Learning objectives are the cornerstone of effective education, clearly stating what a learner should be able to do after a learning experience. They serve as explicit declarations that outline the intended outcomes of instruction, ensuring that both educators and learners are aligned on the goals. These objectives are crucial for measuring the success of any educational endeavor, as they pinpoint the demonstrable behaviors that signify learning has occurred.
Learning objectives are broadly categorized into two distinct yet interconnected types:
- Terminal Objectives (Performance Objectives): Defining the ultimate learning outcomes.
- Enabling Objectives (Supporting Objectives): Building blocks that facilitate the achievement of terminal objectives.
Understanding Terminal Objectives
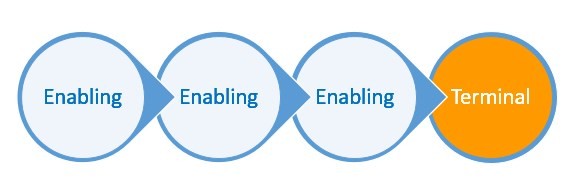
Alt text: Diagram illustrating Terminal Objectives as the overarching goal in learning, emphasizing performance and final outcomes.
Terminal Objectives, also known as Performance Objectives, are specific, measurable statements that articulate what a learner will be capable of doing upon completion of a learning activity. They represent the pinnacle of achievement within a learning program, focusing on the highest level of competency a learner should attain. Each task within a curriculum should ideally have a corresponding Terminal Objective, ensuring comprehensive coverage of learning outcomes.
A well-constructed Terminal Objective comprises three essential components:
- Task or Performance: This clearly states the action the learner will perform to demonstrate their acquired knowledge, skill, or behavior. It’s about observable actions.
- Condition: This component specifies the context or circumstances under which the learner will perform the task. It defines the environment and resources available.
- Standards: This outlines the criteria for acceptable performance. It defines how well the learner must perform the task to be considered competent.
It’s vital to remember that Terminal Objectives are results-oriented, not process-focused. They should be written from the learner’s perspective, emphasizing what they will be able to do after the learning session, rather than detailing what the instructor will teach.
Once a Terminal Objective is formulated, the next step involves analyzing whether it requires Enabling Objectives to support its attainment.
Delving into Enabling Objectives
Enabling Objectives serve as the scaffolding that supports the larger Terminal Objectives. They are derived from a detailed analysis of the Terminal Objective, breaking it down into smaller, more digestible learning increments.
Well-crafted Enabling Objectives clearly articulate the expected performance levels for learners at each stage of learning. They define the specific skills, knowledge, or behaviors learners must master to successfully achieve the overarching Terminal Objective. Each Enabling Objective addresses a constituent part of the Terminal Objective, effectively tracking learner progress towards the ultimate goal.
Alt text: Visual representation showing Terminal Objectives at the top, supported by multiple Enabling Objectives as foundational steps, highlighting the hierarchical relationship in learning design.
Enabling Objectives essentially map out a sequence of learning activities that form the instructional phase of a lesson plan. They delineate the necessary steps for a learner to acquire new competencies and knowledge, progressively leading them towards the performance standard set by the Terminal Objective. Collectively, Enabling Objectives should encompass all the prerequisite skills a learner needs to master to meet the Terminal Objective successfully.
Similar to Terminal Objectives, Enabling Objectives are also learner-centric, focusing on what the learner must accomplish to reach the Terminal Objective.
Illustrative Example
Let’s consider a practical example to differentiate between Terminal and Enabling Objectives:
Terminal Objective:
By the end of this module, the learner will be able to proficiently manage project timelines using project management software.
Enabling Objectives:
- The learner will be able to identify and input project tasks into the software interface.
- The learner will be able to define task dependencies and create a project timeline within the software.
- The learner will be able to track task progress and update the project timeline accordingly.
In this example, the Terminal Objective—managing project timelines—represents the ultimate learning outcome. The Enabling Objectives detail the essential sub-skills and knowledge required to achieve this terminal goal. They break down the complex task into manageable steps, guiding the learning process effectively.
Further Resources
- Learning Objectives
- Writing Learning Objectives
- Creating Learning Objectives
- Components of Learning Objectives