The Battle of Iwo Jima significantly shaped American understanding of the Pacific Theater during World War II, highlighting the tenacity of Japanese resistance and the potential cost of invading the Japanese mainland; LEARNS.EDU.VN offers a wealth of resources to further explore the strategic implications and human cost of this pivotal battle. Understanding these lessons is crucial for grasping the complexities of wartime decision-making and the long-term consequences of conflict. Delve deeper into the strategic thinking, understand war insights, and study battlefield lessons.
1. The Strategic Importance of Iwo Jima
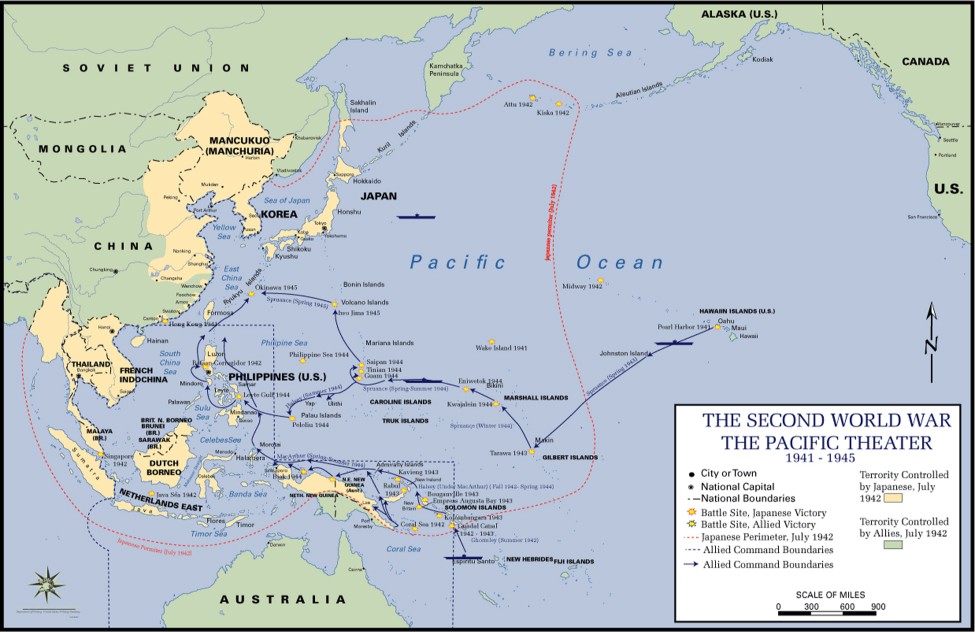
Iwo Jima, a small volcanic island, possessed immense strategic value for the Americans in 1945. Its capture was crucial for several reasons. The island, part of the Bonin Island chain, lay between the American-held Mariana Islands and Japan.
- Airfield Usage: Capturing Iwo Jima would provide airfields for American B-29 bombers, enabling them to refuel on their way to and from bombing missions over Japan. This eliminated the need to detour around the Bonin Islands, streamlining operations.
- Fighter Escort: Iwo Jima could serve as a base for American fighter aircraft. These fighters could escort bombers to Japan, protecting them from enemy fighters and allowing the bombers to fly at lower altitudes for more accurate bombing runs.
- Prelude to Invasion: American planners believed that heavy, targeted bombing of Japan was essential before any potential invasion of the Japanese home islands. Iwo Jima facilitated this bombing campaign.
The island was envisioned as a vital link in the chain of the American “island hopping” strategy, steadily closing in on Japan. This approach involved selectively attacking and capturing key islands while bypassing heavily fortified positions.
2. The Ferocious Japanese Defense
The Japanese forces recognized Iwo Jima’s strategic importance and were determined to defend it at all costs. However, their defensive strategy differed significantly from what the Americans expected.
- Inland Fortifications: Instead of meeting the Americans on the beaches, the Japanese troops established deep, interconnected fortifications far inland. These fortifications were designed to maximize casualties and prolong the battle.
- Kamikaze Tactics: The Japanese also employed kamikaze tactics, where pilots deliberately crashed their explosive-laden planes into American ships. These suicide attacks, named after the “divine wind” that saved Japan from a Mongol invasion centuries earlier, were a desperate measure but initially inflicted significant damage.
The Japanese strategy was to inflict heavy losses on the Americans, slowing their advance and potentially weakening their resolve to invade the home islands.
3. The Brutality of the Battle
The Battle of Iwo Jima was one of the bloodiest and most grueling battles of World War II.
- Heavy Casualties: The fighting lasted for over a month, with both sides suffering immense casualties. Out of approximately 20,000 Japanese troops, all but 200 were killed. The U.S. Marines suffered nearly 6,000 deaths and around 25,000 wounded.
- Difficult Terrain: The volcanic terrain made it extremely challenging for the Marines to advance. They had to fight inch by inch, often using flamethrowers, satchel charges, and other heavy weapons to eliminate the Japanese soldiers entrenched in their underground bunkers and tunnels.
- Relentless Resistance: The Japanese soldiers fought with extreme determination, often to the death. They were deeply entrenched and well-supplied, making each advance a costly struggle for the Marines.
The battle underscored the fierce determination of the Japanese military and the high cost of fighting them.
4. The Symbolism of the Flag Raising
The raising of the American flag on Mount Suribachi became one of the most iconic images of World War II.
- Morale Boost: Joe Rosenthal’s photograph of the flag raising was widely reproduced in the media. It served as a powerful symbol of American resolve and determination to defeat Japan, boosting morale on the home front and among service members.
- Propaganda Value: The image was used for propaganda purposes, portraying the Americans as triumphant and determined in the face of adversity.
- Enduring Legacy: The photograph later became the model for the U.S. Marine Corps War Memorial in Arlington, Virginia, solidifying its place in American history and collective memory.
While the photograph captured a staged event, it nevertheless became a potent symbol of American strength and the sacrifices made during the war.
5. Reassessing Kamikaze Effectiveness
While the kamikaze attacks were a source of concern for the Americans, Iwo Jima provided some insights into their actual impact.
- Limited Success at Iwo Jima: Due to Iwo Jima’s distance from Japan, the kamikaze aircraft were unable to reach the American fleet in significant numbers during the battle.
- Increased Use at Okinawa: However, the Japanese took note of this and prepared for a more extensive kamikaze campaign during the invasion of Okinawa in April 1945. At Okinawa, the kamikaze inflicted serious losses on the American fleet.
Iwo Jima offered a mixed message regarding the effectiveness of kamikaze attacks, highlighting the potential for damage but also the limitations imposed by distance and logistical factors.
6. The High Cost of Invading Japan
The Battle of Iwo Jima, along with the subsequent battle of Okinawa, profoundly influenced American perceptions of the potential cost of invading Japan.
- Japanese Determination: The ferocious resistance at Iwo Jima and Okinawa demonstrated that the Japanese were willing to fight to the death to defend their homeland.
- High Casualties: The heavy casualties suffered by the Americans in these battles suggested that an invasion of Japan would result in even greater losses on both sides.
- Suicidal Defense: American planners realized that Japan would likely mount a suicidal defense of the home islands, making an invasion an extremely costly and protracted affair.
This realization played a significant role in the eventual decision to use atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki, with the aim of forcing Japan’s surrender and avoiding a bloody invasion.
7. The Impact on Post-War Strategic Thinking
The lessons learned from the Battle of Iwo Jima extended beyond the immediate context of World War II and influenced American strategic thinking in the post-war era.
- Emphasis on Air Power: The importance of air power in the Pacific campaign, highlighted by the strategic value of Iwo Jima’s airfields, contributed to the growing emphasis on air power in American military doctrine.
- Nuclear Deterrence: The potential for massive casualties in a conventional invasion of Japan, underscored by the experiences of Iwo Jima and Okinawa, strengthened the argument for nuclear deterrence as a means of preventing future large-scale conflicts.
- Understanding Cultural Differences: The battle also highlighted the importance of understanding cultural differences and the motivations of enemy forces. The Japanese willingness to fight to the death was a stark contrast to American expectations and influenced subsequent military planning.
Iwo Jima served as a harsh lesson in the realities of warfare and the complexities of dealing with determined adversaries.
8. Evolving Military Strategies and Tactics
The Battle of Iwo Jima prompted a reevaluation of military strategies and tactics, leading to several key adjustments.
- Improved Amphibious Assaults: The challenges encountered during the initial landings on Iwo Jima spurred the development of more effective amphibious assault techniques. This included enhanced pre-invasion bombardment and better coordination between naval, air, and ground forces.
- Flame Warfare: The effectiveness of flamethrowers in clearing out Japanese bunkers and tunnels led to increased reliance on flame warfare in subsequent battles. This involved the development of more advanced flamethrower technology and specialized training for flame warfare units.
- Tunnel Warfare: The Japanese defensive strategy on Iwo Jima highlighted the importance of tunnel warfare. American forces developed new tactics and equipment for combating enemy forces in underground environments, including the use of explosives and specialized demolition teams.
These tactical innovations, born out of the harsh lessons of Iwo Jima, significantly improved the effectiveness of American forces in later engagements.
9. Technological Advancements and Innovation
The Battle of Iwo Jima spurred technological advancements and innovation across various fields.
- Improved Communications: The need for reliable communication between units during the battle led to the development of more robust and secure communication systems. This included advancements in radio technology and the use of portable communication devices.
- Medical Advancements: The high casualty rate at Iwo Jima prompted advancements in medical care and evacuation procedures. This included the development of more effective battlefield triage techniques and the use of helicopters for rapid medical evacuation.
- Logistical Improvements: Supplying troops on Iwo Jima was a logistical challenge. This led to innovations in supply chain management, including the use of amphibious vehicles and improved cargo handling techniques.
These technological advancements not only improved the effectiveness of American forces but also had broader applications in civilian life.
10. The Human Cost and Psychological Impact
The Battle of Iwo Jima had a profound human cost and a lasting psychological impact on the soldiers who fought there.
- Post-Traumatic Stress: Many veterans of Iwo Jima suffered from post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) due to the intense combat and the loss of comrades. The battle served as a stark reminder of the psychological toll of war.
- Moral Dilemmas: Soldiers faced difficult moral dilemmas during the battle, such as the decision to use flamethrowers on enemy soldiers trapped in bunkers. These dilemmas had a lasting impact on their consciences.
- Sense of Duty and Sacrifice: Despite the horrors of the battle, many soldiers expressed a strong sense of duty and a willingness to sacrifice for their country. This sense of duty and sacrifice became a defining characteristic of the “Greatest Generation.”
The Battle of Iwo Jima serves as a poignant reminder of the human cost of war and the importance of supporting veterans.
11. Impact on Public Opinion and War Support
The Battle of Iwo Jima significantly impacted public opinion and support for the war effort.
- Awareness of the War’s Brutality: The extensive media coverage of the battle, including graphic photographs and firsthand accounts, brought the brutality of the war home to the American public. This increased awareness of the sacrifices being made by American soldiers.
- Reinforced Determination: Despite the high casualties, the victory at Iwo Jima reinforced the public’s determination to defeat Japan. The iconic image of the flag raising on Mount Suribachi became a symbol of American resolve.
- Debate on War Strategy: The heavy losses at Iwo Jima sparked debate about the effectiveness of the current war strategy. Some questioned whether the “island hopping” campaign was worth the cost in lives.
The battle contributed to a more nuanced understanding of the war and the challenges facing American forces.
12. Influencing the Decision to Use the Atomic Bomb
The Battle of Iwo Jima played a significant role in influencing the decision to use atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
- Alternative to Invasion: The high casualties at Iwo Jima and Okinawa convinced many American leaders that a conventional invasion of Japan would be too costly in terms of lives. The atomic bomb offered an alternative to invasion.
- Ending the War Quickly: The use of the atomic bomb was seen as a way to end the war quickly and avoid further bloodshed. The potential for a prolonged and devastating invasion of Japan was deemed unacceptable.
- Strategic Calculation: While the decision to use the atomic bomb was complex and multifaceted, the experiences of Iwo Jima and Okinawa undoubtedly factored into the strategic calculation.
The battle served as a stark reminder of the potential consequences of a full-scale invasion of Japan.
13. Key Takeaways for Military Leadership
The Battle of Iwo Jima provided several key takeaways for military leadership.
- Importance of Intelligence: Accurate intelligence about enemy strength, fortifications, and tactics is crucial for planning military operations. The underestimation of Japanese defenses on Iwo Jima contributed to the high casualty rate.
- Adaptability and Flexibility: Military leaders must be adaptable and flexible in the face of unexpected challenges. The Japanese defensive strategy on Iwo Jima required American forces to adjust their tactics and strategies on the fly.
- Effective Communication: Clear and effective communication is essential for coordinating military operations. The challenges of communication on Iwo Jima highlighted the need for more robust and reliable communication systems.
These lessons learned from Iwo Jima have had a lasting impact on military leadership and training.
14. Understanding Japanese Culture and Mindset
The Battle of Iwo Jima provided valuable insights into Japanese culture and mindset.
- Bushido Code: The Japanese soldiers’ willingness to fight to the death was rooted in the Bushido code, a traditional samurai code of conduct that emphasized loyalty, honor, and self-sacrifice.
- Rejection of Surrender: Surrender was seen as a sign of weakness and dishonor in Japanese culture. This explains why so few Japanese soldiers surrendered during the battle.
- Emperor Worship: The Japanese emperor was considered a divine figure, and loyalty to the emperor was a central tenet of Japanese society. This motivated soldiers to fight fiercely in defense of their country and their emperor.
Understanding these cultural factors is essential for comprehending the behavior of Japanese soldiers during the war.
15. Long-Term Geopolitical Implications
The Battle of Iwo Jima had long-term geopolitical implications.
- Shifting Power Dynamics: The American victory in the Pacific War marked a shift in global power dynamics. The United States emerged as the dominant power in the Pacific region, while Japan’s influence declined.
- U.S.-Japan Relations: The war left a legacy of mistrust and animosity between the United States and Japan. However, in the decades following the war, the two countries forged a close alliance based on shared interests and mutual respect.
- Regional Stability: The American presence in the Pacific region has contributed to regional stability and security. The U.S.-Japan alliance has played a key role in maintaining peace and stability in the region.
The Battle of Iwo Jima was a pivotal event that shaped the geopolitical landscape of the Pacific.
16. Memorializing the Battle and Honoring Veterans
The Battle of Iwo Jima is memorialized in numerous ways, honoring the veterans who fought there and preserving the memory of the battle.
- U.S. Marine Corps War Memorial: The U.S. Marine Corps War Memorial in Arlington, Virginia, is a prominent symbol of the battle and a tribute to the Marines who fought and died on Iwo Jima.
- Iwo Jima Association of America: The Iwo Jima Association of America is a non-profit organization dedicated to preserving the history of the battle and honoring the veterans who served there.
- Museum Exhibits: Many museums around the world feature exhibits on the Battle of Iwo Jima, providing historical context and personal stories from the battle.
These memorials and organizations ensure that the sacrifices made at Iwo Jima are never forgotten.
17. Iwo Jima’s Influence on War Films and Literature
The Battle of Iwo Jima has been the subject of numerous war films and literary works.
- Flags of Our Fathers: Clint Eastwood’s “Flags of Our Fathers” (2006) explores the story behind the iconic flag raising photograph and the experiences of the soldiers who fought on Iwo Jima.
- Iwo Jima: Amphibious Epic: Richard Wheeler’s “Iwo Jima: Amphibious Epic” (1980) provides a comprehensive account of the battle, based on extensive research and interviews with veterans.
- Letters from Iwo Jima: Clint Eastwood’s “Letters from Iwo Jima” (2006), told the story from the perspective of the Japanese soldiers defending the island.
These films and books have helped to popularize the story of Iwo Jima and to educate the public about the battle.
18. Iwo Jima as a Case Study in Military Academies
The Battle of Iwo Jima is often studied as a case study in military academies around the world.
- Leadership and Decision-Making: The battle provides valuable lessons in leadership and decision-making under pressure. Military leaders can learn from the successes and failures of the commanders who fought on Iwo Jima.
- Logistics and Planning: The battle highlights the importance of logistics and planning in military operations. The challenges of supplying troops on Iwo Jima underscore the need for effective logistical support.
- Tactical Innovation: The battle demonstrates the importance of tactical innovation in the face of a determined enemy. American forces had to adapt their tactics to overcome the Japanese defensive strategy.
Iwo Jima offers a rich learning experience for future military leaders.
19. The Battle’s Ethical and Moral Dimensions
The Battle of Iwo Jima raises important ethical and moral questions.
- Use of Force: The battle prompts reflection on the ethical implications of using overwhelming force against an enemy. The destruction of Japanese fortifications on Iwo Jima resulted in the deaths of thousands of soldiers.
- Treatment of Prisoners: The treatment of Japanese prisoners of war during the battle raises questions about the ethical standards of warfare. Some American soldiers mistreated Japanese prisoners, while others followed the rules of engagement.
- Civilian Casualties: While Iwo Jima was uninhabited, the battle raises broader questions about the ethical responsibility to minimize civilian casualties in war.
These ethical considerations are an important part of understanding the Battle of Iwo Jima.
20. Modern Relevance and Lessons for Future Conflicts
The lessons learned from the Battle of Iwo Jima remain relevant in modern warfare.
- Urban Warfare: The challenges of fighting in underground environments on Iwo Jima are similar to those encountered in modern urban warfare. The battle provides valuable insights into the tactics and strategies needed to succeed in urban combat.
- Asymmetric Warfare: The Japanese defensive strategy on Iwo Jima is an example of asymmetric warfare, where a weaker force uses unconventional tactics to counter a stronger enemy. This type of warfare is increasingly common in modern conflicts.
- Psychological Warfare: The Battle of Iwo Jima highlights the importance of psychological warfare. Both sides used propaganda and other techniques to influence the morale and behavior of their opponents.
The Battle of Iwo Jima offers valuable lessons for understanding and preparing for future conflicts.
In conclusion, the Battle of Iwo Jima was a pivotal event that shaped American understanding of the Pacific War, military strategy, and the human cost of conflict. From its strategic implications to its impact on public opinion and ethical considerations, the battle continues to offer valuable lessons for military leaders, policymakers, and citizens alike. Explore the wealth of resources available at LEARNS.EDU.VN to deepen your understanding of this crucial chapter in history and its lasting impact on the world.
For more information, visit learns.edu.vn or contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States. You can also reach us on WhatsApp at +1 555-555-1212.
FAQ: Battle of Iwo Jima
1. Why was Iwo Jima so strategically important during World War II?
Iwo Jima was strategically vital due to its location between the Mariana Islands (American-held) and Japan. It served as an essential airfield for U.S. bombers and fighter escorts, facilitating air campaigns against the Japanese mainland.
2. What were the main challenges faced by American forces during the Battle of Iwo Jima?
American forces faced heavily fortified Japanese positions, complex tunnel systems, and relentless resistance. The volcanic terrain and harsh conditions also contributed to the difficulties of the battle.
3. How did the Battle of Iwo Jima influence the decision to use atomic bombs on Japan?
The high casualties and fierce resistance at Iwo Jima, along with Okinawa, contributed to the perception that invading Japan would be exceedingly costly. This influenced the decision to use atomic bombs as a means to force Japan’s surrender and avoid a large-scale invasion.
4. What is the significance of the flag raising on Mount Suribachi?
The flag raising on Mount Suribachi became an iconic symbol of American resolve and determination during World War II. It boosted morale at home and among service members, and the image has endured as a symbol of American sacrifice and victory.
5. What role did kamikaze attacks play during the Battle of Iwo Jima?
While kamikaze attacks were not as prevalent at Iwo Jima due to its distance from Japan, the Japanese took note of their potential impact. This led to a more extensive use of kamikaze tactics during the subsequent Battle of Okinawa, causing significant damage to the American fleet.
6. What were the key military lessons learned from the Battle of Iwo Jima?
Key lessons included the importance of accurate intelligence, adaptable tactics, effective communication, and the understanding of enemy culture and mindset. These lessons have influenced military training and strategy ever since.
7. How did the Battle of Iwo Jima impact public opinion in the United States?
The battle’s extensive media coverage, including graphic images and firsthand accounts, brought the brutal realities of war to the American public. While the high casualties caused concern, the victory at Iwo Jima also reinforced the determination to defeat Japan.
8. In what ways is the Battle of Iwo Jima memorialized today?
The Battle of Iwo Jima is memorialized through the U.S. Marine Corps War Memorial in Arlington, Virginia, museum exhibits, and organizations such as the Iwo Jima Association of America. These memorials and organizations ensure that the sacrifices made at Iwo Jima are never forgotten.
9. What ethical and moral questions are raised by the Battle of Iwo Jima?
The battle raises questions about the use of force, the treatment of prisoners, and the responsibility to minimize civilian casualties in war. These ethical considerations are an important part of understanding the complexities of the battle.
10. How does the Battle of Iwo Jima remain relevant in modern warfare?
The lessons learned from Iwo Jima, such as urban warfare tactics and asymmetric warfare strategies, remain relevant in modern conflicts. The battle offers valuable insights into the challenges of fighting determined enemies and the importance of psychological warfare.