Remote learning has become increasingly prevalent in today’s educational landscape. But what exactly is it, and how does it work? This comprehensive guide will delve into the core components of remote learning, exploring its benefits, drawbacks, practical examples, implementation strategies, and key differences from online learning.
What is Remote Learning and How Does it Work?
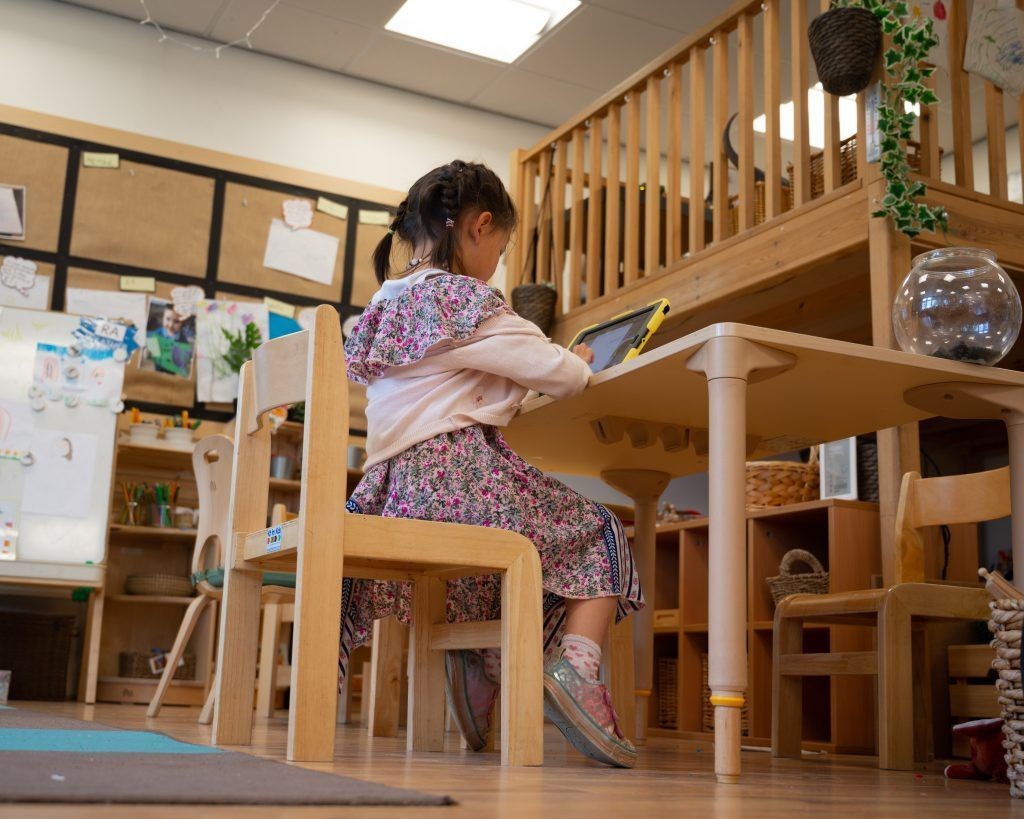
Remote learning, simply defined, is education that takes place outside of a traditional classroom, leveraging technology to connect students and educators. Unlike virtual learning, which is a more established form of online education, remote learning often involves individuals new to the online environment. It’s frequently employed during unforeseen circumstances like scheduling conflicts, illnesses, or widespread disruptions.
A typical remote learning setup involves a virtual classroom platform, such as Google Classroom or Khan Academy, where teachers post assignments, provide feedback, and facilitate communication. Video conferencing tools like Zoom or Skype supplement this platform, enabling direct interaction for lectures, discussions, and check-ins.
Benefits and Disadvantages of Remote Learning
Remote learning presents a unique set of advantages and disadvantages for both educators and students.
Benefits:
- Accessibility: Remote learning expands access to education for those facing geographical barriers, disabilities, or other limitations.
- Flexibility: It offers flexible scheduling, allowing students to learn at their own pace and teachers to customize instruction. Eliminating commutes saves time and resources.
- Personalized Learning: The self-paced nature of remote learning caters to diverse learning styles and allows students to focus on individual needs.
- Enhanced Visual Learning: The visual-heavy nature of online platforms benefits students who thrive in visual learning environments.
Disadvantages:
- Lack of Social Interaction: Reduced face-to-face interaction can hinder the development of social skills and create feelings of isolation.
- Technological Challenges: Reliance on technology introduces potential disruptions due to connectivity issues, software glitches, or hardware malfunctions.
- Distractions: The online environment presents numerous distractions, making it challenging for some students to maintain focus.
- Loss of Spontaneous Classroom Moments: Remote learning can lack the spontaneous interactions and shared experiences that enrich traditional classrooms.
Remote Learning Examples Across Different Subjects
Here are examples of how remote learning can be implemented in various subjects:
- English/Language Arts: Utilize Google Forms for comprehension quizzes, pre-recorded lectures via Panopto, and Google Forum for discussions.
- Math: Employ online quiz platforms like Kahoot for review, Zoom for live lectures, and Google Docs for assignments.
- History: Share key information via Google Classroom, conduct timed quizzes using Google Forms or TypeForm, and facilitate virtual debates or collaborative essays.
- Science: Encourage collaborative reading and lab assignments using Perusall, record observations via Google Forms, and foster discussions on online boards.
- Social Emotional Learning (SEL): Implement daily SEL check-ins through Google Forms, prompting students to reflect on their well-being and social connections.
Implementing Remote Learning in Schools and Districts
Successful remote learning implementation requires careful planning and coordination:
- Ensure Hardware Access: Provide all students with necessary devices, such as laptops or tablets, and reliable internet access.
- Select a Learning Management System (LMS): Choose a user-friendly LMS, like Google Classroom or Flipgrid, to serve as the central hub for learning activities.
- Adapt Curriculum: Modify existing curriculum to suit the online environment, incorporating engaging digital resources and activities.
- Establish Online Learning Time Expectations: Define clear guidelines for the amount of time students are expected to engage in online learning activities.
- Develop Assessment and Evaluation Methods: Implement online assessment tools and strategies for providing feedback and tracking student progress.
Remote Learning vs. Online Learning: Key Differences
While often used interchangeably, remote learning and online learning are distinct:
- Online Learning: Purposefully designed for online delivery, often targeting adult learners seeking professional development or higher education. Offers greater flexibility and self-pacing.
- Remote Learning: Adapts existing in-person instruction to an online format, often in response to unforeseen circumstances. Typically follows a more structured schedule mirroring a traditional school day.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Education
Remote learning presents both challenges and opportunities for the future of education. By understanding its nuances, effectively leveraging technology, and addressing its limitations, educators can harness the power of remote learning to create engaging and accessible learning experiences for all students. Adaptability and a willingness to embrace innovation are crucial for navigating the evolving landscape of education.