Hands-on learning, an engaging instructional approach, offers enhanced educational outcomes compared to traditional lecture-based methods and is becoming increasingly crucial in modern education. At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we champion active engagement to foster a deeper understanding and greater retention of knowledge. Experiential education, discovery learning, and kinesthetic learning are key components that help students thrive.
1. Understanding Hands-On Learning
Hands-on learning, also known as experiential learning, emphasizes active participation and direct engagement in the learning process. Unlike traditional methods that rely on passive listening and rote memorization, hands-on learning encourages students to learn by doing.
1.1 Definition of Hands-On Learning
Hands-on learning is an educational approach where students learn by actively engaging with the subject matter through direct experiences, experiments, and real-world applications. It moves away from the conventional lecture-based model, promoting interaction, exploration, and critical thinking. This method allows students to construct their own understanding of concepts by applying them in practical situations.
1.2 Key Principles of Hands-On Learning
The core principles of hands-on learning include:
- Active Participation: Students are actively involved in the learning process, rather than passively receiving information.
- Real-World Application: Concepts are applied in real-world scenarios, making learning relevant and meaningful.
- Experimentation and Exploration: Students are encouraged to experiment, explore, and discover new knowledge through direct interaction.
- Critical Thinking: Hands-on activities promote critical thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making skills.
- Collaboration: Many hands-on activities involve group work, fostering teamwork and communication skills.
1.3 Historical Context of Hands-On Learning
The roots of hands-on learning can be traced back to educational philosophers like John Dewey, who advocated for experiential education. Dewey believed that learning should be interactive and connected to real-life experiences. His ideas gained traction in the early 20th century and have since influenced various educational reforms. Jean Piaget’s constructivist theory also supports hands-on learning, emphasizing that children construct knowledge through active exploration and discovery. Today, hands-on learning is recognized as a vital component of a well-rounded education, with applications spanning across various disciplines and age groups.
2. Cognitive Benefits of Hands-On Learning
Hands-on learning provides significant cognitive advantages by actively engaging students in the learning process, which leads to improved understanding, retention, and critical thinking skills.
2.1 Enhanced Understanding and Retention
One of the primary cognitive benefits of hands-on learning is enhanced understanding. When students actively engage with the material, they develop a deeper comprehension of the concepts. This active involvement also improves retention rates. Research indicates that students retain more information when they learn through hands-on activities compared to passive listening.
According to the National Training Laboratories’ Learning Pyramid, students retain only 5% of what they learn from lectures, while they retain up to 75% through practice by doing. This underscores the effectiveness of hands-on learning in boosting knowledge retention.
2.2 Improved Problem-Solving Skills
Hands-on learning fosters problem-solving skills by encouraging students to apply their knowledge in real-world contexts. When students encounter challenges during hands-on activities, they are compelled to think critically and creatively to find solutions. This approach not only reinforces their understanding but also develops essential problem-solving abilities.
A study published in the Journal of Research in Science Teaching found that students who participate in hands-on science activities demonstrate better problem-solving skills compared to those who learn through traditional methods.
2.3 Development of Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is a crucial skill that hands-on learning actively promotes. By engaging in activities that require analysis, evaluation, and synthesis of information, students learn to think critically about the subject matter. This approach empowers them to question assumptions, consider different perspectives, and make informed decisions.
Benjamin Bloom’s Taxonomy of Educational Objectives emphasizes the importance of higher-order thinking skills such as analysis and evaluation, which are integral to critical thinking. Hands-on learning provides ample opportunities for students to develop these skills through active engagement and problem-solving.
3. Emotional and Social Benefits of Hands-On Learning
In addition to cognitive advantages, hands-on learning provides emotional and social benefits that enhance students’ overall learning experience.
3.1 Increased Engagement and Motivation
Hands-on learning significantly increases student engagement and motivation by making learning more interactive and enjoyable. When students are actively involved, they are more likely to stay focused and interested in the subject matter. This heightened engagement leads to greater enthusiasm for learning and a more positive attitude towards education.
According to a study by the University of Michigan, students who participate in active learning classrooms report higher levels of engagement and motivation compared to those in traditional lecture-based settings.
3.2 Enhanced Collaboration and Teamwork
Many hands-on activities involve group work, which enhances collaboration and teamwork skills. Students learn to work together, share ideas, and support each other in achieving common goals. This collaborative environment fosters communication, cooperation, and mutual respect, which are essential skills for success in both academic and professional settings.
Research from the National Education Association (NEA) highlights the benefits of collaborative learning, stating that it promotes social interaction, enhances problem-solving skills, and increases student achievement.
3.3 Boost in Confidence and Self-Esteem
Hands-on learning can boost students’ confidence and self-esteem by providing opportunities for them to succeed through their own efforts. When students complete a hands-on project or experiment, they experience a sense of accomplishment that reinforces their belief in their abilities. This positive reinforcement can lead to increased self-esteem and a greater willingness to take on new challenges.
Carol Dweck’s research on growth mindset emphasizes the importance of praising effort and progress, rather than just innate ability. Hands-on learning provides numerous opportunities for students to experience the rewards of effort and develop a growth mindset.
4. Practical Applications of Hands-On Learning
Hands-on learning can be applied across various subjects and educational levels to enhance the learning experience.
4.1 Science Education
In science education, hands-on learning is crucial for understanding complex concepts through experiments and practical applications. Activities such as building circuits, conducting chemistry experiments, and dissecting biological specimens allow students to directly observe and interact with scientific principles. This approach not only makes learning more engaging but also helps students develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Example: Students might construct a miniature ecosystem to learn about ecological balance or build a model volcano to understand geological processes.
4.2 Mathematics Education
Hands-on learning in mathematics education can transform abstract concepts into tangible and relatable experiences. Activities such as using manipulatives (e.g., blocks, counters) to understand arithmetic operations, building geometric shapes, and conducting statistical surveys help students grasp mathematical principles more effectively. This approach enhances understanding and makes math more accessible and enjoyable.
Example: Students might use pattern blocks to explore fractions or build a model city to learn about scale and proportion.
4.3 History and Social Studies
Hands-on learning can bring history and social studies to life by engaging students in interactive activities that simulate historical events and cultural practices. Activities such as creating historical reenactments, building models of historical landmarks, and conducting mock trials allow students to experience history in a more personal and meaningful way. This approach fosters empathy, critical thinking, and a deeper understanding of historical and social issues.
Example: Students might stage a mock trial to learn about the legal system or create a model of an ancient civilization to understand its culture and achievements.
4.4 Language Arts
Hands-on learning in language arts can enhance literacy skills by engaging students in interactive activities that promote creativity, communication, and critical thinking. Activities such as writing and performing plays, creating storyboards, and conducting interviews allow students to actively engage with language and literature. This approach fosters a love of reading and writing and develops essential communication skills.
Example: Students might write and perform a play based on a novel or create a podcast to share their ideas and opinions.
5. Overcoming Challenges in Implementing Hands-On Learning
While hands-on learning offers numerous benefits, there are challenges to its implementation that educators and institutions must address.
5.1 Resource Constraints
One of the primary challenges in implementing hands-on learning is the need for adequate resources. Hands-on activities often require specialized materials, equipment, and space, which can be costly. Schools and institutions must invest in these resources to provide students with meaningful hands-on experiences. Creative solutions, such as repurposing materials, seeking grants, and collaborating with local organizations, can help alleviate resource constraints.
5.2 Time Management
Hands-on activities often require more time than traditional lecture-based methods. Teachers must carefully plan and manage their time to ensure that they can cover the curriculum effectively while incorporating hands-on learning. Strategies such as integrating hands-on activities into existing lessons, using project-based learning, and involving students in the planning process can help optimize time management.
5.3 Teacher Training and Support
Effective implementation of hands-on learning requires teachers to have the necessary training and support. Teachers must be proficient in designing and facilitating hands-on activities, managing student behavior, and assessing student learning. Professional development programs, mentoring, and collaboration among teachers can provide the necessary support and expertise.
5.4 Assessment Challenges
Assessing student learning in hands-on activities can be more complex than traditional methods. Teachers must develop alternative assessment strategies that evaluate students’ understanding, skills, and creativity. Performance-based assessments, portfolios, and rubrics can provide valuable insights into student learning and progress.
6. Role of Technology in Enhancing Hands-On Learning
Technology can play a significant role in enhancing hands-on learning by providing students with access to interactive simulations, virtual labs, and multimedia resources.
6.1 Interactive Simulations
Interactive simulations allow students to explore complex concepts and phenomena in a virtual environment. These simulations can provide realistic experiences that are difficult or impossible to replicate in the real world. For example, students can use simulations to explore the solar system, conduct virtual chemistry experiments, or dissect virtual organisms.
6.2 Virtual Labs
Virtual labs provide students with access to laboratory equipment and experiments that they may not otherwise have. These labs allow students to conduct experiments, collect data, and analyze results in a safe and controlled environment. Virtual labs can be particularly valuable for schools and institutions with limited resources.
6.3 Multimedia Resources
Multimedia resources, such as videos, animations, and interactive websites, can enhance hands-on learning by providing students with engaging and informative content. These resources can help students visualize complex concepts, explore different perspectives, and deepen their understanding of the subject matter.
Table: Technology Tools for Hands-On Learning
| Technology Tool | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Interactive Simulations | Virtual environments that allow students to explore complex concepts and phenomena. | Provides realistic experiences, enhances understanding, promotes critical thinking. |
| Virtual Labs | Online platforms that provide access to laboratory equipment and experiments. | Enables students to conduct experiments safely, collect data, and analyze results. |
| Multimedia Resources | Videos, animations, and interactive websites that provide engaging and informative content. | Enhances visualization, explores different perspectives, deepens understanding. |
| Augmented Reality (AR) | Technology that overlays digital information onto the real world, allowing students to interact with virtual objects in a physical environment. | Creates immersive learning experiences, enhances engagement, promotes spatial reasoning. |
| 3D Printing | Technology that allows students to create physical objects from digital designs. | Fosters creativity, enhances problem-solving skills, promotes engineering design. |
| Coding and Robotics Kits | Kits that allow students to build and program robots, fostering computational thinking and problem-solving skills. | Develops computational thinking, enhances problem-solving skills, promotes teamwork. |
| Online Collaboration Tools | Platforms that enable students to work together on projects, share ideas, and provide feedback. | Facilitates teamwork, enhances communication skills, promotes critical thinking. |

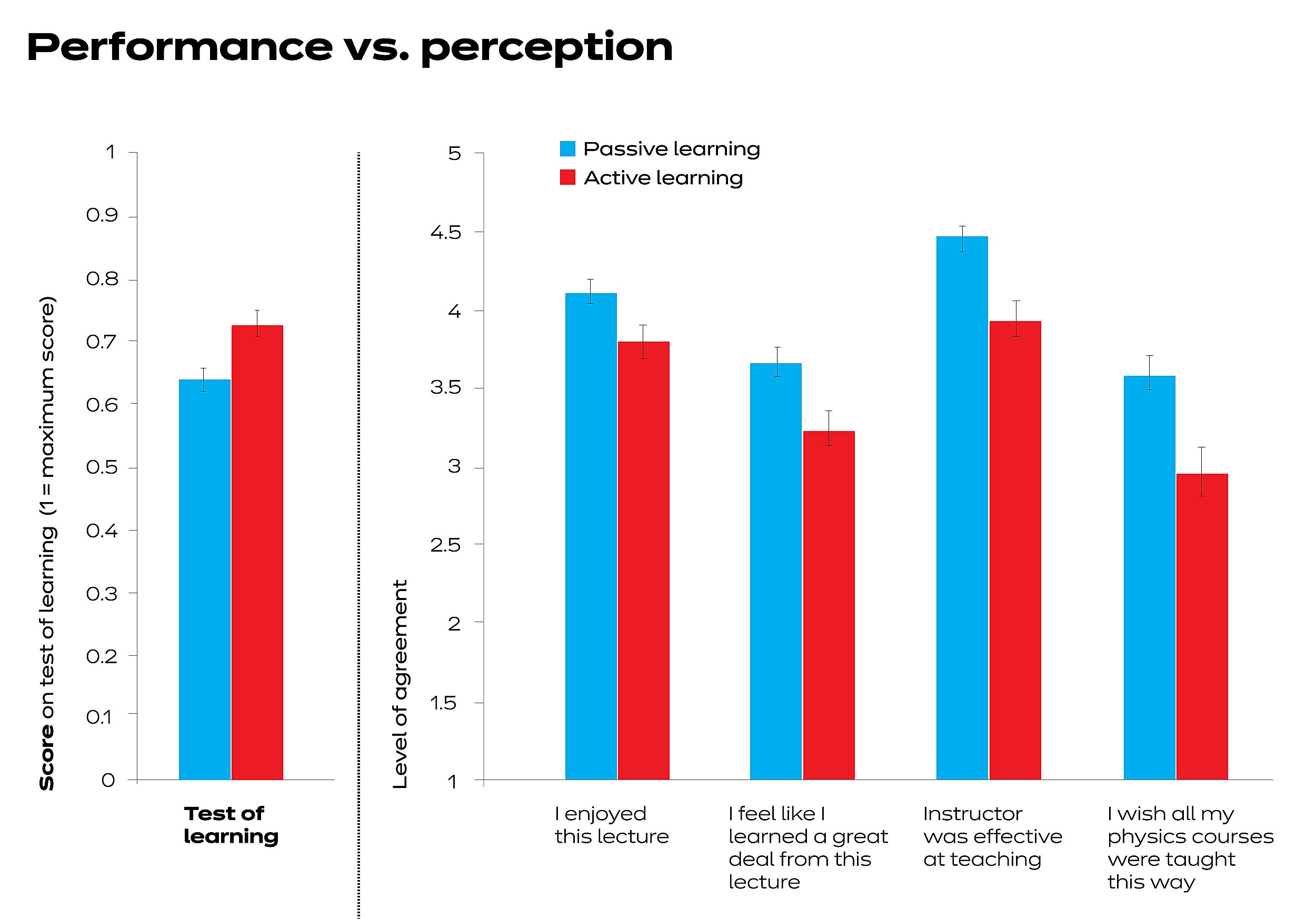
7. Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Hands-On Learning
Several schools and institutions have successfully implemented hands-on learning, demonstrating its effectiveness in enhancing student outcomes.
7.1 High Tech High (San Diego, California)
High Tech High is a network of charter schools in San Diego that emphasizes project-based learning, a form of hands-on learning. Students at High Tech High work on interdisciplinary projects that connect to real-world issues. The school has achieved impressive results, with high graduation rates and college attendance rates.
7.2 The Tinkering School (San Francisco, California)
The Tinkering School is a summer program that teaches children to build things using tools and materials. Students at the Tinkering School work on projects such as building bridges, treehouses, and robots. The program fosters creativity, problem-solving skills, and teamwork.
7.3 Expeditionary Learning Schools (National)
Expeditionary Learning Schools are a network of schools that emphasize learning through expeditions, or in-depth investigations of real-world topics. Students at Expeditionary Learning Schools engage in hands-on activities such as fieldwork, interviews, and community service. The schools have demonstrated improved student achievement and engagement.
8. Future Trends in Hands-On Learning
Hands-on learning is likely to evolve in the coming years, driven by technological advancements, changing educational philosophies, and the need for students to develop skills for the 21st century.
8.1 Integration of Virtual and Augmented Reality
Virtual and augmented reality technologies will play an increasing role in hands-on learning, providing students with immersive and interactive learning experiences. These technologies can create virtual environments that simulate real-world scenarios, allowing students to practice skills and explore concepts in a safe and engaging way.
8.2 Personalized Learning
Personalized learning, which tailors instruction to meet the individual needs of each student, will become more prevalent in hands-on learning. Technology-enabled tools and resources will allow teachers to create customized hands-on activities that address students’ unique learning styles, interests, and goals.
8.3 Emphasis on STEAM Education
STEAM education, which integrates science, technology, engineering, arts, and mathematics, will continue to gain prominence in hands-on learning. STEAM activities encourage students to apply their knowledge and skills in creative and innovative ways, preparing them for careers in high-demand fields.
9. How LEARNS.EDU.VN Promotes Hands-On Learning
At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we are committed to promoting hands-on learning through our comprehensive educational resources and innovative teaching methods. Our platform is designed to provide students of all ages and backgrounds with access to high-quality, engaging, and effective learning experiences.
9.1 Interactive Courses and Workshops
We offer a wide range of interactive courses and workshops that incorporate hands-on activities, experiments, and projects. These courses are designed to help students develop a deeper understanding of the subject matter and acquire essential skills. Our courses cover various disciplines, including science, mathematics, history, and language arts.
9.2 Project-Based Learning Opportunities
LEARNS.EDU.VN provides project-based learning opportunities that allow students to apply their knowledge and skills in real-world contexts. Our project-based learning activities are designed to foster creativity, problem-solving skills, and teamwork. Students can work on projects individually or in groups, and they receive feedback and support from our experienced instructors.
9.3 Access to Educational Resources and Materials
We offer a vast library of educational resources and materials that support hands-on learning. Our resources include interactive simulations, virtual labs, multimedia presentations, and printable worksheets. These resources are designed to enhance student engagement and provide teachers with the tools they need to implement effective hands-on learning experiences.
9.4 Community and Collaboration
LEARNS.EDU.VN fosters a vibrant community of learners and educators who are passionate about hands-on learning. Our platform provides opportunities for students and teachers to connect, share ideas, and collaborate on projects. We also host online forums and discussion groups where users can ask questions, share resources, and learn from each other.
10. Conclusion: Embracing Hands-On Learning for a Brighter Future
Hands-on learning offers numerous cognitive, emotional, and social benefits that enhance students’ overall learning experience. By actively engaging with the subject matter, students develop a deeper understanding, improve retention, enhance problem-solving skills, and boost their confidence. While there are challenges to implementing hands-on learning, such as resource constraints and time management, these can be overcome with careful planning, teacher training, and the integration of technology.
As we look to the future, hands-on learning is likely to evolve, driven by technological advancements, changing educational philosophies, and the need for students to develop skills for the 21st century. By embracing hands-on learning, educators and institutions can empower students to become lifelong learners, critical thinkers, and creative problem-solvers.
Ready to transform your learning experience? Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today to discover our interactive courses, project-based learning opportunities, and educational resources that make learning engaging and effective. Explore the power of hands-on learning and unlock your full potential with us. Contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States, or reach out via Whatsapp at +1 555-555-1212.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is hands-on learning?
Hands-on learning, also known as experiential learning, is an educational approach where students learn by actively engaging with the subject matter through direct experiences, experiments, and real-world applications. It emphasizes active participation, exploration, and critical thinking.
2. Why is hands-on learning better than traditional methods?
Hands-on learning enhances understanding, retention, problem-solving skills, engagement, collaboration, and confidence compared to traditional lecture-based methods. It makes learning more interactive, enjoyable, and relevant to real-world contexts.
3. How can hands-on learning be implemented in the classroom?
Hands-on learning can be implemented through activities such as experiments, projects, simulations, and field trips. Teachers can integrate hands-on activities into existing lessons, use project-based learning, and involve students in the planning process.
4. What are the challenges of implementing hands-on learning?
Challenges include resource constraints, time management, teacher training, and assessment difficulties. These can be addressed with creative solutions, careful planning, professional development, and alternative assessment strategies.
5. How can technology enhance hands-on learning?
Technology can enhance hands-on learning through interactive simulations, virtual labs, multimedia resources, and augmented reality. These tools provide students with access to immersive and engaging learning experiences.
6. What subjects are suitable for hands-on learning?
Hands-on learning can be applied across various subjects, including science, mathematics, history, language arts, and more. The key is to design activities that are relevant, engaging, and aligned with the curriculum.
7. How does LEARNS.EDU.VN promote hands-on learning?
learns.edu.vn promotes hands-on learning through interactive courses, project-based learning opportunities, access to educational resources, and a community of learners and educators.
8. What are some examples of hands-on learning activities?
Examples include building circuits, conducting chemistry experiments, creating historical reenactments, writing and performing plays, and using manipulatives to understand arithmetic operations.
9. How can parents support hands-on learning at home?
Parents can support hands-on learning at home by providing materials and opportunities for exploration, encouraging their children to ask questions and experiment, and engaging in hands-on activities together.
10. What is the role of assessment in hands-on learning?
Assessment in hands-on learning should evaluate students’ understanding, skills, and creativity. Performance-based assessments, portfolios, and rubrics can provide valuable insights into student learning and progress.