Learning to play lead guitar is a rewarding journey, and at LEARNS.EDU.VN, we understand that aspiring guitarists often wonder, “How long will it take?” While there’s no one-size-fits-all answer, we offer a structured approach to learning, ensuring consistent progress and skill development. Let’s explore a realistic timeline and the factors influencing your progress, turning musical dreams into reality with effective guitar lessons and personalized music education. Delve into guitar proficiency, musical journey, and skill development.
1. Understanding the Learning Timeline for Lead Guitar
The question of “How Long To Learn Lead Guitar” is common among aspiring musicians, and it’s essential to approach it with realistic expectations. Several factors influence the timeline, including practice frequency, learning style, and the complexity of the music you aim to play. Let’s break down the typical phases of learning and what you can expect at each stage.
- Consistency is Key: Consistent practice, even in short bursts, is more effective than sporadic long sessions.
- Personalized Learning: Tailoring your learning to your specific goals and preferences can accelerate your progress.
- Realistic Expectations: Understanding that progress is gradual and that plateaus are normal helps maintain motivation.
1.1 Beginner Stage: The First Steps (3-6 Months)
The initial months are crucial for building a solid foundation. This stage involves learning basic chords, understanding rhythm, and developing finger strength and dexterity. Expect to spend time familiarizing yourself with the fretboard and mastering fundamental techniques.
| Skill | Description | Timeframe | Resources at LEARNS.EDU.VN |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Chords | Mastering open chords like A, D, E, G, and C. | 1-2 Months | Beginner Guitar Chords Course, Chord Transition Exercises |
| Rhythm Fundamentals | Understanding time signatures and basic strumming patterns. | 1 Month | Rhythm Guitar for Beginners, Strumming Pattern Masterclass |
| Finger Exercises | Building strength and dexterity in your fingers. | Ongoing | Finger Strength Exercises, Dexterity Drills for Guitarists |
| Basic Music Theory | Understanding basic music notation and terminology. | 1-2 Months | Introduction to Music Theory, Reading Guitar Tabs |
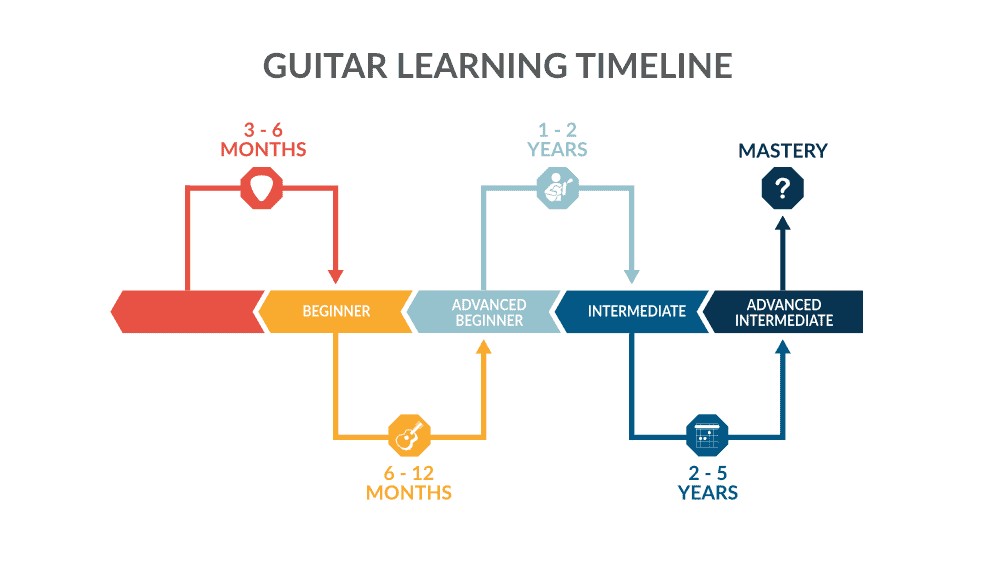

1.2 Advanced Beginner Stage: Building Momentum (6 Months to 1 Year)
As you progress, you’ll delve into more complex chords, scales, and techniques. This stage focuses on expanding your musical vocabulary and improving your ability to play more challenging songs. Be prepared for plateaus and moments of frustration, but remember that persistence is key.
| Skill | Description | Timeframe | Resources at LEARNS.EDU.VN |
|---|---|---|---|
| Barre Chords | Mastering barre chords like F, B♭, and C#. | 2-3 Months | Barre Chord Mastery, Overcoming Barre Chord Challenges |
| Minor Pentatonic Scale | Learning the minor pentatonic scale and its various positions. | 2 Months | Minor Pentatonic Scale Mastery, Pentatonic Licks and Exercises |
| Power Chords | Understanding and using power chords for rock and metal styles. | 1 Month | Power Chord Basics, Power Chord Rhythms and Progressions |
| Basic Lead Techniques | Introduction to techniques like hammer-ons, pull-offs, and slides. | 2-3 Months | Hammer-Ons and Pull-Offs, Slide Guitar Techniques |
1.3 Intermediate Stage: Refining Your Skills (1-2 Years)
At this stage, you’ll focus on refining your technique, developing your own style, and exploring different genres of music. You’ll learn to improvise, write your own songs, and play with other musicians. This is where you’ll start to feel like a true guitarist.
| Skill | Description | Timeframe | Resources at LEARNS.EDU.VN |
|---|---|---|---|
| Major Scales | Learning and applying major scales in different keys. | 3 Months | Major Scale Mastery, Applying Major Scales to Soloing |
| Modes | Understanding and using modes to add color and variety to your playing. | 4 Months | Introduction to Modes, Using Modes in Improvisation |
| Intermediate Lead Techniques | Developing techniques like alternate picking, sweep picking, and tapping. | 6 Months | Alternate Picking Exercises, Sweep Picking Technique, Tapping for Guitarists |
| Improvisation Basics | Learning to improvise over chord progressions using scales and modes. | Ongoing | Improvisation for Beginners, Improvising Over Chord Changes |
1.4 Advanced Intermediate Stage: Mastering the Craft (2-5 Years)
This is where you solidify your skills and develop a deep understanding of music theory and guitar technique. You’ll be able to play complex solos, write sophisticated songs, and perform with confidence in any setting. Continuous learning and exploration are essential at this stage.
| Skill | Description | Timeframe | Resources at LEARNS.EDU.VN |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Scales and Arpeggios | Mastering advanced scales like diminished and whole-tone scales, and using arpeggios in solos. | 6 Months | Diminished Scale Mastery, Whole-Tone Scale Exercises, Arpeggio Techniques for Guitarists |
| Advanced Improvisation | Developing advanced improvisation skills, including using chromaticism and outside playing. | Ongoing | Advanced Improvisation Techniques, Chromaticism in Soloing, Outside Playing Concepts |
| Complex Chord Progressions | Understanding and using complex chord progressions, including jazz chords and substitutions. | 6 Months | Jazz Chord Progressions, Chord Substitution Techniques |
| Professional Performance Skills | Developing stage presence, working with a band, and recording your music. | Ongoing | Stage Presence for Musicians, Working with a Band, Recording Your Guitar Tracks |
2. Factors Influencing Learning Speed
Several factors affect how quickly you learn to play lead guitar. Understanding these can help you optimize your learning process and achieve your goals more efficiently.
2.1 Practice Habits
Consistent and focused practice is the most critical factor. Aim for regular practice sessions, even if they’re short, rather than sporadic long sessions.
- Regularity: Daily practice, even for 30 minutes, is more effective than a three-hour session once a week.
- Focus: Eliminate distractions during practice to maximize your learning.
- Structure: Develop a practice routine that covers all the essential skills.
2.2 Natural Aptitude
Some individuals have a natural inclination for music, which can make learning easier. However, aptitude is not a substitute for hard work and dedication.
- Musical Background: Previous experience with other instruments can provide a head start.
- Ear Training: A good ear for music helps with learning melodies and harmonies.
- Rhythm: A natural sense of rhythm is essential for playing guitar.
2.3 Learning Resources
Access to quality learning resources can significantly impact your progress. This includes teachers, books, online courses, and other learning materials.
- Qualified Teacher: A good teacher can provide personalized guidance and feedback.
- Comprehensive Materials: Books and online courses offer structured learning paths.
- Online Communities: Joining online forums and communities can provide support and motivation.
2.4 Time Commitment
The amount of time you dedicate to learning directly affects your progress. The more time you invest, the faster you’ll improve.
- Realistic Goals: Set achievable goals based on your available time.
- Prioritization: Make learning guitar a priority in your schedule.
- Consistency: Maintain a consistent practice schedule, even when life gets busy.
3. Setting Realistic Goals and Expectations
It’s important to set realistic goals and expectations when learning lead guitar. This will help you stay motivated and avoid frustration.
3.1 Define Your Goals
Clearly define what you want to achieve with your guitar playing. Do you want to play in a band, write your own songs, or simply play for fun?
- Specific Goals: Instead of saying “I want to be a good guitarist,” set specific goals like “I want to learn to play five songs in the next three months.”
- Measurable Goals: Track your progress and measure your achievements.
- Achievable Goals: Set goals that are challenging but within your reach.
3.2 Manage Expectations
Understand that learning guitar takes time and effort. Don’t expect to become a virtuoso overnight.
- Progress is Gradual: Be patient and celebrate small victories.
- Plateaus are Normal: Don’t get discouraged when you hit a plateau. It’s a natural part of the learning process.
- Enjoy the Journey: Focus on the enjoyment of playing guitar, rather than just the end result.
3.3 Seek Feedback
Regularly seek feedback from teachers, mentors, or fellow musicians. This will help you identify areas for improvement and stay on track.
- Constructive Criticism: Be open to constructive criticism and use it to improve your playing.
- Record Yourself: Recording yourself playing can help you identify areas for improvement that you might not notice otherwise.
- Perform for Others: Playing for others can provide valuable feedback and help you build confidence.
4. Practice Techniques for Effective Learning
Effective practice techniques can accelerate your learning and help you achieve your goals more efficiently.
4.1 Focused Practice
Concentrate on specific skills or techniques during each practice session. Avoid aimless noodling, which can be unproductive.
- Warm-Up Exercises: Start each practice session with warm-up exercises to prepare your fingers and mind.
- Targeted Drills: Focus on specific techniques or skills that you want to improve.
- Cool-Down Exercises: End each practice session with cool-down exercises to prevent injuries.
4.2 Active Learning
Engage actively with the material you’re learning. Don’t just passively read or watch tutorials.
- Take Notes: Take notes on important concepts and techniques.
- Ask Questions: Don’t be afraid to ask questions if you don’t understand something.
- Experiment: Experiment with different techniques and approaches to find what works best for you.
4.3 Spaced Repetition
Review material at increasing intervals to reinforce your learning. This technique is more effective than cramming.
- Review Regularly: Regularly review previously learned material to keep it fresh in your mind.
- Use Flashcards: Use flashcards to quiz yourself on important concepts and techniques.
- Teach Others: Teaching others is a great way to reinforce your own learning.
4.4 Deliberate Practice
Identify your weaknesses and focus on improving them. This is more effective than simply playing what you already know well.
- Identify Weaknesses: Identify areas where you struggle and focus on improving them.
- Break Down Complex Tasks: Break down complex tasks into smaller, more manageable steps.
- Seek Feedback: Regularly seek feedback on your playing to identify areas for improvement.
5. Overcoming Challenges and Staying Motivated
Learning lead guitar can be challenging, and it’s important to have strategies for overcoming obstacles and staying motivated.
5.1 Dealing with Frustration
Frustration is a normal part of the learning process. Don’t let it discourage you.
- Take Breaks: Take breaks when you feel frustrated to clear your head.
- Focus on Progress: Focus on the progress you’ve made, rather than the challenges you face.
- Seek Support: Talk to a teacher, mentor, or fellow musician for support.
5.2 Avoiding Burnout
Burnout can occur when you push yourself too hard without taking breaks.
- Set Realistic Goals: Set realistic goals and avoid overcommitting yourself.
- Take Breaks: Take regular breaks to rest and recharge.
- Vary Your Routine: Vary your practice routine to keep things interesting.
5.3 Staying Inspired
Inspiration is essential for maintaining motivation.
- Listen to Music: Listen to your favorite guitarists for inspiration.
- Attend Concerts: Attend concerts to see live performances.
- Join a Band: Playing in a band can provide motivation and inspiration.
5.4 Tracking Progress
Tracking your progress can help you stay motivated and see how far you’ve come.
- Keep a Journal: Keep a journal of your practice sessions and track your progress.
- Record Yourself: Regularly record yourself playing to see how you’ve improved.
- Set Milestones: Set milestones and celebrate your achievements.
6. Utilizing Online Resources and Communities
The internet offers a wealth of resources for learning lead guitar.
6.1 Online Courses
Online courses provide structured learning paths and can be a great way to learn at your own pace.
- Comprehensive Curriculum: Look for courses with a comprehensive curriculum that covers all the essential skills.
- Experienced Instructors: Choose courses taught by experienced and qualified instructors.
- Community Support: Look for courses with a supportive online community.
6.2 YouTube Tutorials
YouTube is a great resource for learning specific techniques and songs.
- Variety of Content: YouTube offers a wide variety of content, from beginner lessons to advanced tutorials.
- Free Access: Most YouTube tutorials are free to access.
- Supplement to Learning: Use YouTube tutorials as a supplement to your formal learning.
6.3 Online Communities
Online communities can provide support, motivation, and feedback.
- Forums: Join online forums to ask questions and share your experiences.
- Social Media Groups: Join social media groups to connect with other guitarists.
- Virtual Jam Sessions: Participate in virtual jam sessions to practice playing with others.
7. The Role of a Guitar Teacher
While online resources are valuable, a guitar teacher can provide personalized guidance and feedback.
7.1 Personalized Instruction
A teacher can tailor their instruction to your specific needs and goals.
- Assessment: A teacher can assess your current skill level and identify areas for improvement.
- Customized Plan: A teacher can develop a customized learning plan based on your goals and preferences.
- Progress Tracking: A teacher can track your progress and provide feedback to help you stay on track.
7.2 Real-Time Feedback
A teacher can provide real-time feedback on your playing and help you correct mistakes.
- Technique Correction: A teacher can help you correct your technique and avoid developing bad habits.
- Musicality Guidance: A teacher can provide guidance on musicality and help you develop your own style.
- Motivation: A teacher can provide motivation and encouragement to help you stay on track.
7.3 Structured Learning
A teacher can provide a structured learning environment and help you stay organized.
- Curriculum: A teacher can provide a structured curriculum that covers all the essential skills.
- Assignments: A teacher can give you assignments to help you practice and improve.
- Accountability: A teacher can hold you accountable for your progress and help you stay motivated.
8. Choosing the Right Guitar and Equipment
The right guitar and equipment can make learning more enjoyable and effective.
8.1 Guitar Selection
Choose a guitar that is comfortable to play and suits your style of music.
| Type of Guitar | Description | Suitable For |
|---|---|---|
| Electric | Requires an amplifier; versatile for various genres. | Rock, blues, metal, jazz, pop |
| Acoustic | Does not require an amplifier; great for practice and folk music. | Folk, country, fingerstyle, singer-songwriter |
| Classical | Nylon strings; wider neck, suitable for classical and flamenco music. | Classical, flamenco, nylon-string arrangements |
8.2 Amplifier Considerations
If you choose an electric guitar, select an amplifier that meets your needs.
- Practice Amps: Small, low-wattage amps are ideal for practicing at home.
- Gigging Amps: Larger, higher-wattage amps are suitable for playing in bands and performing live.
- Modeling Amps: Modeling amps offer a variety of amp tones and effects.
8.3 Accessories
Essential accessories include picks, a tuner, a strap, and a case.
- Picks: Experiment with different thicknesses and materials to find what you prefer.
- Tuner: A tuner is essential for keeping your guitar in tune.
- Strap: A strap allows you to play standing up.
- Case: A case protects your guitar from damage.
9. Integrating Music Theory into Your Learning
Understanding music theory can greatly enhance your guitar playing.
9.1 Basic Music Theory Concepts
Learn basic concepts like scales, chords, and key signatures.
- Scales: Scales are the foundation of melodies and solos.
- Chords: Chords are the foundation of harmony and accompaniment.
- Key Signatures: Key signatures indicate the key of a song.
9.2 Applying Theory to the Fretboard
Learn how to apply music theory concepts to the fretboard.
- Chord Construction: Understand how chords are constructed and how to find them on the fretboard.
- Scale Patterns: Learn scale patterns and how to use them to create melodies and solos.
- Improvisation: Use music theory to improvise over chord progressions.
9.3 Ear Training
Develop your ear to recognize intervals, chords, and melodies.
- Interval Recognition: Practice recognizing intervals by ear.
- Chord Recognition: Practice recognizing chords by ear.
- Melody Recognition: Practice recognizing melodies by ear.
10. Developing Your Own Style
As you progress, focus on developing your own unique style.
10.1 Listening to Influences
Listen to a variety of guitarists and identify elements that you admire.
- Analyze Techniques: Analyze the techniques and styles of your favorite guitarists.
- Identify Common Elements: Identify common elements in their playing that you can incorporate into your own style.
- Emulate and Adapt: Emulate their techniques and adapt them to your own playing.
10.2 Experimenting with Techniques
Experiment with different techniques and approaches to find what works best for you.
- Unique Combinations: Combine different techniques to create unique sounds and textures.
- Personalize Your Sound: Develop your own unique sound by experimenting with different equipment and settings.
- Breaking the Rules: Don’t be afraid to break the rules and try new things.
10.3 Writing Your Own Music
Writing your own music is a great way to express your creativity and develop your own style.
- Song Structure: Learn basic song structure and arrangement techniques.
- Melody Creation: Develop your own melodies and harmonies.
- Lyrical Content: Write lyrics that express your thoughts and feelings.
11. Performing and Collaborating with Other Musicians
Performing and collaborating with other musicians can greatly enhance your guitar playing.
11.1 Playing in a Band
Playing in a band can provide motivation, inspiration, and valuable experience.
- Rehearsal Etiquette: Learn proper rehearsal etiquette and how to work effectively with other musicians.
- Stage Presence: Develop your stage presence and learn how to connect with an audience.
- Teamwork: Learn how to work as a team to create a cohesive and compelling performance.
11.2 Jam Sessions
Participating in jam sessions can help you improve your improvisation skills and learn from other musicians.
- Active Listening: Listen actively to other musicians and respond to their playing.
- Communication: Communicate effectively with other musicians through your playing.
- Adaptability: Learn to adapt your playing to different styles and genres.
11.3 Recording Your Music
Recording your music can help you document your progress and share your music with the world.
- Home Recording Basics: Learn the basics of home recording, including microphone techniques and software.
- Mixing and Mastering: Learn how to mix and master your recordings to achieve a professional sound.
- Distribution: Learn how to distribute your music online through streaming services and social media.
12. Continuing Education and Advanced Techniques
The journey of learning lead guitar is a lifelong pursuit.
12.1 Advanced Music Theory
Continue to expand your knowledge of music theory.
- Harmony: Study advanced harmony concepts, such as chord voicings and substitutions.
- Counterpoint: Learn counterpoint techniques to create more complex and interesting melodies.
- Arranging: Study arranging techniques to create full and dynamic arrangements.
12.2 Advanced Guitar Techniques
Explore advanced guitar techniques.
- Sweep Picking: Master sweep picking to play fast and fluid arpeggios.
- Tapping: Develop tapping techniques to create unique and innovative sounds.
- Hybrid Picking: Learn hybrid picking to combine fingerpicking and pick techniques.
12.3 Exploring Different Genres
Explore different genres of music to broaden your musical horizons.
- Jazz: Study jazz harmony and improvisation techniques.
- Classical: Learn classical guitar techniques and repertoire.
- World Music: Explore different styles of world music and incorporate them into your playing.
13. Building a Community and Networking
Connect with other guitarists and industry professionals.
13.1 Attending Guitar Events
Attend guitar events, such as clinics, workshops, and festivals.
- Networking: Network with other guitarists and industry professionals.
- Learning Opportunities: Take advantage of learning opportunities, such as clinics and workshops.
- Inspiration: Get inspired by seeing live performances and meeting other guitarists.
13.2 Joining Guitar Organizations
Join guitar organizations.
- Resources: Access valuable resources, such as educational materials and networking opportunities.
- Community: Connect with a community of like-minded guitarists.
- Support: Receive support and encouragement from fellow musicians.
13.3 Online Presence
Build an online presence.
- Social Media: Use social media to connect with other guitarists and promote your music.
- Website: Create a website to showcase your music and provide information about your services.
- Online Portfolio: Create an online portfolio to showcase your skills and experience.
14. Maintaining Your Guitar and Equipment
Proper maintenance is essential.
14.1 Regular Cleaning
Clean your guitar regularly.
- Body Cleaning: Wipe down the body of your guitar with a soft cloth to remove dirt and fingerprints.
- Fretboard Cleaning: Clean the fretboard with a fretboard cleaner to remove grime and buildup.
- String Cleaning: Wipe down the strings with a string cleaner to prolong their life.
14.2 String Changes
Change your strings regularly.
- Frequency: Change your strings every few weeks or months, depending on how often you play.
- String Gauge: Experiment with different string gauges to find what you prefer.
- Proper Technique: Learn the proper technique for changing strings to avoid damaging your guitar.
14.3 Professional Setups
Have your guitar professionally set up.
- Intonation: Ensure that your guitar is properly intonated so that it plays in tune.
- Action: Adjust the action of your guitar to make it easier to play.
- Neck Adjustment: Adjust the neck of your guitar to ensure that it is straight and comfortable.
15. Resources at LEARNS.EDU.VN for Lead Guitar Mastery
At LEARNS.EDU.VN, we’re committed to providing you with the resources and support you need to master lead guitar. Our comprehensive courses, expert instructors, and supportive community are designed to help you achieve your musical goals.
15.1 Comprehensive Courses
Our courses cover all aspects of lead guitar playing, from basic techniques to advanced improvisation.
- Beginner Courses: Start with our beginner courses to build a solid foundation.
- Intermediate Courses: Progress to our intermediate courses to refine your skills and expand your knowledge.
- Advanced Courses: Challenge yourself with our advanced courses to master complex techniques and develop your own style.
15.2 Expert Instructors
Our instructors are experienced guitarists.
- Personalized Feedback: Receive personalized feedback on your playing from our instructors.
- Live Q&A Sessions: Participate in live Q&A sessions to get your questions answered.
- Mentorship: Connect with our instructors for mentorship and guidance.
15.3 Supportive Community
Connect with a community of fellow guitarists.
- Forums: Join our online forums to ask questions, share your experiences, and get support from other guitarists.
- Social Media Groups: Join our social media groups to connect with other guitarists and share your progress.
- Virtual Jam Sessions: Participate in virtual jam sessions to practice playing with others and get feedback.
Learning lead guitar is a journey that requires dedication, perseverance, and the right resources. By setting realistic goals, practicing effectively, and utilizing the resources available at LEARNS.EDU.VN, you can achieve your musical dreams and become a skilled and confident lead guitarist. Embrace the challenge, enjoy the process, and let your passion for music guide you on this rewarding adventure.
Ready to start your lead guitar journey? Visit LEARNS.EDU.VN today and explore our comprehensive courses, connect with expert instructors, and join our supportive community. Unlock your musical potential and start playing the music you’ve always dreamed of. Contact us at 123 Education Way, Learnville, CA 90210, United States. Whatsapp: +1 555-555-1212. Website: LEARNS.EDU.VN.
FAQ: Your Questions About Learning Lead Guitar Answered
1. How long does it take to learn basic lead guitar skills?
With consistent practice (30-60 minutes daily), you can learn basic lead guitar skills like playing simple scales and riffs in 3-6 months.
2. Can I learn lead guitar without prior musical experience?
Yes, but having some musical background can be helpful. However, anyone can learn with dedication and the right resources.
3. Is it better to learn lead guitar with a teacher or online?
Both have their advantages. A teacher provides personalized feedback, while online resources offer flexibility. A combination of both can be ideal.
4. What are the most important skills to focus on when starting lead guitar?
Focus on mastering basic chords, scales (like the minor pentatonic), and fundamental techniques like bending and vibrato.
5. How often should I practice lead guitar?
Consistent practice is key. Aim for at least 30 minutes to an hour daily for optimal progress.
6. What are some common challenges beginners face when learning lead guitar?
Common challenges include finger pain, developing coordination, and understanding music theory. Patience and persistence are essential.
7. How can I improve my lead guitar improvisation skills?
Practice scales and arpeggios over backing tracks, learn basic music theory, and transcribe solos from your favorite guitarists.
8. What are some good resources for learning lead guitar online?
learns.edu.vn offers comprehensive courses. YouTube tutorials and online communities can also be valuable resources.
9. How important is it to learn music theory for lead guitar?
Music theory is highly beneficial. It provides a deeper understanding of harmony and allows you to improvise and create music more effectively.
10. What should I do if I feel stuck or unmotivated in my lead guitar journey?
Take a break, listen to inspiring music, set new goals, or seek guidance from a teacher or mentor. Remember to enjoy the process.