Self-management is a critical competency, not only for students but also for educators. In the demanding landscape of modern education, teachers who master self-management skills are better equipped to handle stress, enhance their teaching effectiveness, and foster a positive learning environment. This article delves into the importance of self-management for teachers and provides a comprehensive course outline to help educators develop and implement these vital skills. Rooted in the principles of Social and Emotional Learning (SEL) and drawing from the established CASEL framework, this outline is designed to empower teachers and, by extension, their students.
Understanding Self-Management in the Educational Context
Self-management, within the framework of Social and Emotional Learning (SEL), refers to the ability to regulate one’s own emotions, thoughts, and behaviors effectively across different situations. For teachers, this competency is multifaceted, encompassing stress management, emotional regulation, time management, and goal orientation, all within the high-pressure environment of education. Just as the CASEL framework emphasizes the importance of self-management for students to achieve personal and collective goals, the same applies profoundly to teachers. Effective self-management for educators translates to improved classroom management, enhanced instructional delivery, and a more resilient and positive teaching experience.
Consider the daily demands on a teacher: lesson planning, classroom instruction, student assessment, parent communication, administrative tasks, and navigating the emotional needs of diverse students. Without robust self-management skills, teachers can easily become overwhelmed, leading to burnout, reduced teaching efficacy, and ultimately, a less enriching learning experience for students. Conversely, teachers who excel in self-management can model these crucial skills for their students, creating a classroom culture that values emotional intelligence and personal responsibility.
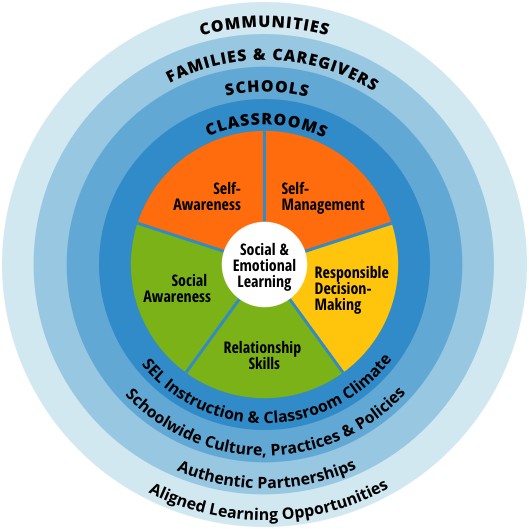 CASEL Wheel
CASEL Wheel
The CASEL framework, widely recognized as a cornerstone of SEL, identifies self-management as one of the five core competencies. Understanding this framework is essential for designing an effective self-management course outline for teachers. The framework underscores that SEL is not merely an add-on to education but an integral part of human development. By focusing on self-management, alongside self-awareness, social awareness, relationship skills, and responsible decision-making, educators can create learning environments that support the holistic development of both themselves and their students.
Designing a Self-Management Course Outline for Teachers
Creating a targeted course outline for teacher self-management requires a structured approach, incorporating key modules that address the core components of this competency. The following outline is designed to be adaptable and comprehensive, providing a robust foundation for teacher professional development in self-management.
Core Modules for a Self-Management Course Outline
-
Introduction to Self-Management and SEL:
- Defining self-management in the context of teaching.
- Exploring the benefits of self-management for teachers and students.
- Overview of the CASEL framework and its five core competencies.
- Understanding the link between teacher well-being and student success.
- Setting personal goals for self-management development within the course.
-
Self-Awareness as a Foundation for Self-Management:
- Recognizing personal emotions and their impact on teaching.
- Identifying personal strengths and areas for growth in self-management.
- Reflecting on personal values and their alignment with teaching practices.
- Understanding personal triggers and stress responses in the classroom environment.
- Activities to enhance self-reflection and emotional literacy.
-
Effective Emotion Management Strategies:
- Techniques for managing stress and anxiety in the teaching profession.
- Strategies for regulating emotions in challenging classroom situations.
- Mindfulness and relaxation techniques for daily practice.
- Developing coping mechanisms for teacher burnout and fatigue.
- Role-playing and scenario-based exercises for practicing emotional regulation.
-
Goal Setting and Time Management for Educators:
- Principles of effective goal setting: SMART goals (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound).
- Prioritization and time management techniques for teachers.
- Planning and organization strategies for lesson preparation and administrative tasks.
- Tools and resources for improving teacher productivity and efficiency.
- Practical exercises in time auditing and schedule optimization.
-
Self-Motivation and Initiative in Teaching:
- Cultivating intrinsic motivation and passion for teaching.
- Strategies for maintaining enthusiasm and engagement throughout the school year.
- Overcoming procrastination and building self-discipline.
- Taking initiative in professional development and classroom innovation.
- Developing a growth mindset and resilience in the face of challenges.
-
Classroom Applications of Self-Management:
- Modeling self-management skills for students.
- Integrating self-management strategies into classroom routines and activities.
- Teaching students self-management techniques for learning and behavior.
- Creating a classroom environment that supports emotional regulation and goal setting.
- Designing lesson plans that incorporate SEL principles and self-management development.
-
Building Resilience and Well-being:
- Understanding the importance of teacher self-care and well-being.
- Strategies for building resilience to stress and adversity.
- Developing healthy habits and lifestyle choices to support well-being.
- Creating a personal support network and seeking help when needed.
- Reflection on personal well-being goals and action planning.
-
Assessment and Continuous Improvement in Self-Management:
- Methods for self-assessment of self-management skills.
- Gathering feedback from peers and mentors on self-management practices.
- Setting goals for continuous improvement and professional growth in self-management.
- Utilizing reflective journaling and action planning for ongoing development.
- Exploring resources and opportunities for continued learning in SEL and self-management.
Each module should incorporate a blend of theoretical knowledge, practical strategies, interactive activities, and reflective exercises. Utilizing case studies, group discussions, role-playing scenarios, and personal reflection prompts can significantly enhance teacher engagement and learning. Furthermore, providing access to resources such as articles, videos, and templates related to self-management and SEL will support ongoing learning beyond the course.
Benefits of Self-Management for Teachers and Students
Investing in teacher self-management through targeted training and course outlines yields significant benefits that ripple outwards, impacting both educators and students positively. For teachers, enhanced self-management translates to:
- Reduced Stress and Burnout: Effective emotional regulation and stress management techniques lead to a more balanced and sustainable teaching career.
- Improved Teaching Effectiveness: Organized, focused, and emotionally regulated teachers are better equipped to deliver high-quality instruction and manage their classrooms effectively.
- Enhanced Professional Well-being: Prioritizing self-care and well-being contributes to greater job satisfaction and overall life quality.
- Stronger Role Modeling: Teachers who demonstrate self-management skills serve as positive role models for their students, fostering a culture of emotional intelligence and personal responsibility.
For students, the benefits of teachers with strong self-management skills are equally profound:
- Positive Learning Environment: Emotionally regulated teachers create a calmer, more supportive, and predictable classroom environment conducive to learning.
- Improved Student Well-being: Students learn self-management skills by observing their teachers and through explicit instruction, leading to improved emotional regulation and stress management.
- Enhanced Academic Performance: Students with better self-management skills are more focused, organized, and motivated, leading to improved academic outcomes.
- Development of Essential Life Skills: Self-management is a critical life skill that prepares students for success in all aspects of their lives, from academics to careers and personal relationships.
Conclusion
Developing a robust self-management course outline for teachers is an investment in the well-being and effectiveness of educators, and consequently, in the success and holistic development of students. By grounding course content in the CASEL framework and focusing on practical, applicable strategies, educational institutions can empower teachers to cultivate essential self-management competencies. This, in turn, creates a positive ripple effect, fostering healthier, more effective teachers, more supportive learning environments, and students equipped with crucial life skills for lifelong success. Embracing self-management as a core component of teacher professional development is not just beneficial – it is essential for creating thriving educational communities.