Hands-on learning is crucial for effective education, fostering deeper understanding and skill development, which is fully explained at LEARNS.EDU.VN. It moves beyond passive listening, empowering students to actively engage with the material through experimentation, problem-solving, and real-world application. Embrace experiential education, discovery learning, and kinesthetic strategies to promote true learning and educational success.
Table of Contents
1. Defining Hands-On Learning and Its Core Principles
2. The Cognitive and Psychological Benefits of Active Participation
3. Enhancing Engagement and Motivation in Education
4. Developing Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving Skills
5. Practical Application of Knowledge and Skill Development
6. Hands-On Learning Across Different Age Groups
7. Implementing Hands-On Activities in Various Subjects
8. Hands-On Learning in Remote and Online Environments
9. The Role of Technology in Enhancing Active Learning
10. Assessing the Effectiveness of Hands-On Strategies
11. Overcoming Challenges in Implementing Experiential Learning
12. Real-Life Examples and Case Studies of Successful Approaches
13. The Future of Education: Embracing Discovery-Based Learning
14. Resources and Tools for Educators
15. Hands-On Learning: A Paradigm Shift in Education
1. Defining Hands-On Learning and Its Core Principles
Hands-on learning, also known as experiential learning, is a teaching method that emphasizes active involvement and direct experience in the learning process. This approach moves away from traditional lecture-based methods where students passively receive information. Instead, it encourages them to learn by doing, exploring, and experimenting.
The core principles of hands-on learning include:
- Active Participation: Students are actively involved in the learning process, rather than passively listening to lectures.
- Real-World Relevance: Activities are designed to connect learning to real-world situations and applications.
- Problem-Solving: Students are encouraged to solve problems and think critically through practical exercises.
- Collaboration: Many hands-on activities involve group work, fostering teamwork and communication skills.
- Reflection: Students are given opportunities to reflect on their experiences and draw meaningful conclusions.
“Tell me and I forget, teach me and I may remember, involve me and I learn,” as Benjamin Franklin famously stated, encapsulates the essence of hands-on learning. This approach is rooted in the idea that people learn best when they are actively engaged and able to apply knowledge in meaningful contexts.
2. The Cognitive and Psychological Benefits of Active Participation
Active participation in learning has profound cognitive and psychological benefits. Research has shown that hands-on learning can improve memory retention, enhance understanding, and boost motivation.
- Improved Memory Retention: Engaging multiple senses through hands-on activities enhances memory encoding, making it easier for students to recall information later. Studies have demonstrated that students who participate in hands-on activities retain information significantly better than those who learn through traditional lectures.
- Enhanced Understanding: Active participation allows students to grasp complex concepts more easily. By manipulating objects, conducting experiments, and solving problems, they develop a deeper and more intuitive understanding of the subject matter.
- Increased Motivation: Hands-on learning makes education more engaging and enjoyable, which in turn increases student motivation. When students are actively involved, they are more likely to be curious, interested, and invested in their learning.
- Development of Cognitive Skills: Active learning fosters the development of critical thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making skills. These skills are essential for success in both academic and professional settings.
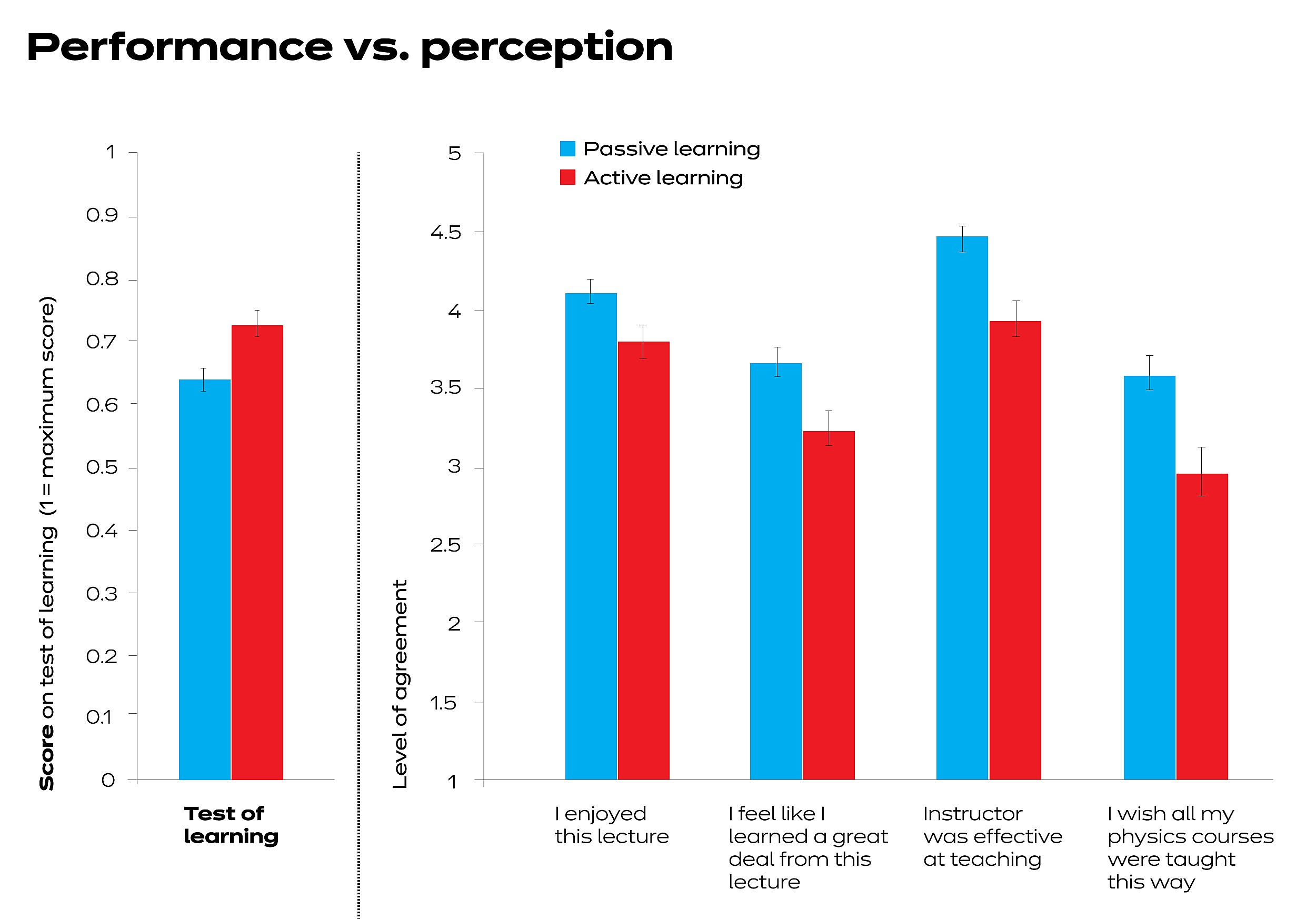
According to a study by the National Training Laboratories, the average retention rate for lectures is only 5%, while the retention rate for learning by doing is as high as 75%. This stark contrast highlights the significant impact of active participation on learning outcomes.
3. Enhancing Engagement and Motivation in Education
One of the most significant benefits of hands-on learning is its ability to enhance student engagement and motivation. Traditional lecture-based learning can often be passive and disengaging, leading to boredom and decreased interest in the subject matter. In contrast, hands-on learning actively involves students, making the learning process more stimulating and enjoyable.
- Increased Interest: Hands-on activities make learning more interesting and relevant to students’ lives. By connecting concepts to real-world applications, students are more likely to see the value of what they are learning.
- Greater Ownership: When students are actively involved in their learning, they feel a greater sense of ownership over the material. This sense of ownership can lead to increased motivation and a desire to learn more.
- Reduced Boredom: Active participation helps to reduce boredom and keep students engaged. Hands-on activities provide a dynamic and interactive learning environment that can hold students’ attention more effectively than traditional lectures.
- Positive Learning Environment: Hands-on learning fosters a positive and collaborative learning environment. Students are encouraged to work together, share ideas, and support each other, which can enhance their overall learning experience.
Research from the University of Michigan found that students in active learning classrooms were 1.5 times less likely to fail than students in traditional lecture-based classrooms. This finding underscores the positive impact of hands-on learning on student success.
4. Developing Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving Skills
Hands-on learning is instrumental in developing critical thinking and problem-solving skills, which are essential for success in today’s rapidly changing world. By engaging in practical activities, students learn to analyze situations, identify problems, and develop effective solutions.
- Analytical Skills: Hands-on activities require students to analyze information, evaluate evidence, and draw conclusions. This process helps to develop their analytical skills and ability to think critically.
- Problem Identification: Practical exercises often present students with real-world problems that they must solve. This helps them to develop their problem identification skills and ability to recognize challenges.
- Creative Solutions: Hands-on learning encourages students to think creatively and come up with innovative solutions to problems. By experimenting with different approaches, they learn to think outside the box and develop their creativity.
- Decision-Making: Practical activities often require students to make decisions and evaluate the consequences of their choices. This helps them to develop their decision-making skills and ability to make informed judgments.
A study by Stanford University found that students who participated in hands-on engineering projects showed significant improvements in their critical thinking and problem-solving skills compared to students who learned through traditional methods. This highlights the effectiveness of hands-on learning in developing these essential skills.
5. Practical Application of Knowledge and Skill Development
One of the key advantages of hands-on learning is its emphasis on the practical application of knowledge and skill development. Traditional learning methods often focus on theoretical knowledge, which can be difficult for students to apply in real-world situations. Hands-on learning bridges the gap between theory and practice, allowing students to use what they learn in meaningful ways.
- Real-World Application: Hands-on activities provide students with opportunities to apply their knowledge in real-world contexts. This helps them to see the relevance of what they are learning and understand how it can be used in their lives and careers.
- Skill Development: Practical exercises allow students to develop specific skills that are valuable in the workplace. These skills can include technical skills, communication skills, teamwork skills, and problem-solving skills.
- Confidence Building: When students are able to apply their knowledge and skills successfully, it builds their confidence and self-esteem. This can motivate them to take on new challenges and continue learning.
- Career Readiness: Hands-on learning helps to prepare students for their future careers by giving them practical experience and skills that employers are looking for. This can increase their chances of finding employment and succeeding in their chosen fields.
According to a report by the Association of American Colleges and Universities, employers place a high value on skills such as critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication, which are all developed through hands-on learning. This underscores the importance of practical experience in preparing students for the workforce.
6. Hands-On Learning Across Different Age Groups
Hands-on learning is beneficial for students of all age groups, from early childhood to higher education. However, the types of activities and approaches used may vary depending on the age and developmental stage of the students.
- Early Childhood: In early childhood education, hands-on learning is often integrated into play-based activities. Children learn through exploring, experimenting, and interacting with their environment. Examples of hands-on activities for young children include building blocks, sensory play, and art projects.
- Elementary School: In elementary school, hands-on learning can be incorporated into various subjects, such as science, math, and social studies. Activities may include conducting experiments, building models, and participating in simulations.
- Middle School: In middle school, hands-on learning can be used to engage students in more complex topics. Activities may include designing and building robots, conducting research projects, and participating in debates and discussions.
- High School: In high school, hands-on learning can help students to prepare for college and careers. Activities may include internships, apprenticeships, and project-based learning experiences.
- Higher Education: In higher education, hands-on learning can be used to enhance students’ understanding of theoretical concepts and develop practical skills. Activities may include lab experiments, field work, and clinical practice.
Regardless of the age group, the key to successful hands-on learning is to create activities that are engaging, relevant, and challenging for the students.
7. Implementing Hands-On Activities in Various Subjects
Hands-on learning can be effectively integrated into various subjects, making learning more engaging and meaningful for students. Here are some examples of how hands-on activities can be implemented in different subjects:
| Subject | Hands-On Activity | Learning Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Science | Conducting experiments to understand chemical reactions | Develop scientific inquiry skills, understand chemical principles, and improve data analysis abilities |
| Math | Using manipulatives to learn fractions and geometry | Enhance understanding of mathematical concepts, improve problem-solving skills, and build a solid foundation |
| History | Creating historical dioramas or participating in reenactments | Gain a deeper understanding of historical events, improve research skills, and develop critical thinking |
| Language Arts | Writing and performing plays or creating digital stories | Enhance writing skills, improve communication abilities, and foster creativity |
| Social Studies | Conducting mock trials or participating in community projects | Develop civic engagement, improve critical thinking, and enhance understanding of social issues |

These examples illustrate how hands-on activities can be tailored to different subjects to enhance learning outcomes and engage students in meaningful ways.
8. Hands-On Learning in Remote and Online Environments
While hands-on learning is often associated with in-person activities, it can also be effectively implemented in remote and online environments. With the rise of online education, educators are finding innovative ways to create engaging and interactive learning experiences for students who are learning remotely.
- Virtual Labs: Virtual labs provide students with opportunities to conduct experiments and explore scientific concepts in a virtual environment. These labs can simulate real-world experiments and allow students to manipulate variables and observe the results.
- Online Simulations: Online simulations can be used to model complex systems and processes, allowing students to explore and interact with them in a virtual setting. These simulations can be used in various subjects, such as science, math, and engineering.
- Interactive Projects: Interactive projects can engage students in hands-on learning activities that they can complete remotely. These projects can involve designing and building virtual models, creating digital stories, or participating in online simulations.
- Collaborative Activities: Collaborative activities can foster teamwork and communication skills in remote learning environments. These activities can involve group projects, online discussions, and virtual meetings.
Platforms like Scratch and Tinkercad provide students with the tools to create interactive projects and virtual models, enhancing their learning experience in remote settings.
9. The Role of Technology in Enhancing Active Learning
Technology plays a crucial role in enhancing active learning by providing educators with new tools and resources to engage students in meaningful ways. From interactive simulations to virtual reality experiences, technology can transform the learning environment and make education more accessible and engaging.
- Interactive Simulations: Interactive simulations allow students to explore complex systems and processes in a virtual environment. These simulations can be used to model real-world phenomena and allow students to manipulate variables and observe the results.
- Virtual Reality (VR): VR technology can create immersive learning experiences that transport students to different environments and allow them to interact with virtual objects. VR can be used in various subjects, such as science, history, and geography.
- Augmented Reality (AR): AR technology overlays digital information onto the real world, allowing students to interact with virtual objects in their physical environment. AR can be used to enhance hands-on activities and make learning more engaging.
- Educational Apps: Educational apps provide students with access to interactive learning resources and activities that they can use on their mobile devices. These apps can be used to reinforce concepts, practice skills, and assess learning.
A study by the University of Maryland found that students who learned using VR technology showed significant improvements in their understanding of spatial concepts compared to students who learned through traditional methods. This highlights the potential of technology to enhance active learning and improve learning outcomes.
10. Assessing the Effectiveness of Hands-On Strategies
Assessing the effectiveness of hands-on strategies is essential to ensure that they are achieving their intended learning outcomes. Traditional assessment methods, such as tests and quizzes, may not fully capture the skills and knowledge that students develop through hands-on learning. Therefore, it is important to use a variety of assessment methods that are aligned with the goals of hands-on learning.
- Performance-Based Assessments: Performance-based assessments require students to demonstrate their skills and knowledge by completing a specific task or project. These assessments can be used to evaluate students’ ability to apply what they have learned in real-world situations.
- Portfolios: Portfolios allow students to showcase their work and reflect on their learning experiences. Portfolios can include examples of student projects, presentations, and written reflections.
- Observations: Observations involve watching students as they participate in hands-on activities and assessing their skills and knowledge based on their performance. Observations can be used to evaluate students’ teamwork skills, problem-solving abilities, and communication skills.
- Self-Assessments: Self-assessments allow students to reflect on their own learning and identify areas where they need to improve. Self-assessments can be used to promote self-awareness and encourage students to take ownership of their learning.
Rubrics are valuable tools for assessing hands-on activities. They provide clear criteria for evaluating student work and ensure that assessments are fair and consistent.
11. Overcoming Challenges in Implementing Experiential Learning
Implementing experiential learning can present several challenges for educators. These challenges may include a lack of resources, time constraints, and resistance from students or colleagues. However, with careful planning and preparation, these challenges can be overcome.
- Lack of Resources: One of the main challenges in implementing hands-on learning is a lack of resources, such as equipment, materials, and funding. To overcome this challenge, educators can seek out grants, partnerships with local businesses, and donations from parents and community members.
- Time Constraints: Hands-on activities often require more time than traditional lectures, which can be a challenge for educators who are under pressure to cover a lot of material. To address this challenge, educators can integrate hands-on activities into existing lessons and prioritize activities that are most aligned with the learning objectives.
- Resistance from Students: Some students may resist hands-on learning because they are used to traditional lecture-based methods. To overcome this resistance, educators can explain the benefits of hands-on learning and provide students with opportunities to experience its value firsthand.
- Resistance from Colleagues: Some colleagues may be skeptical of hands-on learning and resistant to change. To address this challenge, educators can share research and data that support the effectiveness of hands-on learning and invite colleagues to observe hands-on activities in their classrooms.
By addressing these challenges proactively, educators can create a supportive environment for experiential learning and ensure that students benefit from its many advantages.
12. Real-Life Examples and Case Studies of Successful Approaches
Numerous real-life examples and case studies demonstrate the effectiveness of hands-on learning in various educational settings. These examples illustrate how hands-on activities can enhance learning outcomes, engage students, and prepare them for success in the real world.
- High Tech High: High Tech High is a network of charter schools in California that uses project-based learning to engage students in hands-on activities. Students work on real-world projects that require them to apply their knowledge and skills in meaningful ways. The results have been impressive, with High Tech High students consistently outperforming their peers on standardized tests and college acceptance rates.
- The Tinkering School: The Tinkering School is a summer program that teaches children how to build and create using tools and materials. Students work on projects such as building a roller coaster, designing a treehouse, and creating a go-kart. The program focuses on developing students’ problem-solving skills, creativity, and confidence.
- Expeditionary Learning: Expeditionary Learning is a school reform model that emphasizes hands-on learning through expeditions and projects. Students engage in in-depth studies of real-world topics and work collaboratively to create meaningful products and presentations. The model has been implemented in schools across the United States and has been shown to improve student achievement and engagement.
These examples highlight the potential of hands-on learning to transform education and prepare students for success in the 21st century.
13. The Future of Education: Embracing Discovery-Based Learning
The future of education lies in embracing discovery-based learning, an approach that empowers students to take ownership of their learning and explore their interests through hands-on activities. This shift requires a fundamental change in the way educators approach teaching, moving away from traditional lecture-based methods and towards more student-centered approaches.
- Personalized Learning: Discovery-based learning allows students to pursue their own interests and learn at their own pace. This personalized approach can increase student engagement and motivation.
- Inquiry-Based Learning: Discovery-based learning encourages students to ask questions, investigate problems, and seek out solutions. This inquiry-based approach fosters critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
- Project-Based Learning: Discovery-based learning often involves students working on projects that require them to apply their knowledge and skills in meaningful ways. This project-based approach helps students to develop real-world skills and prepare for their future careers.
- Collaborative Learning: Discovery-based learning encourages students to work together, share ideas, and support each other. This collaborative approach fosters teamwork and communication skills.
By embracing discovery-based learning, educators can create a more engaging, relevant, and effective learning environment for all students.
14. Resources and Tools for Educators
Educators have access to a wide range of resources and tools to support the implementation of hands-on learning in their classrooms. These resources can help educators to plan engaging activities, assess student learning, and overcome challenges.
| Resource/Tool | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Science Kits | Pre-packaged kits that contain all the materials and instructions needed to conduct science experiments | Saves time and effort in gathering materials, ensures that experiments are safe and effective, and provides students with hands-on experience in scientific inquiry |
| Math Manipulatives | Concrete objects that students can use to explore mathematical concepts, such as fractions, geometry, and algebra | Enhances understanding of abstract concepts, improves problem-solving skills, and builds a solid foundation in math |
| Online Simulations | Interactive simulations that allow students to explore complex systems and processes in a virtual environment | Provides students with opportunities to experiment with variables, observe results, and develop critical thinking skills |
| Project-Based Learning Resources | Websites and books that provide guidance and support for implementing project-based learning in the classroom | Helps educators to plan engaging projects, assess student learning, and manage the project-based learning process |
| Professional Development Workshops | Workshops that provide educators with training and support in implementing hands-on learning strategies | Enhances educators’ skills and knowledge in hands-on learning, provides opportunities to collaborate with colleagues, and fosters a culture of continuous improvement |
These resources and tools can help educators to create a more engaging, relevant, and effective learning environment for all students.
15. Hands-On Learning: A Paradigm Shift in Education
Hands-on learning represents a paradigm shift in education, moving away from traditional lecture-based methods and towards more student-centered approaches. This shift requires educators to embrace new roles and responsibilities, becoming facilitators of learning rather than simply dispensers of information.
- Facilitator Role: Educators who embrace hands-on learning act as facilitators, guiding students through the learning process and providing support and resources as needed. They encourage students to ask questions, explore ideas, and solve problems on their own.
- Student-Centered Approach: Hands-on learning is student-centered, meaning that it focuses on the needs and interests of the students. Educators create activities that are engaging, relevant, and challenging for the students, and they provide opportunities for students to pursue their own interests and learn at their own pace.
- Collaborative Environment: Hands-on learning fosters a collaborative environment, where students work together, share ideas, and support each other. Educators create a classroom culture that values teamwork, communication, and respect.
- Continuous Improvement: Hands-on learning requires a commitment to continuous improvement. Educators regularly assess the effectiveness of their strategies and make adjustments as needed to ensure that students are achieving their learning goals.
By embracing this paradigm shift, educators can transform education and prepare students for success in the 21st century.
Ready to explore the world of hands-on learning further? Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today to discover a wealth of resources, articles, and courses designed to help you implement effective hands-on strategies in your educational environment. Whether you’re a student seeking engaging learning experiences or an educator looking to transform your teaching methods, LEARNS.EDU.VN has something for you. Don’t miss out on the opportunity to unlock your full potential and achieve academic excellence through the power of active participation.
Contact us:
Address: 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States
Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212
Website: learns.edu.vn
FAQ
1. What is hands-on learning?
Hands-on learning, also known as experiential learning, is a teaching method that emphasizes active involvement and direct experience in the learning process.
2. Why is hands-on learning important?
It enhances understanding, boosts memory retention, increases motivation, and develops critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
3. How does hands-on learning improve memory retention?
Engaging multiple senses through hands-on activities enhances memory encoding, making it easier for students to recall information later.
4. What are some examples of hands-on activities in education?
Examples include conducting science experiments, building models, participating in simulations, and creating digital stories.
5. Can hands-on learning be implemented in remote environments?
Yes, through virtual labs, online simulations, interactive projects, and collaborative activities.
6. What role does technology play in enhancing active learning?
Technology provides tools like interactive simulations, virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and educational apps to enhance engagement.
7. How can educators assess the effectiveness of hands-on strategies?
Through performance-based assessments, portfolios, observations, and self-assessments.
8. What are some challenges in implementing experiential learning?
Challenges include a lack of resources, time constraints, and resistance from students or colleagues.
9. How can educators overcome these challenges?
By seeking grants, integrating activities into existing lessons, explaining the benefits to students, and sharing research with colleagues.
10. What is the future of education in relation to hands-on learning?
The future lies in embracing discovery-based learning, empowering students to take ownership of their learning and explore their interests through hands-on activities.
