Leonardo da Vinci’s mastery of painting is a topic of endless fascination. How Did Leonardo Da Vinci Learn To Paint and reach such unparalleled artistic heights? At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we delve into Da Vinci’s journey, exploring his apprenticeship, innovative techniques, and relentless pursuit of knowledge, offering insights that inspire artists and learners alike. Explore artistic techniques, art history, and educational resources.
1. Leonardo Da Vinci’s Artistic Foundation: Apprenticeship and Early Training
Leonardo da Vinci’s artistic journey began with a solid foundation in the workshop of Andrea del Verrocchio. This apprenticeship provided him with diverse skills and techniques essential for his future masterpieces.
1.1. Verrocchio’s Workshop: A Crucible of Renaissance Art
Andrea del Verrocchio’s workshop in Florence was more than just a studio; it was a vibrant hub of artistic innovation and learning. Here, young Leonardo was immersed in an environment where creativity and skill converged.
- Comprehensive Training: Verrocchio’s apprentices learned a wide range of skills, from painting and sculpture to metalworking and architectural design.
- Exposure to Masters: The workshop attracted established artists and patrons, providing apprentices with opportunities to observe and learn from the best.
- Collaborative Projects: Apprentices often collaborated on large-scale commissions, gaining hands-on experience in teamwork and project management.
1.2. Essential Skills Learned: Drawing, Painting, and Sculpture
Da Vinci’s apprenticeship under Verrocchio equipped him with a comprehensive skillset that formed the bedrock of his artistic genius.
| Skill | Description | Application in Da Vinci’s Work |
|---|---|---|
| Drawing | Mastery of line, form, and perspective. Emphasis on accurate representation and anatomical studies. | Foundation for all his paintings and inventions. Evident in his detailed sketches and preparatory drawings. |
| Painting | Proficiency in various painting techniques, including tempera and oil. Understanding of color theory, blending, and creating depth. | Allowed him to create lifelike portraits and dynamic compositions, such as the Mona Lisa and The Last Supper. |
| Sculpture | Experience in sculpting with different materials like bronze and clay. Understanding of three-dimensional form and spatial relationships. | Influenced his approach to painting, emphasizing volume and depth. Contributed to his understanding of human anatomy. |
| Metalworking | Crafting detailed metal elements, sculpting bronze statues and other metal artwork. | Enhanced detail in painting and sculpture with subtle highlights and shadows, thus increasing realism. |
1.3. Early Works and Collaborations: Showcasing Budding Talent
Da Vinci’s early works demonstrate his rapid development and innovative approach to art, even within the confines of traditional workshop practices.
- “Baptism of Christ”: Da Vinci’s angel in Verrocchio’s Baptism of Christ showcased his exceptional skill, surpassing even his master’s.
- Annunciation: A masterpiece that exemplifies Da Vinci’s early expertise in the use of perspective and light.
- Collaboration and Influence: Working alongside Verrocchio and other apprentices, Leonardo learned to integrate different artistic styles and techniques.
2. Da Vinci’s Self-Directed Learning: Anatomy, Science, and Observation
Leonardo da Vinci’s insatiable curiosity drove him beyond the conventional artistic training of his time. His self-directed learning in anatomy, science, and direct observation of the world around him profoundly shaped his artistic style and innovative techniques.
2.1. Anatomical Studies: Unveiling the Human Form
Da Vinci’s anatomical studies were groundbreaking, blending artistic skill with scientific inquiry.
- Dissections: Da Vinci dissected cadavers to understand the intricacies of human anatomy, a practice uncommon at the time.
- Detailed Drawings: He meticulously documented his findings through detailed anatomical drawings, capturing the structure and function of muscles, bones, and organs.
- Artistic Impact: This deep understanding of anatomy allowed him to create incredibly lifelike figures in his paintings, imbuing them with a sense of realism and vitality.
2.2. Scientific Explorations: Integrating Art and Science
Da Vinci viewed art and science as interconnected disciplines, using scientific principles to enhance his artistic creations.
- Optics and Perspective: Da Vinci studied optics to understand how light and shadow affect perception, applying this knowledge to create depth and realism in his paintings.
- Engineering and Mechanics: His explorations in engineering and mechanics informed his understanding of movement and structure, influencing his depiction of dynamic poses and complex machinery.
- Botanical Studies: Leonardo’s sketches of plants and natural elements revealed a keen eye for detail and an understanding of natural forms.
2.3. Observation and Sketching: Capturing the Essence of Life
Da Vinci was a master of observation, constantly studying the world around him and capturing his insights in detailed sketches.
- Notebooks: He filled notebooks with sketches of people, animals, landscapes, and objects, using these studies as references for his paintings and inventions.
- Capturing Movement: Da Vinci was particularly interested in capturing movement and expression, studying human behavior and animal anatomy to accurately depict dynamic scenes.
- Nature as Inspiration: He found inspiration in nature, observing the patterns of water, the growth of plants, and the formations of clouds, incorporating these observations into his art.
3. Innovative Painting Techniques: Da Vinci’s Artistic Breakthroughs
Da Vinci’s innovative painting techniques revolutionized art, setting new standards for realism, depth, and emotional expression.
3.1. Sfumato: Mastering the Art of Subtlety
Sfumato, derived from the Italian word for “smoke,” is a technique that involves subtle gradations of light and shadow to create a soft, hazy effect. Da Vinci perfected this technique to achieve unparalleled realism in his paintings.
- Blending and Layering: Da Vinci achieved sfumato by applying thin layers of paint and blending them meticulously to create smooth transitions between colors and tones.
- Softening Edges: He softened the edges of his figures, creating a sense of atmospheric perspective and depth.
- Emotional Impact: Sfumato added an air of mystery and emotion to his portraits, enhancing their psychological depth.
3.2. Chiaroscuro: Playing with Light and Shadow
Chiaroscuro, which means “light-dark” in Italian, is the use of strong contrasts between light and shadow to create dramatic effects and model three-dimensional forms.
- Dramatic Contrast: Da Vinci used chiaroscuro to create a sense of drama and intensity in his paintings, highlighting key elements and drawing the viewer’s eye.
- Modeling Forms: By carefully controlling the distribution of light and shadow, he created the illusion of three-dimensional form on a two-dimensional surface.
- Emotional Expression: Chiaroscuro enhanced the emotional impact of his paintings, conveying a sense of tension, mystery, or serenity.
3.3. Aerial Perspective: Creating Depth and Distance
Aerial perspective, also known as atmospheric perspective, is a technique used to create the illusion of depth by simulating the effects of atmosphere on distant objects.
- Color and Tone: Da Vinci used lighter colors and softer tones to depict objects in the distance, simulating the way that atmosphere scatters light and reduces contrast.
- Blurring Details: He blurred the details of distant objects, creating a sense of haziness and distance.
- Creating Realism: Aerial perspective enhanced the realism of his landscapes, making them appear vast and immersive.
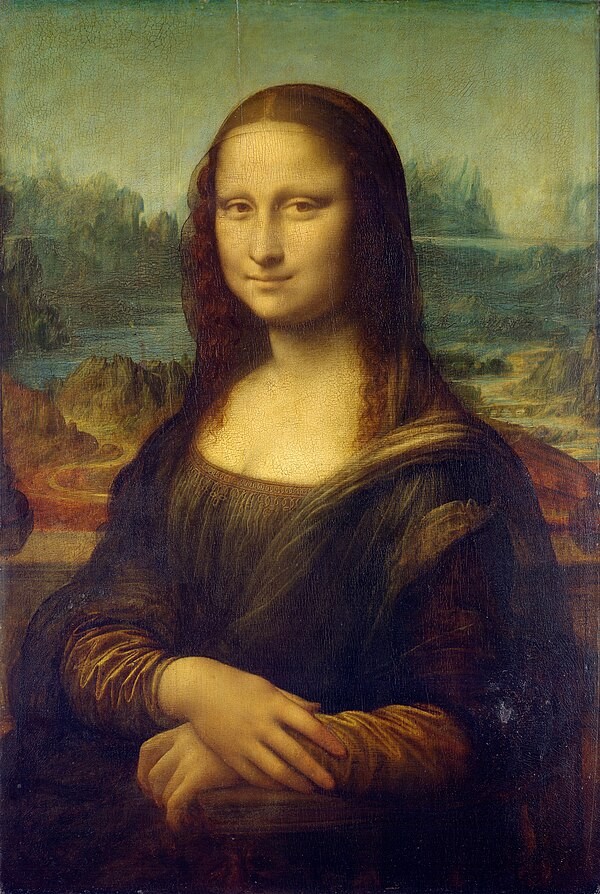 Mona Lisa Sfumato Technique
Mona Lisa Sfumato Technique
4. Key Paintings: Demonstrating Da Vinci’s Mastery
Da Vinci’s key paintings showcase his mastery of technique, innovation, and emotional depth, solidifying his legacy as one of the greatest artists of all time.
4.1. “Mona Lisa”: A Portrait of Enigmatic Beauty
The Mona Lisa is arguably Da Vinci’s most famous painting, renowned for its enigmatic smile, lifelike realism, and groundbreaking use of sfumato.
- Sfumato Technique: The Mona Lisa‘s soft, hazy appearance is achieved through Da Vinci’s mastery of sfumato, creating a sense of depth and mystery.
- Psychological Depth: The subject’s subtle expression and enigmatic gaze invite viewers to contemplate her thoughts and emotions.
- Cultural Icon: The Mona Lisa has become a cultural icon, admired and studied by artists, scholars, and art lovers around the world.
4.2. “The Last Supper”: A Dramatic Narrative
The Last Supper is a monumental fresco depicting the final meal of Jesus Christ with his disciples, capturing the emotional tension and drama of the moment.
- Composition and Perspective: Da Vinci used linear perspective to create a sense of depth and space, drawing the viewer into the scene.
- Emotional Expression: The painting captures the diverse emotions of the disciples as they react to Jesus’ announcement that one of them will betray him.
- Innovative Technique: Da Vinci experimented with new painting techniques in The Last Supper, which unfortunately led to its deterioration over time.
4.3. “Virgin of the Rocks”: A Study in Light and Shadow
Virgin of the Rocks (two versions exist) showcases Da Vinci’s innovative use of light and shadow, atmospheric perspective, and detailed botanical studies.
- Chiaroscuro Technique: The painting features dramatic contrasts between light and shadow, creating a sense of depth and mystery in the grotto setting.
- Botanical Accuracy: Da Vinci’s detailed depictions of plants and rocks reflect his keen observation of nature.
- Symbolic Composition: The arrangement of the figures and the elements of the landscape contribute to the painting’s symbolic meaning and emotional impact.
5. Da Vinci’s Continuous Pursuit of Knowledge: Lifelong Learning
Leonardo da Vinci embodied the spirit of lifelong learning, driven by an insatiable curiosity and a desire to understand the world around him. His dedication to continuous education shaped his artistic and scientific achievements, leaving a lasting legacy of innovation and discovery.
5.1. Interdisciplinary Studies
Da Vinci’s approach to learning transcended traditional boundaries, integrating knowledge from diverse fields to enhance his understanding and creativity.
- Art and Science Integration: He seamlessly blended artistic techniques with scientific principles, using his understanding of anatomy, optics, and mechanics to inform his paintings and inventions.
- Engineering and Architecture: His studies in engineering and architecture influenced his artistic compositions, enabling him to create dynamic poses and structurally sound designs.
- Botanical and Geological Observations: Da Vinci’s keen observations of nature, from botanical studies to geological formations, enriched his artwork with accurate and detailed representations of the natural world.
5.2. Notebooks and Documentation
Da Vinci’s meticulously illustrated notebooks served as a repository of his thoughts, observations, and experiments, capturing the essence of his lifelong learning journey.
- Sketches and Diagrams: His notebooks were filled with detailed sketches and diagrams, documenting his anatomical studies, engineering designs, and artistic ideas.
- Written Observations: He recorded his observations, insights, and reflections in written notes, providing valuable insights into his creative process and intellectual pursuits.
- Preservation of Knowledge: These notebooks preserved his knowledge for future generations, inspiring artists, scientists, and scholars to explore the interconnectedness of art, science, and nature.
5.3. Mentorship and Collaboration
Da Vinci’s interactions with mentors, peers, and students fostered a collaborative learning environment that stimulated intellectual exchange and creative innovation.
- Verrocchio’s Influence: His apprenticeship under Andrea del Verrocchio provided a solid foundation in artistic techniques and exposed him to a community of artists and patrons.
- Collaborative Projects: Working on collaborative projects allowed him to learn from other artists, exchange ideas, and develop his unique style.
- Mentoring Students: As a mentor, Da Vinci shared his knowledge and expertise with aspiring artists, fostering the next generation of creative talent.
6. Da Vinci’s Influence on Art Education: A Lasting Legacy
Leonardo da Vinci’s profound influence on art education continues to inspire artists and educators today, shaping approaches to teaching, learning, and creative expression.
6.1. Emphasis on Observation and Drawing
Da Vinci’s emphasis on observation and drawing as fundamental skills for artists has had a lasting impact on art education.
- Observational Skills: His detailed anatomical studies and botanical drawings underscore the importance of keen observation in understanding the world around us.
- Drawing as Foundation: Da Vinci’s belief in drawing as the foundation for all artistic endeavors has led to its continued prominence in art curricula.
- Realistic Representation: His commitment to realistic representation has influenced generations of artists to strive for accuracy and detail in their work.
6.2. Interdisciplinary Approach to Art
Da Vinci’s interdisciplinary approach to art, integrating science, engineering, and humanities, has inspired educators to adopt holistic and cross-curricular approaches to art education.
- Integrating Science and Art: Educators recognize the value of integrating scientific principles into art curricula, encouraging students to explore the intersection of art and science.
- Cross-Curricular Connections: By making cross-curricular connections, educators aim to provide students with a well-rounded education that fosters creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills.
- Innovation and Creativity: Da Vinci’s legacy of innovation and creativity encourages educators to foster a spirit of experimentation and discovery in their classrooms.
6.3. Lifelong Learning and Curiosity
Da Vinci’s dedication to lifelong learning and his insatiable curiosity serve as a model for artists and educators alike, emphasizing the importance of continuous growth and exploration.
- Cultivating Curiosity: Educators strive to cultivate curiosity in their students, encouraging them to ask questions, explore new ideas, and challenge conventional thinking.
- Promoting Lifelong Learning: By promoting lifelong learning, educators aim to instill a passion for knowledge and a commitment to personal and professional development.
- Creative Problem-Solving: Da Vinci’s approach to problem-solving inspires educators to encourage students to approach challenges with creativity, resilience, and a willingness to learn from their mistakes.
7. Modern Resources for Learning Da Vinci’s Techniques: Embracing Innovation
Today, artists and learners can access a wealth of modern resources to explore Da Vinci’s techniques, embracing innovation and technology to deepen their understanding.
7.1. Online Courses and Tutorials
Online platforms offer a wide array of courses and tutorials that delve into Da Vinci’s techniques, providing learners with structured guidance and expert instruction.
- Comprehensive Curriculum: These online courses cover various aspects of Da Vinci’s art, including sfumato, chiaroscuro, anatomy, and composition.
- Expert Instruction: Industry professionals and art historians provide expert instruction, sharing insights and techniques gleaned from years of study and practice.
- Accessible Learning: Online courses make learning Da Vinci’s techniques accessible to students around the world, regardless of their location or background.
7.2. Digital Tools and Software
Digital tools and software have revolutionized the way artists create and learn, providing new avenues for exploring Da Vinci’s techniques and experimenting with different styles.
- Digital Painting Software: Software like Adobe Photoshop and Corel Painter allows artists to simulate Da Vinci’s techniques digitally, experimenting with blending, layering, and creating subtle gradations of tone.
- 3D Modeling and Animation: 3D modeling and animation software enables artists to study Da Vinci’s anatomical studies in three dimensions, gaining a deeper understanding of human form and movement.
- Virtual Reality Experiences: Virtual reality experiences offer immersive opportunities to explore Da Vinci’s artworks, allowing users to examine details up close and interact with his masterpieces in new ways.
7.3. Museums and Exhibitions
Museums and exhibitions continue to play a vital role in preserving and showcasing Da Vinci’s artworks, providing visitors with opportunities to study his techniques firsthand and appreciate his genius.
- Direct Observation: Visiting museums allows artists and learners to observe Da Vinci’s paintings in person, studying his brushwork, color palette, and composition.
- Curatorial Insights: Museum curators provide valuable insights into Da Vinci’s techniques, sharing historical context and artistic analysis to enhance visitors’ understanding.
- Educational Programs: Museums often offer educational programs, workshops, and lectures that delve into Da Vinci’s life, art, and legacy, engaging audiences of all ages.
8. Practical Exercises to Emulate Da Vinci’s Learning: Hands-On Application
Engaging in practical exercises is essential for emulating Da Vinci’s learning approach and mastering his techniques.
8.1. Sketching from Observation
Da Vinci emphasized the importance of sketching from observation to develop visual acuity and understanding of form.
- Daily Sketching: Commit to sketching from observation daily, capturing the details of everyday objects, landscapes, and people.
- Focus on Detail: Pay close attention to details, capturing subtle nuances of light, shadow, and texture.
- Experiment with Mediums: Experiment with different sketching mediums, such as pencil, charcoal, and ink, to explore different effects and develop your style.
8.2. Anatomical Studies
Studying anatomy is crucial for understanding the human form and creating lifelike figures in your artwork.
- Study Anatomical Drawings: Study Da Vinci’s anatomical drawings, paying attention to the structure and function of muscles, bones, and organs.
- Attend Life Drawing Sessions: Attend life drawing sessions to practice drawing the human figure from live models, focusing on accuracy and proportion.
- Dissection (If Possible): If possible, consider participating in a dissection course to gain firsthand experience with human anatomy, but be mindful of ethical and legal considerations.
8.3. Sfumato Practice
Mastering sfumato requires patience, practice, and a keen eye for subtle gradations of tone.
- Layering Technique: Practice layering thin glazes of paint to create smooth transitions between colors and tones, blending carefully to avoid harsh edges.
- Use of Soft Brushes: Use soft brushes to blend the edges of your figures, creating a hazy, atmospheric effect.
- Experiment with Lighting: Experiment with different lighting conditions to see how light and shadow affect the appearance of your subject.
9. Overcoming Challenges in Learning Da Vinci’s Methods: Strategies for Success
Learning Da Vinci’s methods can present challenges, but with the right strategies, learners can overcome these obstacles and achieve success.
9.1. Patience and Perseverance
Mastering Da Vinci’s techniques requires patience, perseverance, and a willingness to learn from mistakes.
- Embrace the Process: Understand that learning takes time and effort, and embrace the process of experimentation and discovery.
- Don’t Be Afraid to Fail: Don’t be afraid to make mistakes, as they are an essential part of the learning process.
- Stay Committed: Stay committed to your goals, even when faced with challenges, and celebrate your progress along the way.
9.2. Seeking Guidance and Feedback
Seeking guidance from experienced artists and educators can provide valuable insights and feedback to help you improve your skills.
- Join Art Communities: Join online and offline art communities to connect with other artists, share your work, and receive feedback.
- Attend Workshops and Classes: Attend workshops and classes led by experienced instructors to learn new techniques and receive personalized guidance.
- Mentorship Programs: Consider participating in mentorship programs to receive one-on-one guidance from a seasoned artist.
9.3. Balancing Theory and Practice
Balancing theoretical knowledge with practical application is crucial for mastering Da Vinci’s methods.
- Study Art History: Study art history to gain a deeper understanding of Da Vinci’s context, influences, and achievements.
- Read Technical Manuals: Read technical manuals and guides to learn about the materials, tools, and techniques used by Da Vinci.
- Hands-On Practice: Dedicate ample time to hands-on practice, applying what you’ve learned to create your own artwork.
10. The Enduring Relevance of Da Vinci’s Learning Approach: Inspiring Future Generations
Leonardo da Vinci’s learning approach remains highly relevant today, inspiring future generations of artists, scientists, and innovators to embrace curiosity, creativity, and lifelong learning.
10.1. Fostering Curiosity and Exploration
Da Vinci’s insatiable curiosity and thirst for knowledge encourage individuals to cultivate a spirit of exploration and inquiry in their own lives.
- Ask Questions: Embrace the habit of asking questions, challenging assumptions, and seeking deeper understanding in all areas of life.
- Explore New Ideas: Be open to exploring new ideas and perspectives, even if they challenge your existing beliefs.
- Seek Interdisciplinary Knowledge: Seek interdisciplinary knowledge, connecting different fields of study to gain a more holistic understanding of the world.
10.2. Encouraging Creativity and Innovation
Da Vinci’s innovative spirit inspires individuals to think creatively, challenge conventions, and pursue groundbreaking ideas.
- Brainstorming and Ideation: Engage in brainstorming and ideation exercises to generate new ideas and solutions to problems.
- Experimentation and Prototyping: Experiment with different approaches and prototypes to test your ideas and refine your designs.
- Collaboration and Feedback: Collaborate with others and seek feedback to improve your creative output.
10.3. Promoting Lifelong Learning and Personal Growth
Da Vinci’s dedication to lifelong learning serves as a reminder that education is a continuous journey, not a destination.
- Set Learning Goals: Set learning goals for yourself, identifying areas where you want to grow and develop.
- Seek Out New Experiences: Seek out new experiences and challenges that will push you outside of your comfort zone.
- Reflect on Your Learning: Take time to reflect on your learning experiences, identifying what you’ve learned and how you can apply it in the future.
Are you inspired by Leonardo da Vinci’s journey and eager to enhance your artistic skills? Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN for detailed tutorials, comprehensive courses, and expert guidance. Unleash your inner artist with our resources! For more information, visit us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States, contact us on Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212, or explore our website at learns.edu.vn.
FAQ: Leonardo da Vinci’s Artistic Education
Here are some frequently asked questions about how Leonardo da Vinci learned to paint, providing additional insights into his artistic development and techniques.
-
What was Leonardo da Vinci’s early artistic training?
Leonardo da Vinci began his artistic training as an apprentice in the workshop of Andrea del Verrocchio in Florence, where he learned drawing, painting, sculpture, and various technical skills.
-
How did Verrocchio’s workshop influence Da Vinci’s development?
Verrocchio’s workshop provided Da Vinci with a comprehensive artistic education, exposing him to diverse techniques, materials, and collaborative projects that shaped his artistic foundation.
-
What self-directed learning methods did Da Vinci employ?
Da Vinci pursued self-directed learning through anatomical studies, scientific explorations, and meticulous observation of the world around him, documenting his findings in detailed notebooks.
-
How did Da Vinci’s anatomical studies impact his art?
Da Vinci’s anatomical studies provided him with a deep understanding of human anatomy, enabling him to create incredibly lifelike figures in his paintings, imbued with realism and vitality.
-
What is sfumato, and how did Da Vinci master it?
Sfumato is a painting technique that involves subtle gradations of light and shadow to create a soft, hazy effect. Da Vinci mastered it by applying thin layers of paint and blending them meticulously to create smooth transitions.
-
Can you explain Da Vinci’s use of chiaroscuro?
Chiaroscuro is the use of strong contrasts between light and shadow to create dramatic effects and model three-dimensional forms. Da Vinci used it to enhance the emotional impact and realism of his paintings.
-
What role did observation play in Da Vinci’s art?
Observation was crucial to Da Vinci’s art. He constantly studied the world around him, capturing his insights in detailed sketches and incorporating these observations into his paintings.
-
How did Da Vinci integrate science and art?
Da Vinci integrated science and art by applying scientific principles, such as optics and mechanics, to enhance his artistic creations, creating depth, realism, and dynamic compositions.
-
What resources are available today for learning Da Vinci’s techniques?
Today, learners can access online courses, digital tools, museums, and exhibitions to explore Da Vinci’s techniques, embracing innovation and technology to deepen their understanding.
-
What is the enduring relevance of Da Vinci’s learning approach?
Da Vinci’s learning approach remains highly relevant, inspiring future generations to embrace curiosity, creativity, and lifelong learning, fostering innovation and personal growth.