Learning to play an instrument affects the brain in numerous positive ways, boosting cognitive skills and overall brain health; LEARNS.EDU.VN delves into the science behind this fascinating connection. This exploration uncovers how musical training enhances memory, improves language skills, and sharpens executive functions, providing insights into the neurological benefits of playing music. Discover how music education can be a cornerstone for cognitive development, exploring the transferrable skills and long-term advantages that come from engaging with music.
1. How Does Musical Training Influence Brain Development?
Musical training profoundly influences brain development by enhancing sound sensitivity, verbal abilities, and reasoning skills. Studies reveal the brain’s functional and structural plasticity in response to musical education. This is according to research in auditory cognitive neuroscience. Such training impacts areas related to hearing, movement, and sensory integration, suggesting that learning music can cause notable changes in how the brain operates and is structured.
1.1. What Cognitive, Emotional, and Social Functions Are Engaged in Music?
Music engages a broad spectrum of cognitive, emotional, and social functions. These include:
- Perceptual abilities: Skills such as pitch discrimination and auditory memory are essential for processing music.
- Emotional impact: Music influences emotions through brain regions associated with reward, emotion processing, and memory.
- Social Interaction: Group music-making enhances communication, coordination, and empathy.
- Multisensory Motor Experience: Playing an instrument is a multisensory experience that blends symbolic understanding with precise motor skills, fine motor control, and memory, enhancing executive functions crucial for focused learning.
1.2. How Does Playing An Instrument Change Brain Structure And Function?
Playing an instrument leads to significant changes in brain structure and function, especially in areas related to auditory and motor processing. Highly trained musicians often show increased plasticity in brain networks responsible for these functions. Neuroimaging studies have confirmed structural differences, such as increased gray matter volume, in various brain regions including:
- Auditory cortex
- Motor cortex
- Somatosensory areas
- Premotor cortex
- Cerebellum
These changes correlate with the intensity and duration of musical training, indicating that the brain adapts to the demands of playing music.
 Musician's brain
Musician's brain
2. What Are The Effects Of Musical Training In Childhood?
Musical training in childhood provides numerous benefits, from enhancing fine motor skills and rhythm perception to improving phoneme discrimination, vocabulary, and non-verbal reasoning. These enhancements can also lead to better academic performance and general cognitive development.
2.1. What Are Critical And Sensitive Periods In Brain Development And How Do They Relate To Musical Training?
Critical and sensitive periods are specific times in development when the brain is more responsive to certain experiences. The effects of musical training during these periods can be particularly profound.
- Sensitive Periods: Limited periods when experiences have a strong impact on brain development.
- Critical Periods: Strict time windows essential for normal development, permanently altering performance.
The timing of musical initiation is crucial because different brain regions develop at different rates. Early musical training can maximize plasticity in sensory and motor areas, while later training can still influence temporal-parietal and frontal areas.
2.2. How Does Musical Training Affect Brain Plasticity In Children?
Musical training during sensitive periods can significantly enhance brain plasticity in children. Studies show that musical training can accelerate neurofilament development in upper cortical layers, which is crucial for fast, synchronized neuronal firing. Research using MR scans has revealed significant improvements in:
- Fine motor skills
- Auditory discrimination
- Motor brain areas (such as the right precentral gyrus)
- Corpus callosum
- Primary auditory region
These changes are more pronounced when musical training begins early, highlighting the lasting impact of early musical education.
2.3. How Does Musical Training Enhance Listening Skills?
Musical training enhances listening skills by improving sound discrimination, pitch processing, and speech recognition. Studies show that children with musical training are more sensitive to musical keys and harmonics. Training improves the ability to discriminate minor pitch differences and syllabic durations, enhancing the temporal fine-tuning of auditory perception. Enhanced listening skills are crucial for processing speech and voices accurately, allowing for better communication and learning outcomes.
3. What Are The Effects Of Musical Training On Cognitive Functions?
Musical training has a wide array of effects on cognitive functions. These include improved linguistic, spatial, mathematical, and executive function skills. Engagement with music enhances overall intellectual capabilities and academic performance.
3.1. How Does Musical Training Improve Linguistic Skills?
Musical training enhances linguistic skills through shared auditory processing mechanisms. Training improves neural differentiation of sounds, leading to better speech sound discrimination. Specific benefits include:
- Enhanced auditory brainstem responses: Improved neural differentiation of similar sounds.
- Improved syntax processing: Mechanisms underlying syntax processing in both music and language develop earlier in musically trained children.
- Better pitch discrimination: Transfers to speech and reading skills.
- Enhanced verbal memory: Increased abilities in verbal fluency and memory tasks.
- Improved second language acquisition: Enhanced skills in receptive and productive phonology.
The OPERA hypothesis suggests that musical training enhances speech encoding through overlapping brain networks, high precision demands, emotional reinforcement, and attentional focus.
3.2. What Impact Does Musical Training Have On Spatial And Mathematical Skills?
Musical training can enhance spatial skills, though the effects are not always consistent. Some studies show improvements in spatial tasks, such as the Object Assembly subtest of the WISC, while others report no clear association. Meta-analyses suggest that the influence of musical training on math performance is not well-supported. While musical training may aid in the acquisition of spatial abilities in children, it does not consistently provide a permanent advantage in spatial or mathematical skills.
3.3. How Does Learning Music Enhance Executive Functions?
Learning music enhances executive functions by improving cognitive control, working memory, and cognitive flexibility. Musical training requires attention, memory, coordination, and task-switching, which rely on integrating top-down and bottom-up processes. Benefits include:
- Improved cognitive control: Enhanced attention and inhibition.
- Increased working memory capacity: Greater ability to retain and process information.
- Enhanced cognitive flexibility: Improved ability to switch between tasks.
- Faster processing speed: Greater efficiency in performing cognitive tasks.
Short-term musical training programs have been shown to improve executive functions in children, demonstrating that even brief musical interventions can have significant cognitive benefits.
3.4. How Does Musical Training Affect General IQ And Academic Achievement?
Musical training can positively influence general IQ and academic achievement. While some research suggests that children with higher cognitive abilities are more likely to take music lessons, studies controlling for these factors still show a positive correlation between music lessons and IQ. Benefits include:
- Better academic performance: Musical training predicts higher academic scores.
- Improved general IQ scores: Gains across multiple IQ indexes, including verbal comprehension and processing speed.
- Enhanced executive functions: Although the mediating effect of executive functions is debated, some studies show that musical training improves these functions, leading to better cognitive outcomes.
Music lessons act as additional schooling, requiring focused attention, memorization, and mastery of technical skills, which translate into better results in other subjects and higher IQ scores.
3.5. Does Learning Music Affect Social Skills?
The impact of musical training on social skills is still being investigated. Some studies suggest a positive correlation between musical training and emotion comprehension, though this may disappear when controlling for individual intelligence levels. Musical activities enhance communicative and social development in infants, and group musical activities can foster cooperation. Key findings include:
- Enhanced emotion comprehension: Improved ability to understand and recognize emotions.
- Increased prosocial behaviors: Greater cooperation and social affiliation.
- Improved emotional prosody perception: Enhanced recognition of emotions expressed through human voices.
Further research is needed to fully understand how different music teaching methods and group musical activities influence social skills.
4. What Is The Impact Of Musical Activities On Brain Plasticity Throughout Life?
Musical activities have a beneficial impact on brain plasticity and cognitive and physical abilities, even in adulthood. Musical ear training can evoke functional changes in the hippocampus, and engaging in cognitive activities like musical training can help preserve cognitive functions in old age.
4.1. How Can Musical Training Mitigate Age-Related Cognitive Decline?
Musical training can mitigate age-related cognitive decline by maintaining fluid intelligence and preventing the diminishment of hippocampal volume. Benefits include:
- Preserved non-verbal memory: Significant differences between elderly musicians and non-musicians in non-verbal memory tasks.
- Enhanced verbal fluency: Improved abilities in verbal tasks.
- Improved executive functions: Greater cognitive control and flexibility.
- Increased fluid intelligence: Maintained ability to solve new problems and think abstractly.
Even starting to learn an instrument later in life can improve working memory, motor skills, and perceptual speed.
4.2. How Does Rhythm-Based Music Instruction Affect Physical Abilities In Seniors?
Rhythm-based music instruction, such as Dalcroze Eurhythmics, positively influences equilibrium and gait regularity in elderly individuals. This method uses movements and rhythm to teach music, improving physical abilities and reducing the risk of falls. Engagement in training physical abilities combined with musical aspects of rhythmical movement synchronization enhances overall well-being.
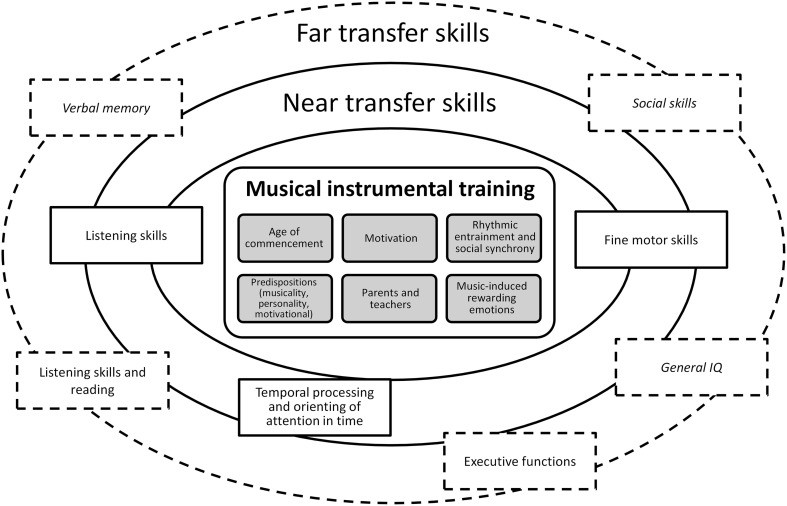
5. What Factors Influence Brain Plasticity Through Musical Training?
Several factors influence brain plasticity through musical training, including genetic predispositions, motivation, and the specific elements of musical engagement such as rhythm and entrainment. These elements play a significant role in determining the extent and nature of the cognitive and neurological benefits derived from musical education.
5.1. How Do Genetic Predispositions Affect Musical Ability And Brain Development?
Genetic predispositions play a role in musical ability and brain development. Attributes of musicality such as pitch perception, absolute pitch, creativity in music, and sensitivity to music have genetic determinants. These predispositions can influence an individual’s likelihood of engaging in musical training and their capacity to benefit from it. However, it’s essential to disentangle innate abilities from the effects of longitudinal training.
5.2. What Role Does Motivation And Reward Play In Musical Training?
Motivation and reward are critical in musical training. A positive affective experience, such as pleasure and pride from music lessons, promotes future practice and duration of training. Intrinsic motivation drives brain plasticity and can be influenced by genetic polymorphisms affecting dopamine receptors. The rewarding value of musical activity enhances memory formation and reinforces the reinforcing quality of music learning.
5.3. What Is The Role Of Rhythm And Entrainment In Transferrable Effects Of Musical Training?
Rhythm and entrainment are key mechanisms underlying the beneficial transferrable effects of musical training. Musical activities, based on rhythm, train attentional processes and enhance other cognitive functions. Entrainment, the synchronization of attentional processes to auditory rhythm, leads to improved:
- Temporal Processing: Enhanced ability to perceive and produce rhythms accurately.
- Attentional Processes: Improved attentional control and focus.
- Sensorimotor Integration: Enhanced coordination of movements and sensory feedback.
- Cognitive Functions: Benefits for reading, executive functions, and verbal memory.
- Emotional Induction: Rhythmic entrainment is an emotion induction mechanism, contributing to the induction of an emotional reaction.
Musical education, through daily training of temporal processing mechanisms, has a beneficial effect on cognitive functions, such as reading, in which attention has to be guided in a specific manner. Learning to perform an activity in synchrony together with others is supported by the activation of the mirror neuron system. These social aspects of musical training contribute to the role of reward and motivation in shaping a developing brain.
6. How Can Musical Training Enhance Executive Functions And Cognitive Skills?
As explored on LEARNS.EDU.VN, musical training uniquely fosters cognitive development through near and far transfer effects, preparing a foundation for a range of skills. Music uniquely supports and develops skills, creating a robust cognitive foundation that benefits academic success, personal growth, and cognitive acuity.
6.1. What Are The Benefits Of Music Education Starting Early In Childhood?
Music education starting early in childhood offers opportunities to tune and train the brain for important cognitive and social functions. Musical training enhances various cognitive functions and is accompanied by neuroplastic changes in brain structure and function. In this review, we pointed to specific factors affecting the relative value of musical education in comparison to other types of longitudinal training in childhood that require similar engagement of cognitive resources and demand a significant overall time investment.
6.2. How Can Parents and Educators Promote Instrumental Training For Young People?
Parents and educators can promote instrumental training in early childhood by:
- Encouraging children to explore different instruments.
- Providing access to music lessons and resources.
- Creating a supportive and motivating learning environment.
- Recognizing and celebrating children’s musical achievements.
Encouraging instrumental training in early childhood may result in life-long advantages. The aspect of motivation is underrepresented in the existing literature on musical training. The link between reward system activity and various forms of learning is well known: for instance, hippocampal learning (spatial, semantic, and episodic memory) is enhanced with the simultaneous activity of the reward system.
Ready to unlock your potential and explore the transformative power of music? Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today to discover courses and resources that will help you or your child harness the cognitive and creative benefits of musical training. Start your musical journey now and experience the remarkable impact it can have on your brain and overall well-being.
Address: 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States
Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212
Website: LEARNS.EDU.VN
FAQ: Learning An Instrument And Its Effects On The Brain
1. How does learning an instrument affect the brain?
Learning an instrument enhances brain plasticity, improves cognitive functions like memory and attention, and strengthens neural connections.
2. What specific cognitive skills are improved by musical training?
Musical training improves linguistic skills, spatial reasoning, executive functions, and overall cognitive abilities.
3. Does the age at which you start learning an instrument matter?
Yes, starting musical training early in childhood during sensitive periods can have a more profound impact on brain development.
4. Can musical training help mitigate age-related cognitive decline?
Yes, engaging in musical activities throughout life can help preserve cognitive functions and maintain brain plasticity.
5. How does musical training enhance listening skills?
Musical training improves sound discrimination, pitch processing, and speech recognition.
6. What is rhythmic entrainment, and how does it contribute to the benefits of musical training?
Rhythmic entrainment is the synchronization of attentional processes to auditory rhythm, which enhances temporal processing, attention, and sensorimotor integration.
7. Are there genetic factors that influence musical ability?
Yes, certain attributes of musicality, such as pitch perception and sensitivity to music, have genetic determinants.
8. How does motivation affect the outcomes of musical training?
Motivation plays a critical role in musical training, with positive emotional experiences promoting practice and enhancing brain plasticity.
9. Can learning an instrument improve social skills?
Musical training can enhance emotion comprehension and prosocial behaviors, particularly in group musical activities.
10. Where can I find resources and courses to start musical training?
Visit learns.edu.vn to discover a wide range of courses and resources designed to help you unlock the cognitive and creative benefits of musical training.