Mastering a new language can unlock personal enrichment and professional opportunities. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we delve into the top 10 most challenging languages for native English speakers to learn, exploring their unique complexities and difficulties. Discover proven techniques to tackle linguistic challenges, gain cultural insights, and achieve fluency effectively. Expand your educational horizons with multilingual expertise, enhancing your cognitive abilities and global career prospects.
1. Understanding Language Learning Difficulty
When we talk about the difficulty of learning a language, it’s important to consider what factors make a language challenging. For English speakers, languages that are vastly different in grammar, pronunciation, and writing systems can present significant hurdles. The Foreign Service Institute (FSI) categorizes languages by the approximate time it takes for a native English speaker to achieve professional working proficiency. This categorization helps learners set realistic goals and allocate study time appropriately.
Understanding the effort required to learn a new language can impact motivation and strategy. Languages in Category I, such as French or Spanish, might take around 600 hours to learn, while Category IV languages, including Arabic and Mandarin Chinese, can require upwards of 2200 hours. LEARNS.EDU.VN offers resources to help you estimate the time investment and plan your language learning journey effectively.
2. Top 10 Hardest Languages for English Speakers
Based on linguistic differences and the time investment required, here’s a rundown of the top 10 hardest languages for English speakers to learn:
2.1. Mandarin Chinese: A Tonal Challenge
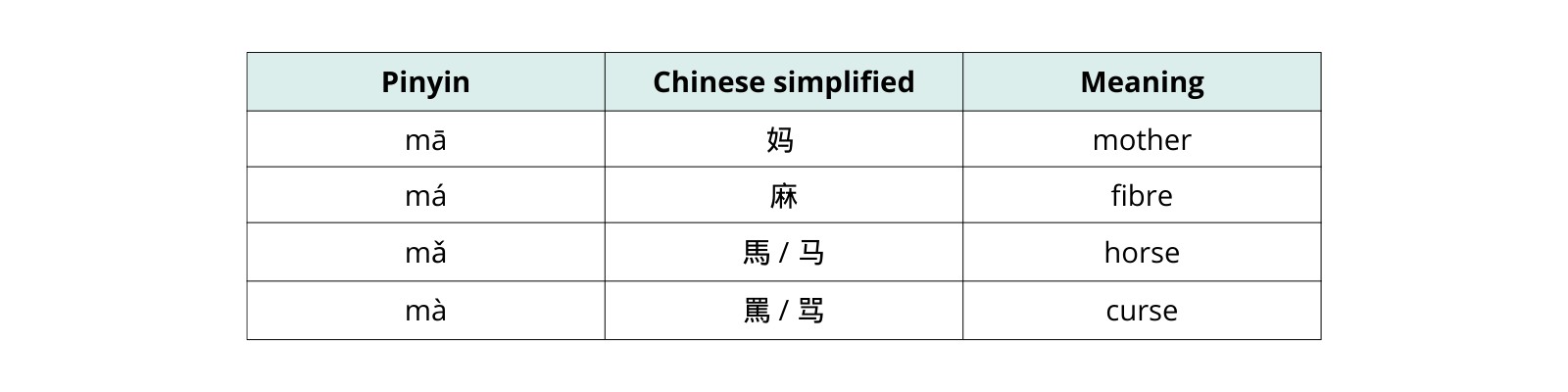
Mandarin Chinese tops the list due to its tonal nature. Each syllable has four main tones, and mispronouncing a tone can completely change the meaning of a word. For example, the syllable “ma” can mean “mother,” “horse,” “hemp,” or “scold,” depending on the tone used.
The writing system, which uses thousands of characters, also poses a considerable challenge. Unlike alphabetic languages, each character represents a word or morpheme, requiring extensive memorization. However, LEARNS.EDU.VN provides mnemonic techniques and structured courses to simplify character learning.
2.2. Arabic: Right-to-Left and Complex Grammar
Arabic presents a unique challenge with its right-to-left script and complex grammatical rules. Arabic verbs have different forms depending on the gender and number of the subject, and the language uses a system of root words from which various forms are derived.
Additionally, the pronunciation of certain sounds can be difficult for English speakers. LEARNS.EDU.VN offers interactive pronunciation guides and cultural immersion materials to help overcome these hurdles.
2.3. Japanese: Multiple Writing Systems
Japanese employs three writing systems: Hiragana, Katakana, and Kanji. Hiragana and Katakana are phonetic scripts, while Kanji consists of thousands of characters borrowed from Chinese. Mastering all three requires significant effort.
Japanese grammar also differs significantly from English. The word order is subject-object-verb, and particles are used to indicate grammatical function. LEARNS.EDU.VN provides detailed grammar explanations and practice exercises to facilitate learning.
2.4. Hungarian: A Unique European Language
Hungarian stands out among European languages due to its Uralic origins, making it unrelated to most other languages in Europe. Its grammar is highly complex, featuring a large number of cases and agglutinative morphology, where suffixes are added to words to express different meanings.
The lack of cognates with English can make vocabulary acquisition challenging. LEARNS.EDU.VN offers thematic vocabulary lists and mnemonics to aid memorization.
2.5. Korean: Linguistic Isolation and Honorifics
Korean is considered a language isolate, meaning it has no known relatives. Its grammar and vocabulary are unique, making it difficult for English speakers to find familiar patterns.
Korean also employs a complex system of honorifics, which are used to show respect based on social status and age. Choosing the correct level of formality is crucial in Korean communication. LEARNS.EDU.VN provides cultural sensitivity training and real-world dialogue examples to master this aspect.
2.6. Finnish: Complex Grammar and Cases
Finnish, like Hungarian, belongs to the Uralic language family and is known for its complex grammar. It has a large number of cases, which indicate the grammatical function of a noun.
Finnish also features vowel harmony, where vowels within a word must belong to certain categories. This can be challenging for English speakers to master. LEARNS.EDU.VN offers interactive exercises to practice vowel harmony and case usage.
2.7. Basque: An Enigmatic Language Isolate
Basque is a language isolate spoken in the Basque Country, a region spanning parts of northern Spain and southwestern France. Its origins are unknown, and it is unrelated to any other known language.
Basque grammar is highly agglutinative, and its phonology includes sounds that are unfamiliar to English speakers. LEARNS.EDU.VN offers phonetic training and cultural insights to aid in learning.
2.8. Navajo: A Verb-Centered Language
Navajo is a Native American language spoken in the Southwestern United States. It is a verb-centered language, meaning that verbs carry much of the meaning in a sentence. Navajo also features complex verb conjugations and sounds that are unfamiliar to English speakers.
The language was famously used as a code during World War II due to its complexity. LEARNS.EDU.VN provides resources to learn Navajo phonology and verb structures.
2.9. Icelandic: Preserving Ancient Roots
Icelandic is a North Germanic language spoken in Iceland. It has changed relatively little since the Old Norse period, making it challenging for modern learners due to its archaic vocabulary and grammar.
Icelandic also features complex noun declensions and verb conjugations. LEARNS.EDU.VN offers historical context and comparative linguistics to enhance understanding.
2.10. Polish: Consonant Clusters and Grammatical Cases
Polish is a West Slavic language known for its complex grammar and challenging pronunciation. It features numerous consonant clusters, making it difficult for English speakers to pronounce words correctly. Polish also has seven cases, which affect the form of nouns, pronouns, and adjectives.
LEARNS.EDU.VN provides pronunciation guides and grammatical exercises to tackle these difficulties effectively.
3. Factors Contributing to Language Learning Difficulty
Several factors contribute to the difficulty of learning a language. These include:
- Linguistic Distance: The greater the differences in grammar, vocabulary, and pronunciation, the harder the language is to learn.
- Writing System: Non-alphabetic scripts or those that read in a different direction can present significant challenges.
- Cultural Differences: Understanding cultural norms and communication styles is crucial for effective language use.
- Motivation and Resources: A learner’s motivation, access to resources, and learning strategies play a significant role in their success.
4. Strategies for Tackling Difficult Languages
While these languages may seem daunting, effective strategies can make the learning process more manageable.
4.1. Setting Realistic Goals and Timeframes
It’s important to set realistic goals and allocate sufficient time for studying. Learning a difficult language requires consistent effort and patience. Plan your study schedule and track your progress to stay motivated.
4.2. Focusing on Pronunciation Early On
Pronunciation is key to understanding and being understood. Use audio resources and practice speaking regularly. Don’t be afraid to imitate native speakers. LEARNS.EDU.VN offers interactive pronunciation tools and feedback.
4.3. Immersing Yourself in the Language
Immerse yourself in the language as much as possible. Watch movies, listen to music, and read books in the target language. This helps you become familiar with the sounds, rhythms, and cultural context of the language.
4.4. Using Spaced Repetition Systems (SRS)
Spaced repetition systems, like Anki, help you memorize vocabulary and grammar through repeated exposure at increasing intervals. This technique is particularly effective for languages with large vocabularies or complex grammar rules.
4.5. Finding a Language Partner or Tutor
Working with a language partner or tutor can provide personalized feedback and support. They can help you practice speaking and writing, and answer any questions you may have. LEARNS.EDU.VN connects learners with experienced tutors.
4.6. Breaking Down Complex Grammar
Complex grammar rules can be overwhelming. Break them down into smaller, more manageable chunks. Focus on understanding the underlying principles and practice applying them in context. LEARNS.EDU.VN offers detailed grammar explanations and exercises.
4.7. Utilizing Online Resources and Apps
Numerous online resources and apps can aid in language learning. These include language learning platforms, dictionaries, and grammar tools. Choose resources that align with your learning style and goals.
4.8. Celebrating Small Wins and Staying Motivated
Learning a difficult language is a marathon, not a sprint. Celebrate small wins and acknowledge your progress. Stay motivated by reminding yourself of your goals and the benefits of learning the language.
5. The Cognitive Benefits of Learning a Difficult Language
Learning a difficult language offers numerous cognitive benefits. These include:
- Improved Memory: Memorizing new vocabulary and grammar rules enhances memory function.
- Enhanced Problem-Solving Skills: Navigating complex grammar and syntax improves problem-solving abilities.
- Increased Cognitive Flexibility: Switching between different languages and cultural contexts enhances cognitive flexibility.
- Better Multitasking Abilities: Managing multiple linguistic systems improves multitasking skills.
- Delayed Onset of Dementia: Research suggests that bilingualism may delay the onset of dementia.
6. Career Opportunities for Multilingual Individuals
In today’s globalized world, multilingual individuals are in high demand. Learning a difficult language can open up numerous career opportunities in fields such as:
- Translation and Interpretation: Translating written and spoken content between languages.
- International Business: Conducting business in foreign markets and communicating with international clients.
- Diplomacy and Government: Representing your country abroad and working on international relations.
- Education: Teaching languages and cultures to others.
- Journalism: Reporting on international news and events.
- Tourism: Guiding and assisting travelers in foreign countries.
7. Cultural Insights Gained Through Language Learning
Language is deeply intertwined with culture. Learning a new language provides insights into the values, beliefs, and customs of another culture. This can lead to greater empathy, understanding, and cross-cultural communication skills.
7.1. Understanding Cultural Nuances
Language learning can reveal cultural nuances that are not always apparent to outsiders. These include nonverbal communication styles, social etiquette, and humor.
7.2. Appreciating Literature and Arts
Learning a language allows you to appreciate literature and arts in their original form. This can provide a deeper understanding of the cultural context and artistic expression.
7.3. Connecting with Native Speakers
Language learning enables you to connect with native speakers on a deeper level. This can lead to meaningful friendships, cultural exchange, and personal growth.
8. How LEARNS.EDU.VN Can Help You Learn
LEARNS.EDU.VN offers a wide range of resources to help you learn difficult languages effectively. Our services include:
- Structured Courses: Comprehensive courses designed to guide you through the language learning process step by step.
- Interactive Exercises: Engaging exercises to practice grammar, vocabulary, and pronunciation.
- Pronunciation Guides: Detailed guides to help you master the sounds of the language.
- Cultural Sensitivity Training: Training to help you understand cultural norms and communication styles.
- Language Tutors: Experienced tutors who can provide personalized feedback and support.
- Community Forums: Forums to connect with other learners and share tips and resources.
- Mobile Apps: Mobile apps to learn on the go.
9. Success Stories of Language Learners
Hearing from others who have successfully learned difficult languages can be inspiring. Here are a few success stories:
- Maria: After years of struggling with Mandarin Chinese, Maria found success by focusing on pronunciation early on and immersing herself in the language through movies and music.
- David: David overcame the challenges of Arabic grammar by breaking down complex rules into smaller chunks and practicing regularly with a language partner.
- Emily: Emily mastered Japanese writing systems by using spaced repetition systems and focusing on learning Kanji characters in context.
10. The Future of Language Learning
Technology continues to transform the landscape of language learning. Innovations such as artificial intelligence, virtual reality, and augmented reality are creating new opportunities for immersive and personalized learning experiences.
10.1. AI-Powered Language Learning
AI-powered language learning platforms can provide personalized feedback on pronunciation and grammar, adapt to your learning style, and offer real-time translation and interpretation.
10.2. Virtual Reality Language Immersion
Virtual reality environments can simulate real-world situations, allowing you to practice speaking and interacting in the target language in a safe and immersive setting.
10.3. Augmented Reality Language Learning
Augmented reality apps can overlay translations and cultural information onto the real world, providing on-the-go learning opportunities.
FAQ: Navigating the Top 10 Hardest Languages to Learn
1. Why are some languages harder to learn than others for English speakers?
The difficulty largely depends on linguistic distance – how different a language is from English in terms of grammar, vocabulary, pronunciation, and writing system. Languages with tonal systems or complex grammatical structures pose greater challenges.
2. How long does it typically take to learn one of the top 10 hardest languages?
Based on the Foreign Service Institute (FSI) data, it can take over 2200 hours of study to achieve professional working proficiency in languages like Mandarin Chinese, Arabic, and Japanese. This translates to approximately 88 weeks of full-time study.
3. What are the most effective strategies for learning a difficult language?
Effective strategies include setting realistic goals, focusing on pronunciation early, immersing yourself in the language, using spaced repetition systems, finding a language partner or tutor, and breaking down complex grammar into manageable parts.
4. How can I stay motivated when learning a challenging language?
Stay motivated by celebrating small wins, reminding yourself of your goals, tracking your progress, connecting with other learners, and finding ways to make the learning process enjoyable, such as watching movies or listening to music in the target language.
5. Are there any cognitive benefits to learning a difficult language?
Yes, learning a difficult language can improve memory, enhance problem-solving skills, increase cognitive flexibility, improve multitasking abilities, and potentially delay the onset of dementia.
6. What career opportunities are available for multilingual individuals?
Multilingual individuals can pursue careers in translation and interpretation, international business, diplomacy and government, education, journalism, tourism, and many other fields that require cross-cultural communication.
7. How does language learning provide cultural insights?
Language learning provides cultural insights by revealing cultural nuances, allowing you to appreciate literature and arts in their original form, and enabling you to connect with native speakers on a deeper level.
8. What resources does LEARNS.EDU.VN offer for learning difficult languages?
LEARNS.EDU.VN offers structured courses, interactive exercises, pronunciation guides, cultural sensitivity training, language tutors, community forums, and mobile apps to support your language learning journey.
9. Can technology help me learn a difficult language more efficiently?
Yes, AI-powered language learning platforms, virtual reality language immersion, and augmented reality apps can provide personalized, immersive, and efficient learning experiences.
10. What is the best approach to tackle languages with different writing systems, like Arabic or Japanese?
Start by focusing on recognizing and writing the individual characters or symbols. Practice regularly, use flashcards or spaced repetition systems, and immerse yourself in texts written in the target script to improve your reading speed and comprehension.
Learning a difficult language is a challenging but rewarding endeavor. By understanding the challenges, implementing effective strategies, and leveraging the resources available at LEARNS.EDU.VN, you can achieve your language learning goals and unlock new opportunities.
Ready to embark on your language learning journey? Visit learns.edu.vn at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States, or contact us via WhatsApp at +1 555-555-1212. Explore our courses and resources to find the perfect fit for your learning style and goals. Start your adventure today!