Table of contents
What is a Learning and Development Manager?
Key Responsibilities of an L&D Manager
Steps to Become a Learning and Development Manager
Salary Expectations for Learning and Development Managers
Learning and Development Manager Job Description Template (PDF)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is a Learning and Development Manager?
A Learning and Development Manager is the linchpin for employee training and professional growth within an organization. Their primary objective is to cultivate and maximize employee talent, enabling individuals to reach their peak potential. Crucially, an L&D manager balances the aspirations and needs of the learners with the overarching objectives of the organization.
In larger corporations, an entire L&D department might exist, where the L&D Manager reports to the Head of Learning and Development and coordinates all training and development programs. Conversely, in smaller enterprises, these responsibilities might be integrated into the duties of an HR Generalist, often in conjunction with team managers.
Key Responsibilities of an L&D Manager
The Learning and Development Manager collaborates extensively with business managers, organizational leaders, L&D specialists, members of the L&D department, and HR to ensure several critical outcomes:
- A robust understanding of organizational objectives is in place, forming the foundation for training programs that directly support these objectives.
- A comprehensive grasp of various business units and their distinct training requirements is achieved, allowing for tailored and effective learning initiatives.
Here are the core tasks and responsibilities that typically fall under the purview of a Learning and Development Manager:
Developing and Implementing Learning Strategies and Programs: An L&D manager’s role begins with understanding the strategic direction of the organization. This involves close consultation with business leaders across different departments to pinpoint specific training needs that align with company-wide goals. For instance, if a company aims to enhance its digital transformation, the L&D manager might develop programs focused on digital literacy and technology adoption.
Once these needs are identified, the L&D manager designs and implements learning strategies and programs. This process is iterative, requiring ongoing communication with stakeholders to ensure that the programs not only meet but exceed expectations and are perfectly aligned with business objectives.
Embracing and Implementing Diverse Training Methodologies: Recognizing that individuals learn in varied ways is fundamental to effective L&D. Some employees thrive in self-paced online environments, while others prefer the structure of traditional classroom settings with expert-led instruction. Many benefit from a blended approach that combines both.
An effective L&D manager champions a broad spectrum of training methodologies. They integrate various learning styles into the L&D program, such as:
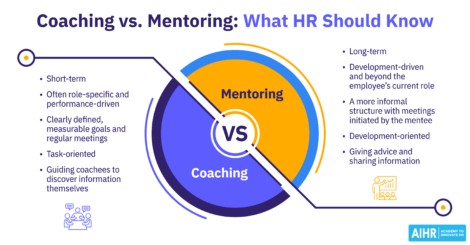
- Coaching: Personalized one-on-one sessions to develop specific skills or address performance gaps.
- E-learning: Online modules and courses that offer flexibility and accessibility.
- Classroom Training: Instructor-led sessions for group learning and interactive discussions.
- Job Shadowing: Practical, on-the-job learning through observation and participation.
- Workshops: Interactive, short-term sessions focused on specific skills or topics.
- Mentoring: Pairing less experienced employees with seasoned professionals for guidance and development.
- Microlearning: Bite-sized learning content delivered in short bursts for better retention and engagement.
Budget Management and Contract Negotiation: Effective L&D programs require careful financial planning. L&D managers are responsible for managing the allocated training budgets, ensuring resources are used efficiently and effectively to maximize the impact of learning initiatives.
This also extends to negotiating contracts with external training providers. To secure the best value and quality, the L&D manager must have a clear understanding of budgetary constraints and explore options that align with the company’s financial and training objectives. Building and maintaining strong relationships with third-party vendors is crucial for ongoing program success and cost-effectiveness.
Creating Training Materials: A significant aspect of the L&D manager’s role involves the creation of training content. In today’s digital-first environment, this often includes designing and delivering engaging e-learning courses. However, it also encompasses a range of other training materials, such as workshop materials, guides, and resources for blended learning programs. The L&D manager ensures that all materials are up-to-date, relevant, and tailored to the specific needs of the audience.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Development Programs: In line with modern HR practices, measuring the impact of L&D initiatives is essential. L&D managers must track the results of development plans to:
- Optimize Programs: Identify areas for improvement and refine training programs to enhance their effectiveness and relevance.
- Maximize Employee Learning: Ensure employees are fully benefiting from the learning opportunities provided and adjust programs to better meet their needs and learning styles.
Key metrics for measuring training effectiveness might include course completion rates, post-training performance improvements, employee feedback, and the application of learned skills in the workplace. Analyzing these metrics allows for data-driven decisions to continually improve the L&D function.
Hiring and Supervising L&D Specialists: In larger organizations with dedicated L&D departments, the L&D manager is responsible for building and leading a team of L&D specialists. This includes recruiting, onboarding, and managing the performance of specialists, ensuring the team has the right mix of skills and expertise to deliver comprehensive learning solutions.
Managing HR Team Development: Given that L&D often falls under the HR umbrella, the L&D manager is uniquely positioned to oversee the training and development of the HR team itself. This ensures that HR professionals are equipped with the latest skills and knowledge in areas such as HR technology, employee relations, and talent management, contributing to the overall effectiveness of the HR function.
Steps to Become a Learning and Development Manager
For those aspiring to become a Learning and Development Manager, a strong educational foundation is typically required. A bachelor’s or master’s degree in fields such as Human Resources, Psychology, Education, Business Administration, or a related discipline is generally preferred. Many successful L&D managers gain initial experience within HR departments or in other management roles, providing them with a solid understanding of organizational dynamics and employee development needs.
Successful candidates are characterized by a proactive approach to learning and staying abreast of the latest trends in learning and development. This includes monitoring changes in learning theories, advancements in learning technologies, and innovative training methodologies. A great L&D manager is also an excellent networker, actively engaging with peers, sharing insights, and staying informed about industry best practices.
While certifications are not always mandatory, they can significantly enhance professional credibility and demonstrate a commitment to the field. Relevant certifications include:
- CIPD Level 5 Diploma in Learning and Development (Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development)
- Certified Professional in Training Management (Training Industry)
- Certified Training and Development Manager (The Knowledge Academy, UK)
- Association for Talent Development (ATD) certifications like Certified Professional in Learning and Performance (CPLP)
Pursuing such certifications can provide a competitive edge and validate expertise in learning and development principles and practices.
Salary Expectations for Learning and Development Managers
Salaries for Learning and Development Managers are influenced by factors such as specific job responsibilities, the size and type of the company, and geographical location.
In the United States, entry-level Learning and Development Manager salaries start around $62,000 annually. Mid-career professionals can expect to earn an average of $73,000.
In the United Kingdom, starting salaries for L&D Managers are approximately £36,000 per year, rising to an average of £40,000 for those with more experience.
In France, the average annual salary for a Learning and Development Manager is around €48,000.
These figures provide a general benchmark, and actual salaries may vary. Senior L&D roles, particularly in larger organizations or those with global responsibilities, can command significantly higher compensation.
Learning and Development Manager Job Description Template (PDF)
The specific job description for a Learning and Development Manager will vary based on organizational context, including company size, the structure of the L&D department, and the precise scope of duties. However, for organizations seeking to create a vacancy for this role, a comprehensive template is a valuable starting point.
A downloadable Learning and Development Manager Job Description is available here. This template outlines typical responsibilities, required qualifications, and desired skills, which can be customized to meet the unique needs of any organization.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is a Learning and Development Manager?
The Learning and Development Manager is accountable for the training and professional growth of an organization’s workforce. They focus on aligning employee development with both individual career goals and organizational needs.
What does an L&D Manager do?
In essence, an L&D Manager ensures they possess a deep understanding of an organization’s strategic objectives and then designs and implements training programs that directly support the achievement of these goals.
What is the average salary of a Learning and Development Manager?
Salaries are variable, depending on factors like responsibilities, company size, and location. Entry-level positions in the US may start around $62,000, while in France, average salaries are approximately €48,000.
Follow us on social media for the latest HR insights and trends:
LinkedIn Facebook Pinterest WhatsApp
Neelie Verlinden
Neelie Verlinden is a seasoned digital content creator at AIHR, specializing in digital HR. With extensive experience, she has authored numerous articles on cutting-edge HR practices. Beyond her writing, Neelie is a sought-after speaker and instructor in prominent HR certificate programs.
Learn More
Related Articles
[ Guides
Training New Employees Effectively: All You Need To Know
Read more ](https://www.aihr.com/blog/training-new-employees/)
[ Guides
Coaching vs. Mentoring: 11 Key Differences & Skills Needed
Read more ](https://www.aihr.com/blog/coaching-vs-mentoring/)
[ Guides
5 Leadership Development Types For Training Leaders (Plus HR Best Practices)
Read more ](https://www.aihr.com/blog/leadership-development/)
New Articles
[ Guides
Progressive Discipline: 5 Steps To Develop a Discipline Policy in 2025
Read more ](https://www.aihr.com/blog/progressive-discipline/)
[ Guides
The Future of Work: HR’s Priorities on AI, ESG and Global Shifts
Read more ](https://www.aihr.com/blog/hr-priorities/)
[ Guides
12 Types of Organizational Culture You Should Know
Read more ](https://www.aihr.com/blog/types-of-organizational-culture/)