Learning, encompassing Self-Awareness, Self-Management, Social Awareness, Relationship Skills, and Responsible Decision-Making.
2. What Are the 5 Core Competencies of Social Emotional Learning?
The 5 core competencies of Social Emotional Learning are self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, relationship skills, and responsible decision-making. These competencies enable individuals to understand and manage their emotions, empathize with others, build positive relationships, and make ethical choices. Developing these skills is crucial for success in school, work, and life.
Each of these competencies plays a crucial role in fostering personal and social development. By understanding and cultivating these skills, individuals can better navigate life’s challenges and build strong, meaningful relationships.
2.1. Self-Awareness: Understanding Yourself
Self-awareness involves understanding your own emotions, strengths, weaknesses, values, and goals. This includes recognizing how your thoughts, feelings, and actions impact others. High self-awareness allows you to:
- Accurately assess your strengths and limitations
- Have a positive mindset
- Possess a well-grounded sense of self-efficacy and optimism
- Recognize the interconnectedness of thoughts, feelings, and actions
Developing self-awareness is the first step toward personal growth and emotional intelligence. According to research by Travis Bradberry, co-author of “Emotional Intelligence 2.0,” only 36% of people are able to accurately identify their emotions as they happen. This underscores the importance of actively cultivating self-awareness.
2.2. Self-Management: Managing Your Emotions and Behaviors
Self-management requires the skills and attitudes that facilitate the ability to regulate your own emotions and behaviors. This includes:
- Delaying gratification
- Managing stress
- Controlling impulses
- Persevering through challenges to achieve personal and educational goals
Effective self-management is essential for achieving success in various aspects of life. A study published in the Journal of Personality and Social Psychology found that individuals with high self-control are more likely to achieve their goals and experience greater life satisfaction.
2.3. Social Awareness: Understanding Others
Social awareness involves the ability to understand, empathize, and feel compassion for those with different backgrounds or cultures. It also includes:
- Understanding social norms for behavior
- Recognizing family, school, and community resources and supports
Cultivating social awareness helps you build stronger relationships and navigate diverse social situations with ease. Research has shown that social awareness is linked to improved communication skills and greater success in collaborative environments.
2.4. Relationship Skills: Building Positive Connections
Relationship skills help you establish and maintain healthy and rewarding relationships and act in accordance with social norms. These skills include:
- Communicating clearly
- Listening actively
- Cooperating
- Resisting inappropriate social pressure
- Negotiating conflict constructively
- Seeking help when needed
Strong relationship skills are crucial for both personal and professional success. A study by the Harvard Business School found that individuals with strong interpersonal skills are more likely to advance in their careers and achieve leadership positions.
2.5. Responsible Decision-Making: Making Ethical Choices
Responsible decision-making involves learning how to make constructive choices about personal behavior and social interactions across diverse settings. This requires the ability to:
- Consider ethical standards
- Assess safety concerns
- Understand accurate behavioral norms for risky behaviors
- Consider the health and well-being of self and others
- Make realistic evaluations of various actions’ consequences
Developing responsible decision-making skills is essential for navigating life’s challenges and making choices that align with your values. According to a report by the National Research Council, responsible decision-making is a key factor in preventing risky behaviors and promoting positive outcomes for youth.
Table 2: Examples of SEL Skills in Action
| Competency | Example in School | Example in the Workplace |
|---|---|---|
| Self-Awareness | A student recognizes they feel anxious before a test and uses relaxation techniques to calm down. | An employee understands their strengths and seeks out tasks that align with those strengths. |
| Self-Management | A student manages their time effectively to complete assignments and study for exams. | An employee manages their stress during a high-pressure project by taking breaks and practicing mindfulness. |
| Social Awareness | A student understands a classmate’s frustration and offers help. | An employee recognizes and respects the diverse perspectives of their colleagues. |
| Relationship Skills | A student works collaboratively with peers on a group project, resolving conflicts constructively. | An employee builds strong relationships with clients and colleagues, fostering a positive work environment. |
| Responsible Decision-Making | A student chooses not to participate in bullying, even when pressured by peers. | An employee makes ethical decisions, even when faced with potential personal gain. |
3. What Are the Short- and Long-Term Benefits of Social Emotional Learning?
The short- and long-term benefits of Social Emotional Learning are significant and far-reaching, impacting academic performance, social behavior, mental health, and overall well-being. In the short term, SEL enhances self-awareness, promotes positive social behaviors, and reduces emotional distress. Over the long term, it increases the likelihood of high school graduation, career success, and positive relationships, contributing to a more fulfilling and productive life.
SEL not only benefits individuals but also contributes to creating more positive and supportive communities. By fostering empathy, respect, and responsible decision-making, SEL helps build a foundation for a more equitable and harmonious society.
3.1. Short-Term Benefits of SEL
The short-term benefits of SEL are numerous and can be observed relatively quickly after implementing SEL programs and practices. These benefits include:
- More Positive Attitudes: Enhanced self-efficacy, confidence, persistence, empathy, connection, and commitment to school, and a sense of purpose.
- Positive Social Behaviors: Improved relationships with peers and adults, increased cooperation, and reduced instances of conflict.
- Reduced Conduct Problems: Decreased instances of bullying, aggression, and other disruptive behaviors.
- Decreased Emotional Distress: Lower levels of stress, anxiety, and depression among students and adults.
- Improved Academic Performance: Higher test scores, grades, and attendance rates.
A meta-analysis of school-based SEL programs found that students participating in these programs showed significant improvements in social and emotional skills, attitudes, behavior, and academic performance (Durlak et al., 2011).
3.2. Long-Term Benefits of SEL
The long-term benefits of SEL extend far beyond the classroom and workplace, impacting various aspects of life. These benefits include:
- Increased Likelihood of High School Graduation: Students with strong SEL skills are more likely to stay in school and graduate.
- Readiness for Postsecondary Education: SEL skills prepare students for the challenges of college and other postsecondary programs.
- Career Success: Employers value SEL skills, such as teamwork, communication, and problem-solving, which are essential for career advancement.
- Positive Family and Work Relationships: Strong SEL skills contribute to healthier and more fulfilling relationships with family members, friends, and colleagues.
- Better Mental Health: Individuals with well-developed SEL skills are more resilient and better equipped to cope with stress and adversity, leading to improved mental health.
- Reduced Criminal Behavior: SEL programs have been shown to reduce involvement in criminal activities and promote responsible citizenship.
- Engaged Citizenship: Individuals with strong SEL skills are more likely to be engaged in their communities and contribute to the greater good.
A longitudinal study published in the American Journal of Public Health found that kindergarten social competence was significantly associated with key outcomes in adulthood, including educational attainment, employment, and reduced risk of criminal behavior (Jones, Greenberg, & Crowley, 2015).
3.3. How LEARNS.EDU.VN Supports Long-Term SEL Development
LEARNS.EDU.VN is committed to supporting long-term SEL development by providing resources and tools that can be used throughout life. The platform offers:
- Ongoing Learning Opportunities: A wide range of articles, courses, and workshops designed to enhance SEL skills at every stage of life.
- Practical Strategies: Actionable tips and techniques that can be applied in various settings, from the classroom to the workplace to personal relationships.
- Expert Guidance: Access to expert advice and support from experienced educators and SEL professionals.
- Community Support: A supportive community where individuals can connect with others, share experiences, and learn from each other.
Table 3: The Impact of SEL on Key Life Outcomes
| Outcome | Impact of SEL | Supporting Research |
|---|---|---|
| Academic Achievement | Improved test scores, grades, and attendance rates | Durlak et al., 2011 |
| Social Behavior | Increased prosocial behaviors, such as kindness, empathy, and cooperation | Farrington et al., 2012 |
| Mental Health | Reduced stress, anxiety, and depression | Sklad et al., 2012 |
| High School Graduation | Increased likelihood of graduating from high school | Hawkins, Kosterman, Catalano, Hill, & Abbott, 2008 |
| Career Success | Greater job satisfaction, higher earnings, and increased opportunities for advancement | Jones, Greenberg, & Crowley, 2015 |
| Positive Relationships | Healthier and more fulfilling relationships with family, friends, and colleagues | Williford & Wolcott, 2015 |
4. How Can Schools Effectively Support Social Emotional Learning?
Schools can effectively support Social Emotional Learning by integrating SEL into the curriculum, fostering a positive school climate, and providing professional development for teachers. Creating a safe and supportive environment where students feel valued and respected is crucial for promoting SEL. Additionally, engaging families and the community can strengthen the impact of SEL initiatives.
By making SEL a priority, schools can help students develop the skills they need to succeed academically, socially, and emotionally. This not only benefits individual students but also contributes to creating a more positive and inclusive school community.
4.1. Integrating SEL into the Curriculum
Integrating SEL into the curriculum involves embedding social and emotional skills into existing academic subjects. This can be done through:
- Explicit Lessons: Teaching specific social and emotional skills through structured lessons and activities.
- Content Integration: Incorporating SEL themes and concepts into subjects such as English language arts, social studies, and math.
- Real-World Applications: Providing opportunities for students to apply SEL skills in real-world situations, such as group projects, community service, and extracurricular activities.
For example, a history lesson could explore themes of empathy and perspective-taking by examining historical events from multiple viewpoints. Similarly, a math lesson could incorporate teamwork and communication skills through collaborative problem-solving activities.
4.2. Fostering a Positive School Climate
Fostering a positive school climate involves creating a safe, supportive, and inclusive environment where students feel valued and respected. This can be achieved through:
- Positive Relationships: Promoting positive relationships between students, teachers, and staff members.
- Clear Expectations: Establishing clear expectations for behavior and providing consistent consequences for violations.
- Bullying Prevention: Implementing comprehensive bullying prevention programs that address both prevention and intervention.
- Conflict Resolution: Teaching students conflict resolution skills and providing opportunities for them to practice these skills in a safe and supportive environment.
Research has shown that a positive school climate is strongly associated with improved academic outcomes, reduced behavioral problems, and greater student well-being (Thapa, Cohen, Gulley, & Higgins-D’Alessandro, 2013).
4.3. Providing Professional Development for Teachers
Providing professional development for teachers is essential for ensuring that they have the knowledge and skills necessary to effectively implement SEL in the classroom. This can include:
- SEL Training: Providing teachers with training on the core competencies of SEL and how to integrate them into their teaching practices.
- Classroom Management Strategies: Teaching teachers effective classroom management strategies that promote positive behavior and create a supportive learning environment.
- Trauma-Informed Practices: Training teachers on how to recognize and respond to students who have experienced trauma.
- Cultural Competence: Providing teachers with training on cultural competence and how to create a culturally responsive classroom environment.
According to a report by the Wallace Foundation, high-quality professional development is a key factor in the successful implementation of SEL programs.
4.4. Engaging Families and the Community
Engaging families and the community can strengthen the impact of SEL initiatives by extending learning into the home and neighborhood. This can be done through:
- Family Workshops: Providing workshops for parents and families on SEL and how to support their children’s social and emotional development.
- Community Partnerships: Collaborating with community organizations to provide students with additional opportunities to refine and apply SEL skills.
- Volunteer Opportunities: Engaging community members as volunteers in schools to support SEL initiatives.
- Communication: Maintaining open communication with families and the community about SEL initiatives and student progress.
Research has shown that family and community involvement is a key factor in the success of SEL programs (Catalano et al., 2004).
Table 4: Strategies for Supporting SEL in Schools
| Strategy | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Integrate SEL into the Curriculum | Embedding social and emotional skills into existing academic subjects. | Incorporating SEL themes into literature lessons, such as empathy and perspective-taking. |
| Foster a Positive School Climate | Creating a safe, supportive, and inclusive environment where students feel valued and respected. | Implementing anti-bullying programs and promoting positive relationships between students and staff. |
| Provide Professional Development | Providing teachers with the knowledge and skills necessary to effectively implement SEL in the classroom. | Offering training on the core competencies of SEL and how to integrate them into teaching practices. |
| Engage Families and the Community | Strengthening the impact of SEL initiatives by extending learning into the home and neighborhood. | Hosting family workshops on SEL and collaborating with community organizations to provide students with additional opportunities to refine and apply SEL skills. |
5. How Can Social Emotional Learning Be Built in the Classroom?
Social Emotional Learning can be built in the classroom by teaching and modeling social and emotional skills, providing opportunities for students to practice and hone those skills, and giving students opportunities to apply these skills in various situations. An effective approach involves training teachers to deliver explicit lessons on social and emotional skills and then finding opportunities for students to reinforce their use throughout the day.
By creating a classroom environment that supports and encourages SEL, teachers can help students develop the skills they need to succeed both academically and personally.
5.1. Teaching and Modeling Social and Emotional Skills
One of the most effective ways to build SEL in the classroom is by directly teaching and modeling social and emotional skills. This can be done through:
- Explicit Lessons: Delivering structured lessons on topics such as self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, relationship skills, and responsible decision-making.
- Role-Playing: Engaging students in role-playing activities to practice applying SEL skills in different situations.
- Modeling: Demonstrating social and emotional skills in your own interactions with students and colleagues.
- Discussions: Facilitating discussions about emotions, relationships, and ethical dilemmas.
For example, a teacher might lead a lesson on empathy, explaining what it means to understand and share the feelings of others. Students could then participate in a role-playing activity where they practice responding empathetically to different scenarios.
5.2. Providing Opportunities for Practice and Refinement
In addition to teaching social and emotional skills, it’s important to provide students with opportunities to practice and refine these skills. This can be done through:
- Group Projects: Assigning group projects that require students to collaborate, communicate, and resolve conflicts.
- Classroom Meetings: Holding regular classroom meetings where students can share their thoughts and feelings, practice active listening, and solve problems together.
- Reflection Activities: Engaging students in reflection activities, such as journaling, to help them process their experiences and identify areas for growth.
- Feedback: Providing students with constructive feedback on their social and emotional skills.
For example, a teacher might assign a group project that requires students to work together to research and present a topic. During the project, students would need to practice skills such as communication, cooperation, and conflict resolution.
5.3. Providing Opportunities for Application
Finally, it’s important to provide students with opportunities to apply their social and emotional skills in various situations. This can be done through:
- Service-Learning Projects: Engaging students in service-learning projects that allow them to apply their skills to address real-world problems in their community.
- Peer Mentoring: Pairing students with younger students to provide them with guidance and support.
- Conflict Resolution Programs: Training students to mediate conflicts between their peers.
- Leadership Opportunities: Providing students with opportunities to take on leadership roles in the classroom and school.
For example, a teacher might organize a service-learning project where students volunteer at a local homeless shelter. During the project, students would need to apply skills such as empathy, communication, and problem-solving.
Table 5: Examples of SEL Activities in the Classroom
| Activity | Description | SEL Skill(s) Addressed |
|---|---|---|
| Emotion Charades | Students act out different emotions, and their classmates guess which emotion they are portraying. | Self-Awareness, Social Awareness |
| Active Listening Exercises | Students pair up and practice active listening skills, such as summarizing and asking clarifying questions. | Relationship Skills, Communication |
| Conflict Resolution Scenarios | Students role-play different conflict scenarios and practice using conflict resolution strategies to find mutually agreeable solutions. | Relationship Skills, Responsible Decision-Making |
| Gratitude Journaling | Students write in a journal about things they are grateful for, reflecting on the positive aspects of their lives. | Self-Awareness, Self-Management |
| Goal-Setting Activities | Students set personal and academic goals and create action plans to achieve them, developing self-management and responsible decision-making skills. | Self-Management, Responsible Decision-Making |
6. What Is the SAFE Framework for Social Emotional Learning?
The SAFE framework for Social Emotional Learning is an acronym that represents four key elements of effective SEL programs: Sequenced, Active, Focused, and Explicit. This framework ensures that SEL programs are well-organized, engaging, skill-focused, and clearly defined, maximizing their impact on students’ social and emotional development. By incorporating these elements, schools and organizations can create high-quality SEL programs that promote positive outcomes for all participants.
The SAFE framework provides a roadmap for designing and implementing SEL programs that are both effective and sustainable. By focusing on these four key elements, educators can ensure that their SEL efforts are making a meaningful difference in the lives of their students.
6.1. Sequenced: Connected and Coordinated Activities
The first element of the SAFE framework is Sequenced, which refers to the need for connected and coordinated sets of activities to foster skill development. This means that SEL programs should be structured in a way that builds upon previous learning and provides a clear progression of skills. A sequenced program includes:
- Clear Learning Objectives: Each activity should have a clear and specific learning objective that aligns with the overall goals of the program.
- Logical Progression: Activities should be sequenced in a logical order, building upon previous learning and gradually increasing in complexity.
- Reinforcement: Opportunities to reinforce previously learned skills through review and practice.
- Integration: Connections to other areas of the curriculum or program to promote generalization of skills.
For example, a sequenced SEL program might begin with activities that focus on identifying and labeling emotions, followed by activities that focus on managing emotions, and then activities that focus on expressing emotions in healthy ways.
6.2. Active: Active Forms of Learning
The second element of the SAFE framework is Active, which refers to the need for active forms of learning to help students master new skills. This means that SEL programs should engage students in hands-on activities, discussions, and role-playing exercises that allow them to actively participate in the learning process. Active learning strategies include:
- Role-Playing: Engaging students in role-playing activities to practice applying SEL skills in different situations.
- Group Discussions: Facilitating group discussions where students can share their thoughts and feelings, ask questions, and learn from each other.
- Games and Activities: Using games and activities to make learning fun and engaging.
- Projects: Assigning projects that require students to apply SEL skills to solve real-world problems.
For example, an active learning activity might involve students role-playing different conflict scenarios and practicing using conflict resolution strategies to find mutually agreeable solutions.
6.3. Focused: Emphasis on Personal and Social Skills
The third element of the SAFE framework is Focused, which refers to the need for an emphasis on developing personal and social skills. This means that SEL programs should prioritize the development of specific social and emotional skills, such as self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, relationship skills, and responsible decision-making. A focused program includes:
- Clear Skill Targets: Identifying specific social and emotional skills to be developed.
- Targeted Activities: Designing activities that are specifically targeted to develop those skills.
- Assessment: Assessing students’ progress in developing those skills.
- Feedback: Providing students with feedback on their progress.
For example, a focused SEL program might prioritize the development of empathy by providing students with opportunities to practice perspective-taking and understand the feelings of others.
6.4. Explicit: Targeting Specific Social and Emotional Skills
The fourth element of the SAFE framework is Explicit, which refers to the need for targeting specific social and emotional skills. This means that SEL programs should clearly define the social and emotional skills that are being taught and provide explicit instruction on how to develop those skills. Explicit instruction includes:
- Direct Teaching: Directly teaching students about social and emotional skills.
- Modeling: Modeling social and emotional skills for students.
- Practice: Providing students with opportunities to practice social and emotional skills.
- Feedback: Providing students with feedback on their progress in developing social and emotional skills.
For example, an explicit SEL program might directly teach students about the importance of active listening and provide them with opportunities to practice active listening skills in pairs.
Table 6: The SAFE Framework for Social Emotional Learning
| Element | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Sequenced | Connected and coordinated sets of activities to foster skill development. | A program that begins with identifying emotions, progresses to managing emotions, and then focuses on expressing emotions healthily. |
| Active | Active forms of learning to help students master new skills. | Role-playing conflict scenarios to practice conflict resolution strategies. |
| Focused | Emphasis on developing personal and social skills. | Prioritizing the development of empathy through perspective-taking activities. |
| Explicit | Targeting specific social and emotional skills. | Directly teaching active listening skills and providing opportunities to practice them in pairs. |
7. What Is the Role of Family and Community Partnerships in Social Emotional Learning?
The role of Family and Community Partnerships in Social Emotional Learning is to strengthen the impact of school approaches by extending learning into the home and neighborhood. When families and community members are actively involved in supporting SEL, students receive consistent messages and opportunities to practice their skills in various settings. This collaboration enhances the effectiveness of SEL programs and promotes positive outcomes for students.
By working together, schools, families, and communities can create a comprehensive support system that fosters students’ social and emotional development. This collaborative approach is essential for ensuring that all students have the opportunity to thrive.
7.1. Strengthening the Impact of School Approaches
Family and community partnerships can strengthen the impact of school approaches to SEL by:
- Reinforcing Skills: Providing opportunities for students to practice and reinforce SEL skills in different settings.
- Modeling: Modeling social and emotional skills for students in the home and community.
- Supporting School Initiatives: Supporting school SEL initiatives through volunteerism, advocacy, and financial contributions.
- Communication: Maintaining open communication with schools about student progress and challenges.
For example, parents can reinforce SEL skills by encouraging their children to use active listening when communicating with family members or by helping them to identify and manage their emotions when they are feeling stressed.
7.2. Extending Learning into the Home and Neighborhood
Family and community partnerships can extend learning into the home and neighborhood by:
- Creating Supportive Environments: Creating supportive environments where students feel safe, valued, and respected.
- Providing Resources: Providing students with access to resources that support their social and emotional development, such as mentoring programs, after-school activities, and counseling services.
- Promoting Positive Relationships: Promoting positive relationships between students, families, and community members.
- Engaging in Collaborative Activities: Engaging in collaborative activities that bring together schools, families, and community members to support SEL.
For example, community organizations can partner with schools to offer after-school programs that focus on developing SEL skills, such as teamwork, communication, and problem-solving.
7.3. The Role of After-School Activities
After-school activities play a crucial role in fostering SEL by providing students with additional opportunities to connect with supportive adults and peers. These activities can help students:
- Develop New Skills: Develop new skills and personal talents.
- Apply Skills: Apply new skills in a safe and supportive environment.
- Build Relationships: Build positive relationships with peers and adults.
- Increase Self-Esteem: Increase self-esteem and confidence.
Research has shown that after-school programs focused on social and emotional development can significantly enhance student self-perceptions, school connectedness, positive social behaviors, school grades, and achievement test scores, while reducing problem behaviors (Durlak et al., 2010).
7.4. Community Organizations Supporting SEL
Community organizations can support SEL in various ways, including:
- Providing Mentoring Programs: Offering mentoring programs that pair students with positive adult role models.
- Offering Counseling Services: Providing access to counseling services for students who are struggling with social or emotional challenges.
- Organizing Community Events: Organizing community events that promote positive relationships and a sense of community.
- Advocating for SEL: Advocating for SEL in schools and the community.
For example, a local Boys & Girls Club might offer a mentoring program that pairs students with adult mentors who provide guidance and support, helping them to develop social and emotional skills.
Table 7: Strategies for Building Family and Community Partnerships
| Strategy | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Family Workshops | Providing workshops for parents and families on SEL and how to support their children’s social and emotional development. | Hosting a workshop on effective communication skills for parents and children. |
| Community Partnerships | Collaborating with community organizations to provide students with additional opportunities to refine and apply SEL skills. | Partnering with a local Boys & Girls Club to offer after-school programs focused on developing SEL skills. |
| Volunteer Opportunities | Engaging community members as volunteers in schools to support SEL initiatives. | Recruiting volunteers to serve as mentors or tutors for students. |
| Communication | Maintaining open communication with families and the community about SEL initiatives and student progress. | Sending regular newsletters to families with updates on SEL activities and resources. |
8. How Can LEARNS.EDU.VN Help You Implement Social Emotional Learning?
LEARNS.EDU.VN can help you implement Social Emotional Learning by providing comprehensive resources, practical strategies, and expert guidance. Whether you are an educator, parent, or student, LEARNS.EDU.VN offers a wealth of information and tools to support your SEL journey. From articles and courses to workshops and community forums, LEARNS.EDU.VN is your go-to platform for all things SEL.
By leveraging the resources available on LEARNS.EDU.VN, you can create a positive and supportive environment that fosters social and emotional development for yourself and others.
8.1. Comprehensive Resources for Educators
For educators, LEARNS.EDU.VN offers a wide range of resources to support the implementation of SEL in the classroom, including:
- Lesson Plans: Access to a library of lesson plans that integrate SEL into various academic subjects.
- Activities: Engaging activities that promote social and emotional skills development.
- Assessments: Tools for assessing students’ social and emotional skills.
- Professional Development: Opportunities for professional development on SEL best practices.
- Expert Articles: Articles written by leading experts in the field of SEL.
With these resources, educators can effectively integrate SEL into their teaching practices and create a classroom environment that supports students’ social and emotional well-being.
8.2. Practical Strategies for Parents
For parents, LEARNS.EDU.VN offers practical strategies for supporting their children’s social and emotional development at home, including:
- Tips for Building Emotional Intelligence: Tips for helping children understand and manage their emotions.
- Communication Skills: Guidance on effective communication skills for parents and children.
- Conflict Resolution Techniques: Techniques for resolving conflicts peacefully and constructively.
- Resources for Supporting Mental Health: Information and resources for supporting children’s mental health.
- Family Activities: Activities that promote positive family relationships and social-emotional learning.
By implementing these strategies, parents can create a home environment that nurtures their children’s social and emotional growth.
8.3. Guidance for Students
For students, LEARNS.EDU.VN offers guidance on developing their own social and emotional skills, including:
- Self-Awareness Exercises: Exercises for increasing self-awareness and understanding their own emotions.
- Self-Management Techniques: Techniques for managing stress, controlling impulses, and achieving goals.
- Relationship Skills Tips: Tips for building positive relationships with peers and adults.
- Responsible Decision-Making Strategies: Strategies for making ethical and responsible decisions.
- Success Stories: Inspiring stories of students who have used SEL skills to overcome challenges and achieve their goals.
By utilizing these resources, students can take an active role in their own social and emotional development and build the skills they need to succeed in school and life.
8.4. Community and Support
LEARNS.EDU.VN also offers a supportive community where educators, parents, and students can connect with each other, share experiences, and learn from each other. This community includes:
- Forums: Forums for discussing SEL topics, asking questions, and sharing resources.
- Webinars: Webinars featuring leading experts in the field of SEL.
- Success Stories: Inspiring stories of individuals and organizations that have successfully implemented SEL.
- Contact Information:
- Address: 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States
- WhatsApp: +1 555-555-1212
- Website: LEARNS.EDU.VN
Table 8: How learns.edu.vn Supports SEL Implementation
| Audience | Resources and Support | Example