The learning cycle, also known as experiential learning, is a powerful concept that emphasizes the role of experience in the learning process. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we believe understanding the learning cycle is fundamental for anyone seeking effective and engaging educational experiences. This cycle involves concrete experiences, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation. Let’s explore how this model boosts understanding, critical thinking, and practical skills, leading to enhanced knowledge acquisition, skills development, and effective learning strategies.
1. Understanding the Essence of the Learning Cycle
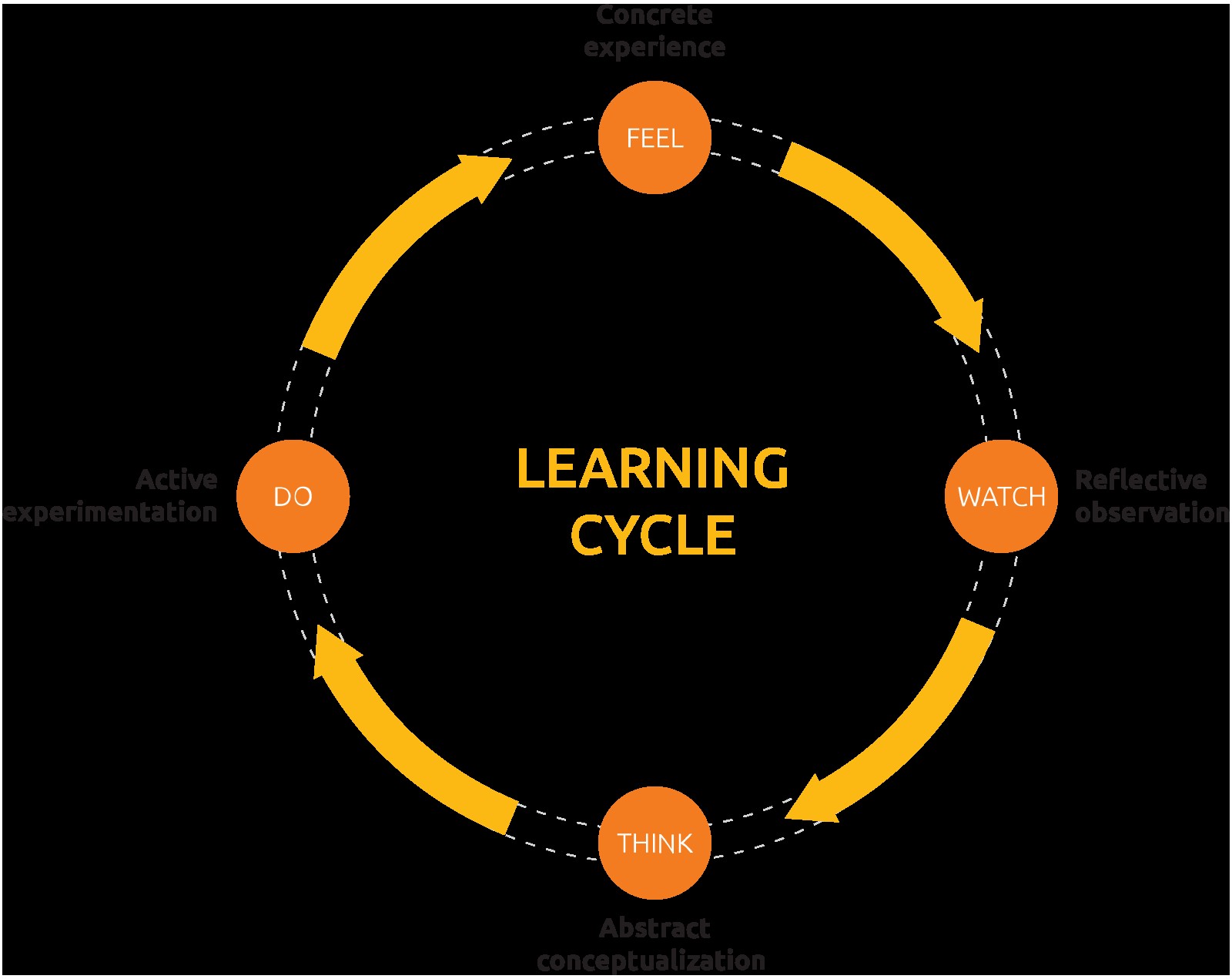
The learning cycle, formalized by David Kolb in 1984, isn’t just a theoretical framework; it’s a dynamic approach to education that acknowledges how individuals learn best. It’s a continuous loop, a journey where experience is the starting point and the destination is a deeper understanding of the world around us. This theory is grounded in the idea that learning is more than just passively receiving information; it’s about actively constructing knowledge through experience.
1.1. The Four Pillars of Kolb’s Learning Cycle
Kolb’s learning cycle is built upon four interconnected stages, each playing a crucial role in transforming experience into knowledge:
- 1.1.1. Concrete Experience (CE): This is where learning begins – an actual experience, a real-life situation, or even a simulation. It’s the foundation upon which all other stages are built. Think of participating in a group project, conducting an experiment, or engaging in a hands-on activity.
- 1.1.2. Reflective Observation (RO): After the experience, comes reflection. This involves carefully observing and thinking about what happened. What worked well? What could have been done differently? It’s about stepping back and analyzing the experience from different perspectives.
- 1.1.3. Abstract Conceptualization (AC): This is the stage where you start making sense of your observations. You begin to form theories, models, or concepts that explain the experience. You connect the experience to existing knowledge and draw conclusions.
- 1.1.4. Active Experimentation (AE): Finally, you put your newly formed concepts to the test. You plan and try out new actions based on what you’ve learned. This leads to new experiences, and the cycle begins again.
1.2. The Significance of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning stands out because it acknowledges that people learn in diverse ways. Some thrive on direct experience, others on reflection, while some prefer theoretical models, and others are driven by action. Kolb’s learning cycle caters to these different learning styles by providing a framework that integrates all four stages.
2. Why Embrace the Learning Cycle?
The learning cycle isn’t just a nice theory; it’s a practical approach that offers numerous benefits for learners of all ages and backgrounds. Embracing this model can lead to a more engaging, effective, and fulfilling learning journey.
2.1. Catering to Diverse Learning Styles
One of the key strengths of the learning cycle is its ability to accommodate different learning preferences. Kolb identified four dominant learning styles based on the combination of two dimensions: “Feeling vs. Thinking” and “Watching vs. Doing.”
- 2.1.1. Diverging (Feeling & Watching): These learners excel at brainstorming and generating ideas. They are imaginative, open-minded, and prefer working in groups.
- 2.1.2. Assimilating (Thinking & Watching): These learners thrive on structure, logical explanations, and clear concepts. They enjoy lectures, reading, and working with models.
- 2.1.3. Converging (Thinking & Doing): These learners are practical problem-solvers. They are technical, application-oriented, and enjoy experimenting with new ideas.
- 2.1.4. Accommodating (Feeling & Doing): These learners are hands-on and intuitive. They enjoy challenges and learn best through trial and error.
2.2. Fostering Deeper Understanding and Retention
By actively engaging in the learning process, learners develop a deeper understanding of the material. The cycle encourages critical thinking, problem-solving, and the ability to apply knowledge to real-world situations. This leads to better retention of information and a more meaningful learning experience.
2.3. Enhancing Motivation and Engagement
The learning cycle makes learning more engaging and enjoyable. By starting with a concrete experience, learners are immediately drawn into the topic. The cycle encourages active participation, collaboration, and a sense of ownership over the learning process, boosting motivation and fostering a love of learning.
3. Practical Applications of the Learning Cycle
The learning cycle is a versatile model that can be applied in various educational settings, from classrooms to corporate training programs. Here are some practical examples of how to integrate the learning cycle into different contexts:
3.1. In the Classroom
- 3.1.1. Science Experiments: Instead of just reading about scientific concepts, students can conduct experiments to experience them firsthand. They can then reflect on their observations, develop theories, and test their hypotheses through further experimentation.
- 3.1.2. Group Projects: Group projects provide opportunities for students to work together, share ideas, and learn from each other’s experiences. By reflecting on the project process, students can identify areas for improvement and develop more effective teamwork skills.
- 3.1.3. Simulations and Role-Playing: Simulations and role-playing activities allow students to experience real-world scenarios in a safe and controlled environment. They can then reflect on their actions, analyze the consequences, and develop strategies for future situations.
3.2. In the Workplace
- 3.2.1. On-the-Job Training: On-the-job training provides employees with practical experience in their roles. By reflecting on their performance, employees can identify areas where they need to improve and develop new skills.
- 3.2.2. Case Studies: Case studies present employees with real-world business challenges. By analyzing the case, developing solutions, and implementing their strategies, employees can learn from their mistakes and develop better decision-making skills.
- 3.2.3. Simulations and Business Games: Business simulations allow employees to experiment with different business strategies in a risk-free environment. By reflecting on the outcomes of their decisions, employees can develop a better understanding of the business and improve their strategic thinking skills.
3.3. In Personal Development
- 3.3.1. Learning a New Skill: Whether it’s playing a musical instrument, learning a new language, or mastering a new software program, the learning cycle can be applied to personal development. Start by trying out the skill, reflect on your progress, develop strategies for improvement, and continue practicing.
- 3.3.2. Overcoming a Challenge: The learning cycle can also be used to overcome personal challenges. By reflecting on past experiences, identifying patterns, developing new approaches, and testing them out, you can learn from your mistakes and develop more effective coping mechanisms.
- 3.3.3. Setting and Achieving Goals: The learning cycle can help you achieve your personal goals. By setting a goal, taking action, reflecting on your progress, adjusting your approach, and continuing to work towards your goal, you can increase your chances of success.
4. Integrating the Learning Cycle with Technology
In today’s digital age, technology can play a significant role in enhancing the learning cycle. From online simulations to virtual reality experiences, technology offers new and exciting ways to engage learners and facilitate deeper understanding.
4.1. Online Simulations and Virtual Reality
Online simulations and virtual reality environments provide immersive and interactive learning experiences. Learners can experiment with different scenarios, make decisions, and see the consequences of their actions in a safe and controlled environment.
4.2. Collaborative Learning Platforms
Collaborative learning platforms enable learners to connect with peers, share ideas, and learn from each other’s experiences. These platforms often include features such as discussion forums, group project tools, and online whiteboards, which facilitate collaboration and knowledge sharing.
4.3. Data Analytics and Personalized Learning
Data analytics can be used to track learner progress, identify areas of weakness, and personalize the learning experience. By analyzing learner data, educators can provide targeted feedback and support, ensuring that each learner receives the attention they need to succeed.
5. The Micro Cycle: Learning Within the Team
As Jan H. G. Klabbers explains in “The Magic Circle: Principles of Gaming & Simulation,” the learning cycle extends beyond the individual to the team dynamic. Within a team, especially during activities like business simulation games, a “micro cycle” emerges, fostering collaborative learning.
5.1. The Four Stages of the Micro Cycle
The micro cycle mirrors the broader learning cycle, but it operates within the context of a team working together on a task. It involves:
- 5.1.1. Action: The team takes action based on their understanding of the situation.
- 5.1.2. Sense Making: The team analyzes the results of their actions and tries to make sense of what happened.
- 5.1.3. Formation and Adjustment of Schemes and Mental Models: The team members adjust their understanding and mental models based on the feedback they receive.
- 5.1.4. Adjusting Repertoire of Actions: The team refines their strategies and approaches based on their new understanding.
5.2. Learning From Each Other
The micro cycle highlights the importance of learning from each other within a team. By sharing their experiences, insights, and perspectives, team members can collectively develop a deeper understanding of the task at hand.
6. Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
While the learning cycle offers a powerful framework for learning, it’s important to be aware of common pitfalls that can hinder its effectiveness. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
6.1. Neglecting Reflection
Reflection is a crucial stage in the learning cycle, but it’s often overlooked. Make sure to allocate sufficient time for reflection and encourage learners to think critically about their experiences.
6.2. Focusing Too Much on Theory
While abstract conceptualization is important, it’s crucial to balance theory with practical experience. Avoid spending too much time on lectures and readings and provide learners with opportunities to apply their knowledge in real-world situations.
6.3. Failing to Adapt to Learning Styles
The learning cycle is most effective when it’s tailored to individual learning styles. Be aware of the different learning preferences and provide a variety of activities that cater to all learners.
6.4. Lack of Follow-Through
The learning cycle is a continuous process, but it’s easy to lose momentum after the initial experience. Make sure to provide ongoing support and encouragement to learners as they continue to experiment and refine their understanding.
7. The Learning Cycle at LEARNS.EDU.VN
At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we are committed to providing educational experiences that are engaging, effective, and tailored to individual learning styles. We believe that the learning cycle is a powerful tool for achieving these goals, and we integrate it into our courses and programs in a variety of ways.
7.1. Experiential Learning Opportunities
We offer a wide range of experiential learning opportunities, including simulations, case studies, group projects, and hands-on activities. These experiences provide learners with the opportunity to apply their knowledge in real-world situations and develop valuable skills.
7.2. Personalized Learning Paths
We understand that every learner is unique, and we offer personalized learning paths that cater to individual learning styles and preferences. Our adaptive learning platform tracks learner progress and provides customized feedback and support, ensuring that each learner receives the attention they need to succeed.
7.3. Expert Instruction and Guidance
Our team of experienced educators and industry experts are dedicated to providing high-quality instruction and guidance. They are passionate about helping learners achieve their goals and are committed to creating a supportive and engaging learning environment.
8. Real-World Examples of the Learning Cycle in Action
To further illustrate the power of the learning cycle, let’s examine some real-world examples of how it’s being used in various settings:
8.1. Medical Education
Medical schools are increasingly incorporating the learning cycle into their curriculum. Students participate in simulations where they diagnose and treat patients, reflect on their performance, and develop strategies for improvement.
8.2. Business Management
Business schools use case studies to present students with real-world business challenges. Students analyze the case, develop solutions, and present their recommendations to a panel of experts.
8.3. Teacher Training
Teacher training programs incorporate the learning cycle by having student teachers observe experienced teachers, reflect on their teaching practices, and develop their own teaching styles.
8.4. Software Development
Software development teams use agile methodologies that emphasize iterative development and continuous feedback. Developers experiment with new features, reflect on their performance, and adjust their approach based on user feedback.
9. The Future of the Learning Cycle
As technology continues to evolve and learning environments become more dynamic, the learning cycle will remain a valuable framework for designing effective and engaging educational experiences.
9.1. Immersive Learning Environments
Virtual reality and augmented reality technologies will create more immersive learning environments that allow learners to experience real-world scenarios in a safe and controlled setting.
9.2. Artificial Intelligence and Personalized Learning
Artificial intelligence will be used to personalize the learning experience and provide learners with customized feedback and support. AI-powered tutors will be able to adapt to individual learning styles and provide targeted instruction.
9.3. Lifelong Learning
The learning cycle will become increasingly important for lifelong learners who need to continuously adapt to new technologies and challenges. Online learning platforms and mobile learning apps will provide learners with access to educational resources anytime, anywhere.
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About the Learning Cycle
To further clarify any questions you may have about the learning cycle, here are some frequently asked questions:
- 10.1. What are the benefits of using the learning cycle? The learning cycle enhances understanding, retention, motivation, and engagement. It also caters to diverse learning styles and promotes critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
- 10.2. How can I implement the learning cycle in my classroom? Incorporate hands-on activities, group projects, simulations, and reflection exercises into your lessons.
- 10.3. Is the learning cycle suitable for all ages? Yes, the learning cycle can be adapted for learners of all ages and backgrounds.
- 10.4. What are the four learning styles in Kolb’s model? Diverging, assimilating, converging, and accommodating.
- 10.5. How does technology enhance the learning cycle? Technology provides immersive learning environments, collaborative platforms, and personalized learning paths.
- 10.6. What is the micro cycle in team learning? The micro cycle involves action, sense-making, formation and adjustment of mental models, and adjusting actions within a team.
- 10.7. How can I avoid common pitfalls when using the learning cycle? Allocate time for reflection, balance theory with practice, adapt to learning styles, and provide ongoing support.
- 10.8. What role does experience play in the learning cycle? Experience is the foundation upon which all other stages are built, transforming experience into knowledge.
- 10.9. Can the learning cycle be used for personal development? Yes, it can be used for learning new skills, overcoming challenges, and achieving personal goals.
- 10.10. How does LEARNS.EDU.VN integrate the learning cycle into its programs? Through experiential learning opportunities, personalized learning paths, and expert instruction.
Conclusion: Embrace the Power of Experiential Learning
The learning cycle is more than just a theory; it’s a roadmap for effective and engaging learning. By embracing the power of experiential learning, you can unlock your full potential and achieve your educational goals. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we are dedicated to providing you with the tools and resources you need to succeed. Explore our courses, connect with our experts, and embark on a journey of lifelong learning.
Ready to take your learning to the next level? Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today and discover a world of knowledge and opportunity. Explore our diverse range of courses and resources designed to empower you with the skills and knowledge you need to thrive in today’s dynamic world. Contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States, or reach out via Whatsapp at +1 555-555-1212. Let learns.edu.vn be your partner in achieving your educational aspirations.
Disclaimer: This article is intended for informational purposes only and does not constitute professional advice. Always consult with qualified professionals for personalized guidance. Information is sourced from reputable educational institutions and research, but readers should verify details independently.