Learning objectives are the cornerstone of effective education, providing clarity and direction for both instructors and learners. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we believe in empowering educators and students with the tools they need to succeed. This comprehensive guide explores “What Are Examples Of Learning Objectives,” offering practical insights, real-world examples, and actionable strategies to enhance your teaching and learning experiences. Discover how well-defined learning objectives can transform your approach to education, making it more focused, engaging, and impactful. Let’s delve into the world of learning objectives, exploring effective learning outcomes and assessment criteria.
1. Understanding the Essence of Learning Objectives
Learning objectives are specific statements that describe what a student should know, understand, or be able to do as a result of a learning experience. They are the foundation of effective instructional design and play a crucial role in aligning teaching methods with desired outcomes. Think of them as the roadmap for a course, guiding both the instructor and the student toward a clear destination.
1.1. Defining Learning Objectives
Learning objectives, often called learning outcomes, are concise declarations detailing the knowledge, skills, and attitudes students will acquire upon completing a course, module, or lesson. They provide a clear benchmark for assessing whether educational goals have been met. Unlike broad learning goals, learning objectives offer specific criteria for evaluation, ensuring students meet the desired academic standards.
For instance, consider the distinction between a learning goal and a learning objective:
- Learning Goal: “I want students to understand the principles of effective communication.”
- Learning Objective: “Students will be able to demonstrate effective communication skills through written and verbal presentations.”
1.2. The Significance of Well-Defined Objectives
Well-crafted learning objectives act as a compass for instructors, directing the development of fair assessment strategies, the selection of relevant content and activities, and the integration of appropriate teaching methodologies and technologies. For students, these objectives provide a clear understanding of the course’s direction and the expectations for success. By continually referring back to these objectives, students can effectively manage and monitor their learning progress throughout the course.
1.3. Key Characteristics of Effective Learning Objectives
Effective learning objectives are SMART – Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Result-oriented, and Time-bound.
- Specific: They break down broad topics into manageable components, clearly stating the desired outcomes related to each component.
- Measurable: They enable instructors to determine how well students have achieved the desired learning outcomes through observable and measurable indicators.
- Achievable: They are attainable given the resources, timeframe, and students’ background and readiness, ensuring the cognitive level aligns with the course and student level.
- Result-oriented: They focus on the results, such as the knowledge, skills, or attitudes students should acquire, rather than the process or activities involved.
- Time-bound: They clearly state the timeline for achieving the objectives, helping to determine competency levels.
2. The Multifaceted Benefits of Learning Objectives
Learning objectives offer numerous benefits to both instructors and students, enhancing the overall educational experience and ensuring that learning is targeted, effective, and measurable. They provide a structured framework that supports better teaching and learning outcomes.
2.1. Benefits for Instructors
Learning objectives serve as a guide for instructors in several key areas:
- Course Design: They help in designing a well-structured course by ensuring that all elements align with the desired outcomes.
- Assessment Planning: They facilitate the creation of fair and relevant assessment plans that accurately measure student achievement.
- Content Selection: They guide the selection of appropriate content, activities, and teaching strategies that support student learning.
- Technology Integration: They inform the effective use of technology to enhance the learning process.
2.2. Benefits for Students
For students, learning objectives provide clarity and direction, leading to:
- Clear Expectations: Students understand what is expected of them, reducing confusion and anxiety.
- Focused Learning: They can direct their learning efforts toward achieving specific goals.
- Self-Monitoring: They can monitor their progress and make adjustments as needed.
- Increased Motivation: Clear objectives can enhance motivation by providing a sense of purpose and direction.
2.3. Enhancing Educational Outcomes
By providing a clear framework for teaching and learning, learning objectives contribute to improved educational outcomes. They ensure that students are not only acquiring knowledge but also developing the skills and attitudes necessary for success in their academic and professional lives.
3. Examples Of Learning Objectives
 Bloom's Taxonomy
Bloom's Taxonomy
To illustrate the practical application of learning objectives, let’s explore various examples across different disciplines and educational levels. These examples demonstrate how to formulate clear, measurable, and achievable objectives that drive effective instruction.
3.1. Science Education
- Objective: Students will be able to describe the scientific method and provide examples of its application.
- Explanation: This objective is specific, measurable through descriptions and examples, achievable for an introductory science course, result-oriented by focusing on description and examples, and time-bound to the end of a unit.
- Objective: Students will be able to apply fundamental principles of physics to real-world situations.
- Explanation: This objective aims to enable students to use their physics knowledge in practical contexts, making learning relevant and applicable.
- Objective: Students will be able to analyze the impact of climate change on local ecosystems.
- Explanation: This objective focuses on critical thinking and analytical skills, encouraging students to evaluate complex environmental issues.
3.2. History Education
- Objective: Students will be able to critique primary source material from the 18th and 19th centuries.
- Explanation: This objective develops students’ critical thinking skills by evaluating historical documents for authenticity, reliability, and bias.
- Objective: Students will be able to compare and contrast the causes and consequences of major historical events.
- Explanation: This objective requires students to understand historical context and analyze the relationships between different events.
- Objective: Students will be able to evaluate the impact of social movements on policy changes.
- Explanation: This objective focuses on the ability to assess the effectiveness and long-term effects of social activism.
3.3. Mathematics Education
- Objective: Students will be able to solve linear equations and inequalities.
- Explanation: This objective ensures students can perform basic algebraic operations, a foundational skill in mathematics.
- Objective: Students will be able to apply calculus concepts to solve optimization problems.
- Explanation: This objective requires students to use calculus in practical scenarios, enhancing their problem-solving abilities.
- Objective: Students will be able to analyze statistical data and draw meaningful conclusions.
- Explanation: This objective focuses on data interpretation and analytical skills, essential for understanding statistical information.
3.4. Language Arts Education
- Objective: Students will be able to write persuasive essays with clear arguments and supporting evidence.
- Explanation: This objective develops writing and critical thinking skills, enabling students to construct well-reasoned arguments.
- Objective: Students will be able to analyze literary texts and identify key themes and motifs.
- Explanation: This objective focuses on literary analysis and comprehension, encouraging students to delve deeper into the meaning of texts.
- Objective: Students will be able to deliver effective oral presentations with clarity and confidence.
- Explanation: This objective enhances communication skills, preparing students to present information effectively in various settings.
3.5. Professional Development
- Objective: Participants will be able to apply project management principles to real-world projects.
- Explanation: This objective provides practical skills for managing projects effectively, relevant for professionals in various fields.
- Objective: Participants will be able to demonstrate leadership skills and motivate team members.
- Explanation: This objective focuses on developing leadership qualities and interpersonal skills, essential for career advancement.
- Objective: Participants will be able to analyze market trends and develop effective marketing strategies.
- Explanation: This objective equips professionals with the ability to understand market dynamics and create successful marketing campaigns.
4. Crafting SMART Learning Objectives: A Step-by-Step Guide
Creating effective learning objectives involves a systematic approach to ensure they are clear, measurable, and aligned with your course goals. By following a step-by-step guide, you can develop objectives that enhance student learning and provide a clear framework for assessment.
4.1. Step 1: Identify the Object
The first step is to identify the core knowledge, skills, or attitudes students should gain. Consider what specific abilities or understanding students should have by the end of the course or lesson.
- Example 1: Fundamental principles of economics
- Example 2: Effective communication techniques
4.2. Step 2: Determine the Mastery Level
Next, determine the level of cognitive activity required. Bloom’s Taxonomy is a valuable tool for this, helping you select appropriate action verbs that match the desired level of understanding.
- Example 1: Apply
- Example 2: Evaluate
4.3. Step 3: Complete the Learning Objective Statement
Combine the object and the action verb to create a complete learning objective statement. Ensure the statement is clear, concise, and focused on what students will be able to do.
- Example 1: Students will be able to apply fundamental principles of economics to analyze market trends.
- Example 2: Students will be able to evaluate effective communication techniques in professional settings.
4.4. Step 4: Refine and Tweak
Review the learning objectives using a checklist to ensure they are specific, measurable, achievable, result-oriented, and time-bound. Make any necessary adjustments to improve clarity and focus.
- Example 1: Students will be able to apply fundamental principles of economics to analyze market trends and predict future outcomes in both written and verbal reports.
- Example 2: Students will be able to evaluate effective communication techniques in professional settings, considering factors such as audience, context, and purpose.
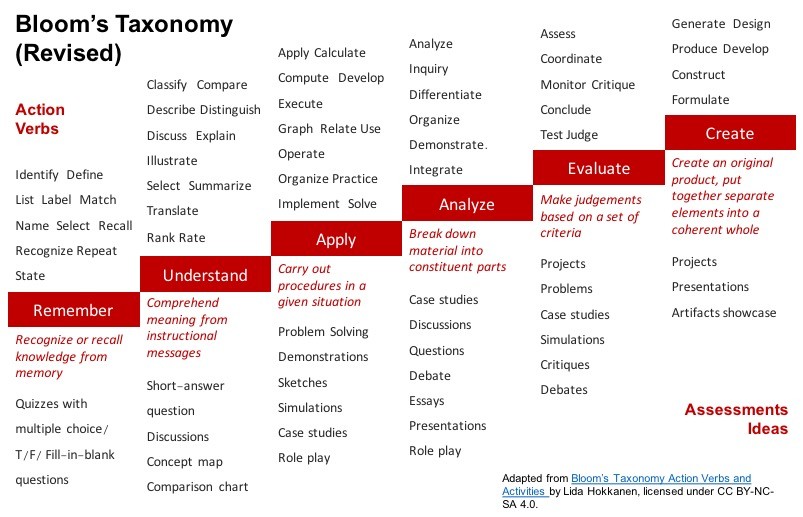
5. Bloom’s Taxonomy: A Framework for Mastery
Bloom’s Taxonomy is a hierarchical framework used to classify educational learning objectives into levels of complexity and specificity. It provides a structured approach to designing learning objectives that align with different cognitive processes, from basic recall to high-level evaluation.
5.1. Understanding Bloom’s Taxonomy
Bloom’s Taxonomy categorizes learning objectives into six main levels: Remember, Understand, Apply, Analyze, Evaluate, and Create. Each level represents a different cognitive skill, with higher levels requiring more complex thinking.
- Remember: Recalling basic facts and concepts.
- Understand: Explaining ideas and concepts.
- Apply: Using information in new situations.
- Analyze: Drawing connections among ideas.
- Evaluate: Justifying a decision or course of action.
- Create: Producing new or original work.
5.2. Using Bloom’s Taxonomy to Write Learning Objectives
When writing learning objectives, consider the level of cognitive skill you want students to achieve. Choose action verbs that align with the appropriate level of Bloom’s Taxonomy.
- Remember: Define, list, recall, recognize.
- Understand: Explain, summarize, interpret, classify.
- Apply: Use, solve, demonstrate, apply.
- Analyze: Compare, contrast, differentiate, analyze.
- Evaluate: Assess, critique, justify, evaluate.
- Create: Design, create, develop, formulate.
5.3. Examples of Learning Objectives Based on Bloom’s Taxonomy
- Remember: Students will be able to define the key terms related to climate change.
- Understand: Students will be able to explain the causes and effects of climate change.
- Apply: Students will be able to apply strategies to reduce their carbon footprint.
- Analyze: Students will be able to analyze the different perspectives on climate change policies.
- Evaluate: Students will be able to evaluate the effectiveness of various climate change mitigation strategies.
- Create: Students will be able to create a plan to address climate change in their local community.
6. Aligning Learning Objectives with Course Components
For learning objectives to be truly effective, they must be aligned with all aspects of the course, including instructional content, activities, and assessments. This alignment ensures that students are learning what they are expected to learn and that their progress is being accurately measured.
6.1. Why Alignment Matters
When course components are aligned with learning objectives, students receive a clear and consistent message about what is important and how they will be evaluated. This clarity can enhance motivation, improve learning outcomes, and reduce confusion.
6.2. How to Align Course Components
- Review Learning Objectives: Start by reviewing your learning objectives to ensure they are clear, specific, and measurable.
- Select Content: Choose content that directly supports the achievement of the learning objectives.
- Design Activities: Create activities that provide opportunities for students to practice and apply the knowledge and skills described in the learning objectives.
- Develop Assessments: Develop assessments that accurately measure student achievement of the learning objectives.
6.3. Examples of Aligned Course Components
6.3.1. Misaligned Objectives & Assessments
- Learning Objective: Students will be able to compare and contrast the benefits of qualitative and quantitative research methods.
- Assessment: Write a 500-word essay describing the features of qualitative and quantitative research methods.
6.3.2. Well-Aligned Objectives & Assessments
- Learning Objective: Students will be able to analyze features and limitations of various sampling procedures and research methodologies.
- Assessment: Comparison chart assignment.
In the first example, the assessment does not require students to analyze the benefits of the research methods, whereas the second example directly assesses students’ analytical skills.
7. Tools and Technologies for Implementing Learning Objectives
In today’s digital age, various tools and technologies can assist in implementing and tracking learning objectives. These resources enhance the educational experience, making it more engaging, efficient, and accessible.
7.1. Learning Management Systems (LMS)
Learning Management Systems like Moodle, Canvas, and Blackboard are invaluable for organizing course content, tracking student progress, and facilitating communication.
- Features:
- Objective Tracking: Monitor student achievement of learning objectives.
- Assessment Tools: Create and administer quizzes, exams, and assignments.
- Communication Tools: Facilitate discussions and provide feedback.
7.2. Assessment and Feedback Tools
Tools like Google Forms, SurveyMonkey, and Gradescope provide efficient ways to assess student understanding and provide timely feedback.
- Features:
- Automated Grading: Simplify the grading process for multiple-choice and short-answer questions.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Provide detailed feedback on assignments and exams.
- Data Analytics: Analyze student performance to identify areas for improvement.
7.3. Interactive Learning Platforms
Platforms like Coursera, edX, and Khan Academy offer interactive learning experiences with built-in objective tracking and assessment tools.
- Features:
- Engaging Content: Access a wide range of interactive lessons and activities.
- Progress Tracking: Monitor your progress toward learning objectives.
- Certification: Earn certifications upon completion of courses.
7.4. Collaborative Tools
Tools like Google Docs, Microsoft Teams, and Slack enhance collaboration and communication among students and instructors.
- Features:
- Real-Time Collaboration: Work together on projects and assignments in real-time.
- Communication Channels: Stay connected through messaging and video conferencing.
- File Sharing: Easily share documents and resources.
8. Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Learning Objectives
Real-world case studies illustrate the impact of well-defined learning objectives on educational outcomes. These examples highlight how different institutions and educators have successfully used learning objectives to enhance teaching and learning.
8.1. Case Study 1: University of California, Berkeley
At the University of California, Berkeley, the Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences (EECS) department implemented a comprehensive set of learning objectives for its undergraduate courses. The objectives were designed to align with the university’s broader educational goals and the specific needs of the EECS field.
- Results:
- Improved student performance on exams and assignments.
- Increased student engagement in course activities.
- Enhanced alignment between course content and industry standards.
8.2. Case Study 2: Khan Academy
Khan Academy, a non-profit educational organization, uses learning objectives to structure its online courses and track student progress. Each lesson is aligned with specific learning objectives, and students receive personalized feedback based on their performance.
- Results:
- Significant improvement in student understanding of core concepts.
- Increased student motivation and self-directed learning.
- Enhanced accessibility to high-quality educational resources.
8.3. Case Study 3: Google’s Internal Training Programs
Google utilizes learning objectives in its internal training programs to ensure employees acquire the necessary skills and knowledge for their roles. The objectives are designed to be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Results:
- Improved employee performance and productivity.
- Increased employee satisfaction and retention.
- Enhanced alignment between training programs and business goals.
9. Overcoming Challenges in Implementing Learning Objectives
While learning objectives offer numerous benefits, their implementation can present challenges. Addressing these challenges effectively ensures that learning objectives are used to their full potential.
9.1. Challenge 1: Lack of Clarity
If learning objectives are not clearly defined, students may struggle to understand what is expected of them.
- Solution: Use specific and measurable language when writing learning objectives. Ensure that objectives are aligned with course content and assessments.
9.2. Challenge 2: Overambitious Objectives
Setting objectives that are too difficult or unrealistic can discourage students and lead to frustration.
- Solution: Ensure that learning objectives are achievable given the resources, timeframe, and students’ background and readiness.
9.3. Challenge 3: Misalignment
When learning objectives are not aligned with course content, activities, and assessments, students may receive conflicting messages about what is important.
- Solution: Regularly review and align all course components with the learning objectives. Ensure that assessments accurately measure student achievement of the objectives.
9.4. Challenge 4: Resistance to Change
Some instructors may resist implementing learning objectives, particularly if they are used to a more traditional approach to teaching.
- Solution: Provide professional development and support to help instructors understand the benefits of learning objectives and how to implement them effectively.
10. The Future of Learning Objectives in Education
As education continues to evolve, learning objectives will play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of teaching and learning. Emerging trends and technologies are likely to further enhance the use of learning objectives in education.
10.1. Personalized Learning
Personalized learning approaches tailor instruction to meet the individual needs and learning styles of students. Learning objectives can be customized to reflect each student’s goals and progress.
10.2. Competency-Based Education
Competency-based education focuses on the mastery of specific skills and knowledge rather than the completion of coursework. Learning objectives are used to define the competencies that students must demonstrate.
10.3. Microlearning
Microlearning involves delivering content in small, focused bursts. Learning objectives are used to ensure that each microlearning module addresses a specific learning outcome.
10.4. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI-powered tools can assist in the development and implementation of learning objectives. AI can analyze student data to identify areas where they need additional support and suggest appropriate learning objectives.
FAQ: Understanding Learning Objectives
1. What are learning objectives?
Learning objectives are specific statements that describe what a student should know, understand, or be able to do as a result of a learning experience.
2. Why are learning objectives important?
They provide clarity and direction for both instructors and students, enhancing the overall educational experience and ensuring that learning is targeted, effective, and measurable.
3. How do you write effective learning objectives?
Use the SMART criteria: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Result-oriented, and Time-bound.
4. What is Bloom’s Taxonomy and how does it relate to learning objectives?
Bloom’s Taxonomy is a hierarchical framework used to classify educational learning objectives into levels of complexity and specificity, helping you select appropriate action verbs.
5. How do you align learning objectives with course components?
Ensure that all aspects of the course, including instructional content, activities, and assessments, directly support the achievement of the learning objectives.
6. What tools and technologies can help with implementing learning objectives?
Learning Management Systems (LMS), assessment and feedback tools, interactive learning platforms, and collaborative tools.
7. What are some common challenges in implementing learning objectives?
Lack of clarity, overambitious objectives, misalignment, and resistance to change.
8. How can learning objectives be used in personalized learning?
Learning objectives can be customized to reflect each student’s goals and progress, tailoring instruction to meet individual needs.
9. What is competency-based education and how do learning objectives fit in?
Competency-based education focuses on the mastery of specific skills and knowledge, with learning objectives defining the competencies students must demonstrate.
10. How might artificial intelligence (AI) impact the future of learning objectives?
AI-powered tools can assist in the development and implementation of learning objectives, analyzing student data to identify areas where they need additional support and suggest appropriate learning objectives.
At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing educators and students with the resources and support they need to succeed. We encourage you to explore our website for more articles, tutorials, and tools to enhance your teaching and learning experiences.
Ready to take your teaching and learning to the next level? Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today to discover a wealth of resources and courses designed to help you achieve your educational goals. Our expert team is here to support you every step of the way. Contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States, or via Whatsapp at +1 555-555-1212. Let’s transform education together at learns.edu.vn.
