Peer to peer learning is transforming education and workplace training. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we believe in empowering individuals through collaborative learning experiences. This comprehensive guide explores peer-to-peer learning, its benefits, implementation strategies, and how it can revolutionize your learning journey. Dive in to discover how this powerful approach fosters knowledge sharing, skill development, and a vibrant learning community. Discover effective learning techniques and collaborative study methods that enhance educational outcomes.
1. Defining Peer-to-Peer Learning
Peer-to-peer learning, often abbreviated as P2P learning, represents a dynamic and collaborative educational approach where individuals with similar levels of understanding engage in mutual learning and teaching. This methodology moves away from traditional hierarchical models where knowledge flows solely from instructor to student, fostering an environment of shared responsibility and active participation. The core principle is that learning becomes a reciprocal process, with peers alternating roles as both learners and educators, enhancing comprehension and retention through shared experiences and diverse perspectives.
 Peer-to-peer learning environment
Peer-to-peer learning environment
2. Peer Learning in Education and the Workplace: Key Differences
While the essence of peer learning remains consistent, its application differs significantly between educational settings and professional environments. In schools and universities, peer learning is often integrated into the curriculum to enhance understanding of academic subjects, promote teamwork, and develop social skills. Activities may include group projects, study sessions, and peer tutoring, all aimed at reinforcing concepts and fostering a collaborative spirit.
In the workplace, peer-to-peer learning is more focused on professional development, skills enhancement, and knowledge sharing. It takes various forms such as mentoring programs, job shadowing, and collaborative problem-solving sessions. The emphasis is on practical application and continuous improvement, leveraging the expertise within the organization to foster a culture of learning and innovation. Here’s a detailed comparison:
| Feature | Classroom Setting | Workplace Setting |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Academic understanding, teamwork | Professional development, skills enhancement |
| Activities | Group projects, peer tutoring | Mentoring, job shadowing |
| Focus | Theoretical knowledge | Practical application |
| Environment | Structured, curriculum-based | Informal, experience-based |
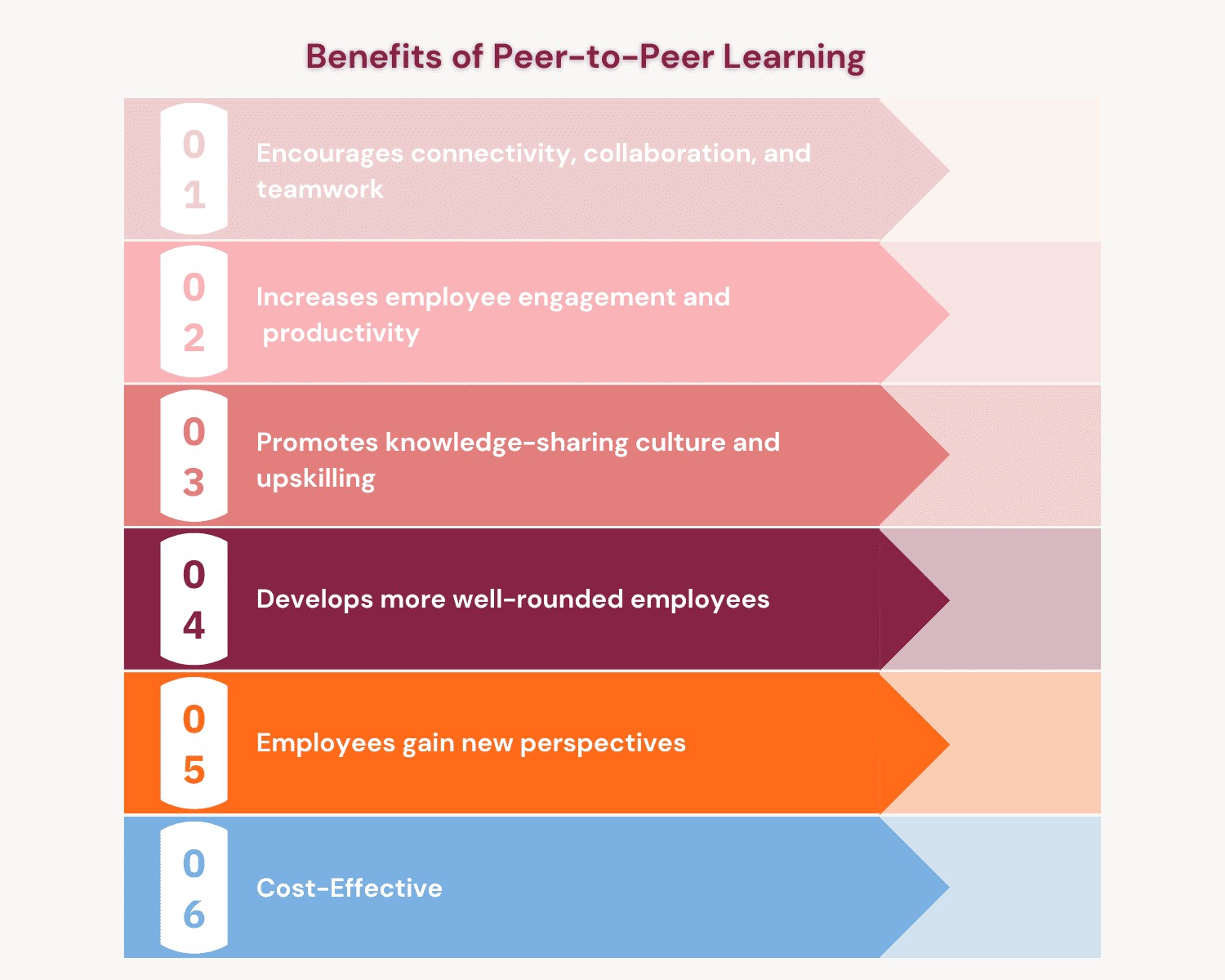
3. Exploring the Benefits of Peer-to-Peer Learning
Peer-to-peer learning offers a multitude of advantages, making it an invaluable asset in both academic and professional spheres. By fostering collaboration, enhancing engagement, and promoting knowledge sharing, P2P learning creates a dynamic and effective learning ecosystem. Let’s delve into the specific benefits:
3.1. Enhanced Collaboration and Teamwork
Peer learning naturally encourages collaboration and teamwork. When individuals work together to understand and solve problems, they develop essential collaborative skills. They learn to communicate effectively, share ideas, and leverage each other’s strengths, which are crucial in any team-oriented environment.
3.2. Increased Engagement and Motivation
Traditional learning environments can sometimes lead to passive participation. Peer learning, however, actively engages participants, making them more invested in the learning process. The act of teaching others reinforces one’s own understanding and provides a sense of accomplishment, thereby boosting motivation.
3.3. Personalized Learning Experience
Peer-to-peer learning allows for a more personalized learning experience. Individuals can learn at their own pace and focus on areas where they need the most help. This tailored approach can be particularly beneficial for those who struggle with traditional teaching methods.
3.4. Development of Critical Thinking Skills
Engaging in discussions, debates, and problem-solving activities with peers fosters critical thinking skills. Participants learn to analyze information, evaluate different perspectives, and formulate well-reasoned arguments. These skills are invaluable in both academic and professional settings.
3.5. Cost-Effectiveness
Implementing peer-to-peer learning can be a cost-effective alternative to traditional training programs. By leveraging the existing knowledge and skills within an organization or educational institution, it reduces the need for external instructors and resources.
3.6. Promotion of Knowledge Sharing
Peer learning fosters a culture of knowledge sharing. Participants are encouraged to share their expertise, insights, and experiences, creating a rich and diverse learning environment. This collective knowledge benefits everyone involved and promotes continuous improvement.
3.7. Improved Communication Skills
Teaching and explaining concepts to peers enhances communication skills. Participants learn to articulate their thoughts clearly, listen actively, and adapt their communication style to different audiences. These skills are essential for effective collaboration and leadership.
3.8. Increased Confidence
Helping others understand complex topics can significantly boost self-confidence. As individuals see the positive impact of their teaching, they gain a greater sense of competence and self-worth, which can translate into improved performance and greater willingness to take on new challenges.
4. Practical Examples of Peer-to-Peer Learning in the Workplace
Peer-to-peer learning manifests in various forms within the workplace, each designed to foster specific skills and address unique challenges. Here are some common and effective examples:
4.1. Action Learning Groups
Action learning groups consist of small teams, typically comprising five to seven individuals, who collaborate to tackle complex, often seemingly insurmountable problems. These groups emphasize insightful questioning, reflective listening, and the generation of innovative actions. By working together, team members not only develop problem-solving skills but also cultivate leadership qualities and a sense of autonomy.
4.2. Debates
Debates offer a structured platform for employees to present and defend different viewpoints. This activity encourages critical thinking, analytical skills, and the ability to articulate ideas persuasively. While not always focused on generating immediate actions, debates foster a deeper understanding of diverse perspectives and enhance decision-making capabilities.
4.3. Discussion Groups
Discussion groups provide a collaborative space for employees to share insights, opinions, and expertise on specific topics. These sessions facilitate the exchange of ideas, promote research and argumentation, and help identify and rectify errors. By engaging in thoughtful discussions, participants broaden their understanding and develop their communication skills.
4.4. Coaching
Peer coaching involves a mutually beneficial relationship where colleagues support each other in learning new concepts, sharing ideas, and resolving work-related challenges. Coaches can be supervisors, mentors, or experienced employees who offer guidance and support. Unlike traditional coaching, peer coaching emphasizes a give-and-take approach, fostering a collaborative and supportive environment.
4.5. Mentoring
Peer mentoring pairs experienced individuals with junior employees to provide guidance, advice, and support. Mentors share their knowledge, skills, and experiences to help mentees develop professionally and personally. This relationship is typically less structured than coaching and focuses on the mentee’s specific needs and goals.
4.6. Lunch and Learns
Lunch and learns, also known as “brown bag” events, are informal sessions where employees gather during lunch breaks to discuss topics of interest or address work-related challenges. These sessions provide a relaxed and social environment for knowledge sharing and networking. Employees can learn from each other, exchange ideas, and build relationships.
4.7. Peer Performance Reviews
Peer performance reviews involve colleagues evaluating each other’s performance, skills, and attitudes. These reviews provide managers with a more comprehensive understanding of an employee’s strengths, weaknesses, and potential. Peer reviews can also foster a culture of accountability and continuous improvement.
5. How to Successfully Implement Peer-to-Peer Learning in Your Organization
Implementing peer-to-peer learning effectively requires careful planning, a supportive environment, and the right tools. Here are some key steps to ensure a successful implementation:
5.1. Identify Learning Needs and Objectives
Before launching a peer-to-peer learning program, identify the specific learning needs and objectives of your organization. Determine which skills and knowledge areas would benefit most from a collaborative learning approach.
5.2. Select and Train Facilitators
Nominate peer learning facilitators who can guide the learning process, keep conversations flowing, and ensure that all participants are actively involved. Provide facilitators with training on effective communication, facilitation techniques, and conflict resolution.
5.3. Implement a Buddy System
Pair new hires with experienced colleagues who can act as their buddies during onboarding. Buddies help new employees integrate into the workplace, provide essential skills training, and foster social connections.
5.4. Incentivize Participation
Encourage participation in peer-to-peer learning by offering incentives such as recognition, career development opportunities, or other rewards. Make it clear that participation is valued and contributes to employees’ professional growth.
5.5. Invest in Collaborative Learning Tools
Invest in collaborative learning tools and platforms that facilitate communication, knowledge sharing, and project management. These tools can include online forums, shared document repositories, video conferencing software, and project management applications.
5.6. Create a Supportive Environment
Foster a supportive and inclusive environment where employees feel comfortable sharing their knowledge, asking questions, and providing feedback. Encourage open communication, respect for diverse perspectives, and a willingness to learn from each other.
5.7. Measure and Evaluate Results
Regularly measure and evaluate the results of your peer-to-peer learning program to assess its effectiveness and identify areas for improvement. Collect feedback from participants, track key metrics such as knowledge retention and skill development, and make adjustments as needed.
6. LEARNS.EDU.VN: Your Partner in Peer-to-Peer Learning
At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing you with the resources and tools you need to implement successful peer-to-peer learning programs. Our comprehensive platform offers:
6.1. A Wide Range of Learning Resources
Access a vast library of learning materials, including articles, videos, tutorials, and case studies, covering a wide range of topics and skills.
6.2. Collaborative Learning Tools
Utilize our collaborative learning tools, such as online forums, shared document repositories, and video conferencing software, to facilitate communication and knowledge sharing among your peers.
6.3. Expert Guidance and Support
Benefit from the guidance and support of our experienced educators and trainers, who can help you design and implement effective peer-to-peer learning programs.
6.4. Personalized Learning Paths
Create personalized learning paths tailored to your specific needs and goals, allowing you to focus on the skills and knowledge areas that are most important to you.
7. Optimizing Peer Learning with Technology
The integration of technology significantly enhances the effectiveness and reach of peer learning initiatives. Digital tools facilitate seamless communication, knowledge sharing, and collaboration, making peer learning more accessible and engaging. Here are some key technologies that can optimize peer learning:
7.1. Learning Management Systems (LMS)
LMS platforms provide a centralized hub for organizing and delivering learning content, tracking progress, and facilitating communication. Features such as discussion forums, group project spaces, and peer assessment tools enable collaborative learning experiences.
7.2. Collaboration Platforms
Tools like Microsoft Teams, Slack, and Google Workspace facilitate real-time communication, document sharing, and project collaboration. These platforms enable peers to connect, share ideas, and work together on projects, regardless of their physical location.
7.3. Video Conferencing Tools
Video conferencing tools such as Zoom, Google Meet, and Skype enable face-to-face interactions, fostering a sense of connection and community among peers. These tools are particularly useful for virtual mentoring sessions, group discussions, and collaborative problem-solving.
7.4. Social Learning Platforms
Social learning platforms create a social network for learners to connect, share knowledge, and collaborate. Features such as profiles, activity feeds, and discussion groups enable peers to learn from each other’s experiences and insights.
7.5. Mobile Learning Apps
Mobile learning apps provide learners with access to learning content and collaborative tools on their smartphones and tablets. This enables learning on the go, making it easier for peers to connect and collaborate at any time and from anywhere.
8. Addressing Challenges in Peer-to-Peer Learning
While peer-to-peer learning offers numerous benefits, it is not without its challenges. Addressing these challenges proactively is essential for ensuring the success of peer learning initiatives. Some common challenges include:
8.1. Unequal Participation
In some peer learning groups, certain individuals may dominate the conversation while others remain passive. To address this, facilitators should encourage active participation from all members and ensure that everyone has an opportunity to share their ideas and perspectives.
8.2. Knowledge Gaps
Peers may have varying levels of knowledge and expertise, which can create challenges in the learning process. To address this, facilitators should provide resources and support to help peers bridge knowledge gaps and ensure that everyone has a solid understanding of the subject matter.
8.3. Personality Conflicts
Personality conflicts can arise in any group setting, including peer learning groups. To address this, facilitators should establish clear guidelines for respectful communication and conflict resolution. They should also be prepared to mediate conflicts and help peers find common ground.
8.4. Lack of Motivation
Some individuals may lack the motivation to participate in peer learning activities. To address this, facilitators should emphasize the benefits of peer learning and provide incentives for participation. They should also create a fun and engaging learning environment that encourages active involvement.
8.5. Time Constraints
Peers may have limited time to devote to peer learning activities due to work or other commitments. To address this, facilitators should schedule activities at convenient times and provide flexible options for participation. They should also ensure that activities are focused and efficient, maximizing the use of available time.
9. Peer-to-Peer Learning vs. Traditional Learning: A Detailed Comparison
Understanding the differences between peer-to-peer learning and traditional learning methods is crucial for determining which approach is most suitable for specific educational or training needs. Here’s a detailed comparison:
| Feature | Peer-to-Peer Learning | Traditional Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Role of the Learner | Active participant, both learner and teacher | Passive recipient of information |
| Role of the Instructor | Facilitator, guide | Primary source of knowledge |
| Learning Environment | Collaborative, interactive | Structured, teacher-centered |
| Pace of Learning | Flexible, self-paced | Fixed, predetermined |
| Focus | Application of knowledge, skill development | Acquisition of theoretical knowledge |
| Engagement | High, actively involved | Can be passive, dependent on teaching style |
| Feedback | Immediate, from peers | Delayed, from instructor |
| Cost | Typically lower, leveraging existing resources | Can be higher, requiring external instructors and resources |
| Customization | Highly personalized, tailored to individual needs | Less personalized, standardized curriculum |
| Skill Development | Emphasizes teamwork, communication, and critical thinking | Focuses on individual knowledge acquisition |
10. The Future of Peer-to-Peer Learning
The future of peer-to-peer learning is bright, with increasing recognition of its effectiveness and potential in both educational and professional contexts. As technology continues to evolve and learning needs become more diverse, peer learning is poised to play an even greater role in shaping the future of education and training.
10.1. Increased Use of Technology
Technology will continue to drive the evolution of peer-to-peer learning, with the development of new tools and platforms that facilitate communication, collaboration, and knowledge sharing. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) may also be used to personalize learning experiences and match peers with complementary skills and knowledge.
10.2. Greater Emphasis on Personalized Learning
Personalized learning will become increasingly important, with peer learning playing a key role in tailoring learning experiences to individual needs and goals. Adaptive learning technologies may be used to assess learners’ strengths and weaknesses and recommend specific peer learning activities to address their individual needs.
10.3. Integration with Formal Education
Peer-to-peer learning will become more integrated with formal education, with schools and universities incorporating collaborative learning activities into their curricula. This will help students develop essential teamwork, communication, and critical thinking skills, preparing them for success in the workplace.
10.4. Expansion into New Industries and Sectors
Peer-to-peer learning is already being used in a wide range of industries and sectors, including healthcare, finance, and technology. As its benefits become more widely recognized, it is likely to expand into new areas such as government, non-profit organizations, and community development.
10.5. Focus on Lifelong Learning
Peer-to-peer learning will play an increasingly important role in lifelong learning, providing individuals with opportunities to continuously update their skills and knowledge throughout their careers. Online peer learning communities will enable individuals to connect with experts and peers from around the world, fostering a culture of continuous learning and professional development.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About Peer-to-Peer Learning
Here are some frequently asked questions about peer-to-peer learning:
- What is peer-to-peer learning? Peer-to-peer learning is a collaborative educational approach where individuals with similar levels of understanding engage in mutual learning and teaching.
- How does peer-to-peer learning differ from traditional learning? In peer-to-peer learning, learners are active participants, while in traditional learning, they are often passive recipients of information.
- What are the benefits of peer-to-peer learning? Benefits include enhanced collaboration, increased engagement, personalized learning, and cost-effectiveness.
- How can I implement peer-to-peer learning in my organization? Identify learning needs, select facilitators, implement a buddy system, and invest in collaborative learning tools.
- What technologies can optimize peer learning? Learning Management Systems (LMS), collaboration platforms, video conferencing tools, and social learning platforms.
- What are some challenges of peer-to-peer learning? Challenges include unequal participation, knowledge gaps, and personality conflicts.
- How can I address challenges in peer-to-peer learning? Encourage active participation, provide resources to bridge knowledge gaps, and establish clear guidelines for communication.
- Is peer-to-peer learning suitable for all subjects? Yes, peer-to-peer learning can be adapted for various subjects and skill sets.
- How do I measure the success of peer-to-peer learning programs? Track key metrics such as knowledge retention, skill development, and participant satisfaction.
- Where can I find resources to support peer-to-peer learning? LEARNS.EDU.VN offers a wide range of resources, tools, and expert guidance for implementing peer-to-peer learning programs.
Conclusion: Embrace Peer-to-Peer Learning for Enhanced Growth
Peer-to-peer learning is more than just a trend; it’s a powerful approach that transforms how we learn and grow. By fostering collaboration, enhancing engagement, and promoting knowledge sharing, P2P learning empowers individuals and organizations to achieve their full potential. Embrace this dynamic methodology and unlock a world of learning opportunities.
Ready to revolutionize your learning experience? Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today to discover the resources, tools, and expertise you need to implement successful peer-to-peer learning programs. Explore our comprehensive platform and embark on a journey of continuous growth and development. Contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States. Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212. Website: learns.edu.vn. Start learning together, today!
